|
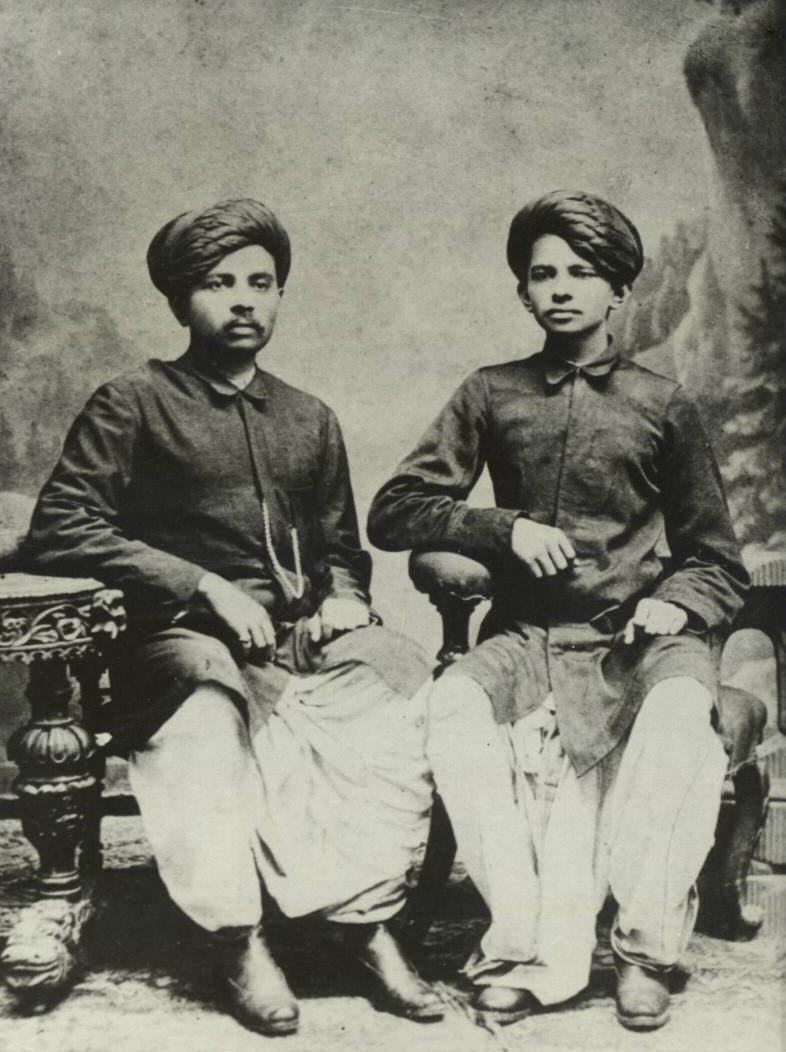
Umashankar Joshi
Umashankar Jethalal Joshi () (21 July 1911 – 19 December 1988) was an Indian poet, scholar and writer known for his contributions to Gujarati literature. He wrote most of his works in Gujarati. Biograpy Early years Umashankar Joshi was born to Jethalal Kamalji and Navalbai in a small village named Bamna (now in Bhiloda Taluka of Aravalli district, Gujarat). He had eight siblings including six brothers and two sisters. Umashankar Joshi's father, Jethalal who worked as a Karbhari of several Jagirs, wanted his sons to get an English education. In 1916, Joshi started his education at Primary school in Bamna and spent two years in 4th standard due to the absence of the teacher for a long time. Upon learning this Jethalal joined Joshi in Sir Pratap High School of Idar, Gujarat, Idar. As a boy who was raised in an orthodox environment, Joshi always heard "highly sensitive and expressive language" which shaped his future style, especially in writing plays. As a child, he had e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
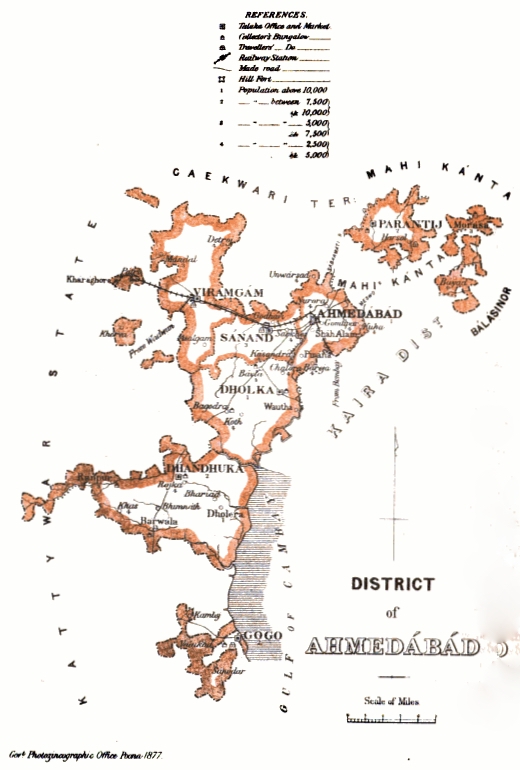
Viramgam
Viramgam is a town and former princely state in the Indian state of Gujarat. The town is located in the Ahmedabad district, which contains the city of Ahmedabad, the state's largest city. Gateway Distriparks notably flagged off the first export train service from the newly built inland container depot (ICD) at Viramgam. History Recorded history Around 1090, Minaldevi, the mother of Jayasimha Siddharaja of Chaulukya dynasty who ruled from Anhilwad Patan, commissioned the Munsar lake. Siddhraj added several shrines and temples later. Viramgam state was founded in . Under the strong Mandal chief, Viramgam did not become part of the Muslim Gujarat Sultanate until 1530. Commanding the entrance to Kathiawar, the Mughal governors chose it as the headquarters of the Jhalavad ''prant'' (district), and in the disturbances of the eighteenth century, it was the scene of several struggles. Historical and legendary references According to Dr. Savliya, author of "Ancient lakes of Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purna Swaraj
The declaration of Purna Swaraj was made because the youth of India and many leaders of INC were not satisfied with the Dominion Status. The word Purna Swaraj was derived , or Declaration of the Independence of India, it was promulgated by the Indian National Congress on 26 January 1930, resolving the Congress and Indian nationalists to fight for ''Purna Swaraj'', or ''complete self-rule'' independent of the British Empire The flag of India was hoisted by Jawaharlal Nehru on 31 December 1929 on the banks of Ravi river, in Lahore. The Congress asked the people of India to observe 26 January as Independence Day (see Legacy). The flag of India was hoisted publicly across India by Congress volunteers, Nehru, nationalists, and the public. Background Dadabhai Naoroji in his presidential address at the 1886 National Congress in Calcutta advocated for Swaraj as the sole aim of the nationalist movement, but along the lines of Canada and Australia, which was colonial self-government un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
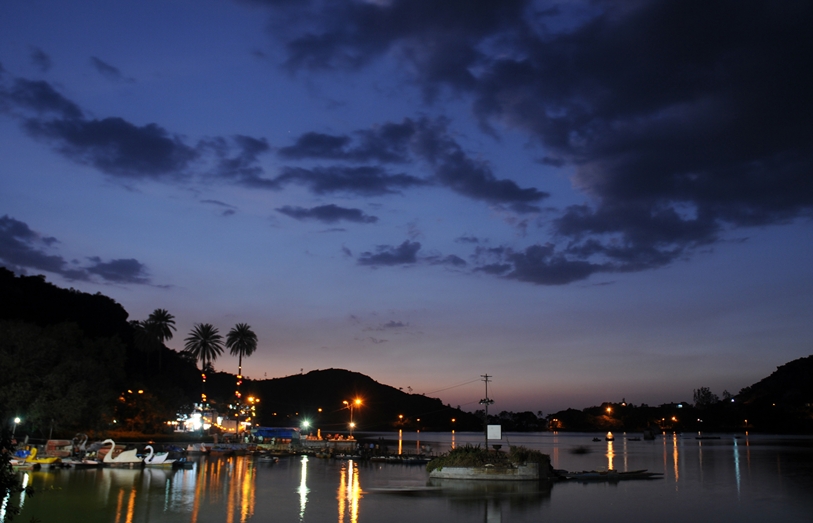
Nakki Lake
Nakki Lake is a lake situated in the Indian hill station of Mount Abu in Aravalli range. Geography The lake is in length of about a half mile and in width about of a quarter of mile and 20 to 30 ft. deep towards the dam on the west. It is an important tourist attraction of Mount Abu. There is the Toad Rock on a hill near the lake. Toad rock is so called as it looks like a toad about to jump into the lake, from the side of the rock facing the lake. There are two ways to go up and down the rock; to climb the rocky hill side or to use the steps leading down to Nakki Lake. By the side of the lake there is a path leading to Sunset Point. It is forbidden to climb to Sunset Point due to wild animals such as bears and leopards roaming around the path to Sunset Point. Raghunath Temple and Maharaja Jaipur Palace are also on hills near the Lake. Boating in the lake and horse rides around the lake are available. Mahatma Gandhi's ashes were immersed in this holy lake on 12 February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above sea level. It is referred to as 'an oasis in the desert' as its heights are home to rivers, lakes, waterfalls and evergreen forests. The nearest train station is Abu Road railway station 28 km away. History The ancient name of Mount Abu is Arbuda. In the Puranas, the region has been referred to as ''Arbudaranya'' ("forest of ''Arbhuda''") and 'Abu' is a diminutive of this ancient name. It is believed that sage Vashistha retired to the southern spur at Mount Abu following his differences with sage Vishvamitra. There is another history story according to which a serpent named "Arbuda" saved the life of Nandi (Lord Shiva's bull). The incident happened on the mountain that is currently known as Mount Abu and so the mountain is named "Arb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divya Bhaskar
''Divya Bhaskar'' () is a Gujarati newspaper in Gujarat, India, owned by D B Corp Ltd. It is one of the highest circulation Gujarati dailies. With the most local editions in Gujarat, it is published from Ahmedabad, Vadodara, Surat, Rajkot, Jamnagar, Mehsana, Bhuj, Bhavnagar (as ''Saurashtra Samachar'') and Junagadh (as ''Sorath Bhaskar''). DivyaBhaskar is published in Junagadh from 27 March 2011. History In 2003, the -based identified |
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per the 2011 population census) makes it the fifth-most populous city in India, and the encompassing urban agglomeration population estimated at 6,357,693 is the seventh-most populous in India. Ahmedabad is located near the banks of the Sabarmati River, from the capital of Gujarat, Gandhinagar, also known as its twin city. Ahmedabad has emerged as an important economic and industrial hub in India. It is the second-largest producer of cotton in India, due to which it was known as the 'Manchester of India' along with Kanpur. Ahmedabad's stock exchange (before it was shut down in 2018) was the country's second oldest. Cricket is a popular sport in Ahmedabad; a newly built stadium, called Narendra Modi Stadium, at Motera can accommodate 132,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakki Lake In The Evening , a lake in India
{{Disambiguation ...
Nakki may refer to: * Näkki, a water spirit in Finnic mythologies * Nakki (crater), a crater on Callisto * Nakki Lake Nakki Lake is a lake situated in the Indian hill station of Mount Abu in Aravalli range. Geography The lake is in length of about a half mile and in width about of a quarter of mile and 20 to 30 ft. deep towards the dam on the west. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idar, Gujarat
Idar is a town in Sabarkantha district, Gujarat, India. It is known for the manufacture of handmade wooden toys, tiles, its temples and various beautiful architectural monuments on its hills, and its historical background. Idar is at the southern end of the Aravalli Range. Etymology Idar was historically named Ilvadurg, which means ''the fortress of Ilvan''. Its name was later corrupted into Idar. It was mentioned in ''Padma Purana'' as well as in the ''Mahabharata'' as Ila. History Legends The town is mentioned in ''Mahabharata'' and ''Bhavishottar Puran'' as 'Ilvadurg'. The exact date of its origin is not known; but it is believed that it came into existence at the time when Yudhishthira was ruling over Hastinapur at the end of the Kurukshetra War of Mahabharata. According to tradition, Idar has been celebrated from the earliest times. Even in the past cycle, ''yuga'', it was known, and in the present cycle, before the days of Vikram, the legendary king Veni Vachh Raj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, starting in the early 13th century, wherein the powers to govern and collect tax from an estate was granted to an appointee of the state.Jāgīrdār system: INDIAN TAX SYSTEM Encyclopædia Britannica (2009) The tenants were considered to be in the servitude of the jagirdar. There were two forms of jagir, one being conditional and the other unconditional. The conditional jagir required the governing family to maintain troops and provide their service to the state when asked. The land grant w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |