|
Umbellic Acid
Umbellic acid (2,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid) is a hydroxycinnamic acid. It is an isomer of caffeic acid. It is a precursor in the umbelliferone biosynthesis pathway. Umbelliferone is a phenylpropanoid and as such is synthesized from L-phenylalanine, which in turn is produced via the shikimate pathway. Phenylalanine is lysated into cinnamic acid, followed by hydroxylation by cinnamate 4-hydroxylase to yield 4-coumaric acid. The 4-coumaric acid is again hydroxylated by cinnamate/coumarate 2-hydroxylase to yield 2,4-dihydroxy-cinnamic acid followed by a bond rotation of the unsaturated bond adjacent to the carboxylic acid group. Finally an intramolecular attack from the hydroxyl group of C2' to the carboxylic acid group closes the ring and forms the lactone umbelliferone. : \xrightarrow \xrightarrow \xrightarrow \longrightarrow The enzyme 4-hydroxycinnamate decarboxylase, induced in bacteria species such as ''Klebsiella oxytoca ''Kle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxycinnamic Acid
Hydroxycinnamic acids (hydroxycinnamates) are a class of aromatic acids or phenylpropanoids having a C6–C3 skeleton. These compounds are hydroxy derivatives of cinnamic acid. In the category of phytochemicals that can be found in food, there are : * α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid * Caffeic acid – burdock, hawthorn, artichoke, pear, basil, thyme, oregano, apple * Cichoric acid * Cinnamic acid – aloe * Chlorogenic acid – echinacea, strawberries, pineapple, coffee, sunflower, blueberries * Diferulic acids * Coumaric acid * Ferulic acid (3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid) – oats, rice, artichoke, orange, pineapple, apple, peanut * Sinapinic acid (3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid or sinapic acid) Hydroxycinnamoyltartaric acids * Caftaric acid – grapes and wine, mainly the ''trans'' isomer * Coutaric acid Coutaric acid is a hydroxycinnamoyltartaric acid found in wine, pomace and grape. It is an ester formed from coumaric acid and tartaric acid Tartaric ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
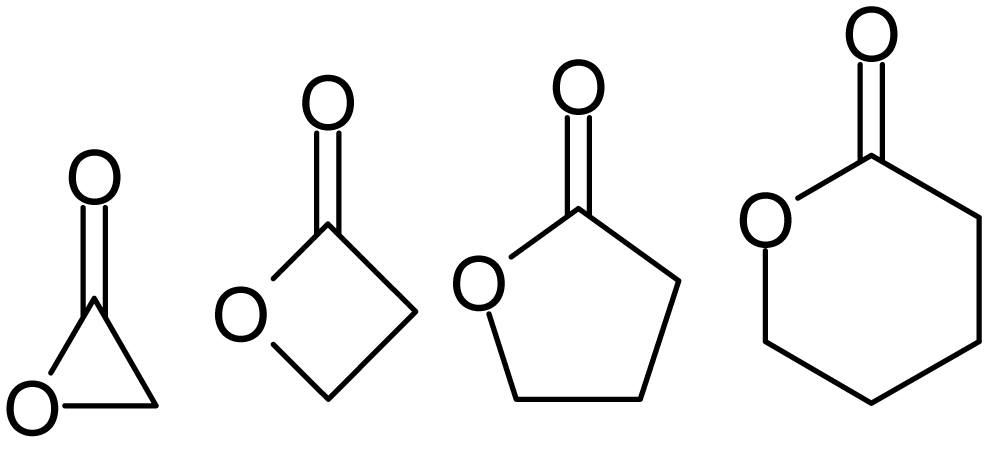
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxycinnamic Acids
Hydroxycinnamic acids (hydroxycinnamates) are a class of aromatic acids or phenylpropanoids having a C6–C3 skeleton. These compounds are hydroxy derivatives of cinnamic acid. In the category of phytochemicals that can be found in food, there are : * α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid * Caffeic acid – burdock, hawthorn, artichoke, pear, basil, thyme, oregano, apple * Cichoric acid * Cinnamic acid – aloe * Chlorogenic acid – echinacea, strawberries, pineapple, coffee, sunflower, blueberries * Diferulic acids * Coumaric acid * Ferulic acid (3-methoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid) – oats, rice, artichoke, orange, pineapple, apple, peanut * Sinapinic acid (3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxycinnamic acid or sinapic acid) Hydroxycinnamoyltartaric acids * Caftaric acid – grapes and wine, mainly the ''trans'' isomer * Coutaric acid – grapes and wine, both ''trans'' and ''cis'' isomers * Fertaric acid Fertaric acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid found in wine and grapes. It is an ester formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klebsiella Oxytoca
''Klebsiella oxytoca'' is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that is closely related to ''K. pneumoniae'', from which it is distinguished by being indole-positive; it also has slightly different growth characteristics in that it is able to grow on melezitose, but not 3-hydroxybutyrate. It was first described in 1886 when it was isolated from sour milk and named ''Bacillus oxytocus perniciosus'' (from Greek ''oxus'' 'sour' + ''-tokos'' 'producing'). ''Klebsiella oxytoca'' is characterized by negative methyl red, positive VP, positive citrate, urea and TSI gas production, is AA, and negative for TSI sulfide, DNAse, growth on sulfide-indole motility medium and the phenylalanine deaminase test. It is a diazotroph, able to colonise plant hosts and fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form which the plant can use. Association of ''K. oxytoca'' with the barley rhizosphere during an entire vegetative period has been demonstrated. The bacteria adhere strongly to root hairs, and less stron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-hydroxycinnamate Decarboxylase
4-Hydroxycinnamate decarboxylase is an enzyme that uses ''p''-coumaric acid to produce 4-ethylphenol. ''p''-Coumaric acid is the precursor of 4-ethylphenol produced by the yeast ''Saccharomyces'' and '' Brettanomyces'' in wine. The yeast converts this to 4-vinylphenol via the enzyme cinnamate decarboxylase. 4-Hydroxycinnamate decarboxylase can also be induced in bacteria species such as ''Klebsiella oxytoca'' and works also with p-coumaric acid analogs such as caffeic acid, ferulic acid and E-2,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid. References See also * Wine chemistry Wine is a complex mixture of chemical compounds in a hydro-alcoholic solution with a pH around 4. The chemistry of wine and its resultant quality depend on achieving a balance between three aspects of the berries used to make the wine: their sugar ... {{enzyme-stub Hydroxycinnamic acids metabolism EC 4.1.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbelliferone
Umbelliferone, also known as 7-hydroxycoumarin, hydrangine, skimmetine, and ''beta''-umbelliferone, is a natural product of the coumarin family. It absorbs ultraviolet light strongly at several wavelengths. There are some indications that this chemical is antimutagenic, it is used in sunscreens. Umbelliferone has been reported to have antioxidant properties. It is a yellowish-white crystalline solid that has a slight solubility in hot water, but high solubility in ethanol. Natural occurrences and name Umbelliferone's name is from the umbelliferae family of plants, and the plant family in turn was named for their umbrella-shaped inflorescences, each called an umbel. Umbelliferone occurs in many familiar plants from the Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) family such as carrot, coriander and garden angelica, as well as in plants from other families, such as the mouse-ear hawkweed (''Hieracium pilosella'', Asteraceae) or the bigleaf hydrangea (''Hydrangea macrophylla'', Hydrangeaceae, under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is or , with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They at oftentimes have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid (C3H7CO2H) is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named as a "carboxy" or "carboxylic acid" substituent on another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeic Acid
Caffeic acid is an organic compound that is classified as a hydroxycinnamic acid. This yellow solid consists of both phenolic and acrylic functional groups. It is found in all plants because it is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, one of the principal components of woody plant biomass and its residues. Natural occurrences Caffeic acid can be found in the bark of ''Eucalyptus globulus'' the barley grain ''Hordeum vulgare'' and the herb ''Dipsacus asperoides''. It can also be found in the freshwater fern ''Salvinia molesta'' and in the mushroom ''Phellinus linteus''. Occurrences in food Free caffeic acid can be found in a variety of beverages, including brewed coffee at 0.13 mg per 100 ml and red wine at 2 mg per 100 ml. It is found at relatively high levels in herbs of the mint family, especially thyme, sage and spearmint (at about 20 mg per 100 g), and in spices, such as Ceylon cinnamon and star anise (at about 22 mg per 100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |