|
Uatsdin
Assianism (, ''Watsdin'') is a modern Pagan religion derived from the traditional mythology of the Ossetians, modern descendants of the Scythians of the Alan tribes, believed to be a continuation of the ancient Scythian religion. The religion is known as "Assianism" among its Russian-speaking adherents ("Assianism" means the religion of the "As" or "Oss"—an ancient name of the Alans, from which the Greeks possibly drew the name of "Asia", which is preserved in the Russian and Georgian-derived name "Ossetians"), and as Watsdin (Уацдин), Ætsæg Din (Æцæг Дин; both meaning "True Faith"), Æss Din (Æсс Дин, Ossetian-language rendering of "Assianism"), or simply Iron Din (Ирон Дин, "Ossetian Faith") by Ossetians in their own language. It started to be revived in a conscious and organised way in the 1980s, as an ethnic religion among the Ossetians. The religion has been incorporated by some organisations, chiefly in North Ossetia–Alania within Russia, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assianism Symbol
Assianism (, ''Watsdin'') is a modern Pagan religion derived from the traditional mythology of the Ossetians, modern descendants of the Scythians of the Alan tribes, believed to be a continuation of the ancient Scythian religion. The religion is known as "Assianism" among its Russian-speaking adherents ("Assianism" means the religion of the "As" or "Oss"—an ancient name of the Alans, from which the Greeks possibly drew the name of "Asia", which is preserved in the Russian and Georgian-derived name "Ossetians"), and as Watsdin (Уацдин), Ætsæg Din (Æцæг Дин; both meaning "True Faith"), Æss Din (Æсс Дин, Ossetian-language rendering of "Assianism"), or simply Iron Din (Ирон Дин, "Ossetian Faith") by Ossetians in their own language. It started to be revived in a conscious and organised way in the 1980s, as an ethnic religion among the Ossetians. The religion has been incorporated by some organisations, chiefly in North Ossetia–Alania within Russia, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetians
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label=Ossetic) are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains. They natively speak Ossetic, an Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European language family, with most also being fluent in Russian as a second language. Ossetic, a remnant of the Scytho-Sarmatian dialect group which was once spoken across the Pontic–Caspian Steppe, is one of the few Iranian languages remaining inside Europe. Currently, the Ossetian homeland of Ossetia is politically divided between North Ossetia–Alania in Russia, and the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Their closest historical and linguistic relatives, the Jász people, live in the Jászság region withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Ossetia–Alania
The Republic of North Ossetia–Alania; os, Республикӕ Цӕгат Ирыстон — Алани, ''Respublikæ Cægat Iryston — Alani'', ) is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. Its population according to the 2010 Census was 712,980. The republic's capital city is the city of Vladikavkaz, located on the foothills of the Caucasus Mountains. Forming 65.1% of the republic's population as of 2010, the Ossetians are an Iranian ethnic group native to the republic and neighboring South Ossetia. Ossetian is an east Iranian language descended from medieval Alanic and ancient Sarmatian. Unlike many groups in the North Caucasus, Ossetians are predominantly Christians. However, almost 30% of the population adheres to Ossetian ethnic religion, generally called Uatsdin (Уацдин, "True Faith"), and a sizable Muslim minority exists. Ethnic Russians and Ingush, who form a majority in neighboring Ingushetia, form substantial minoritie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
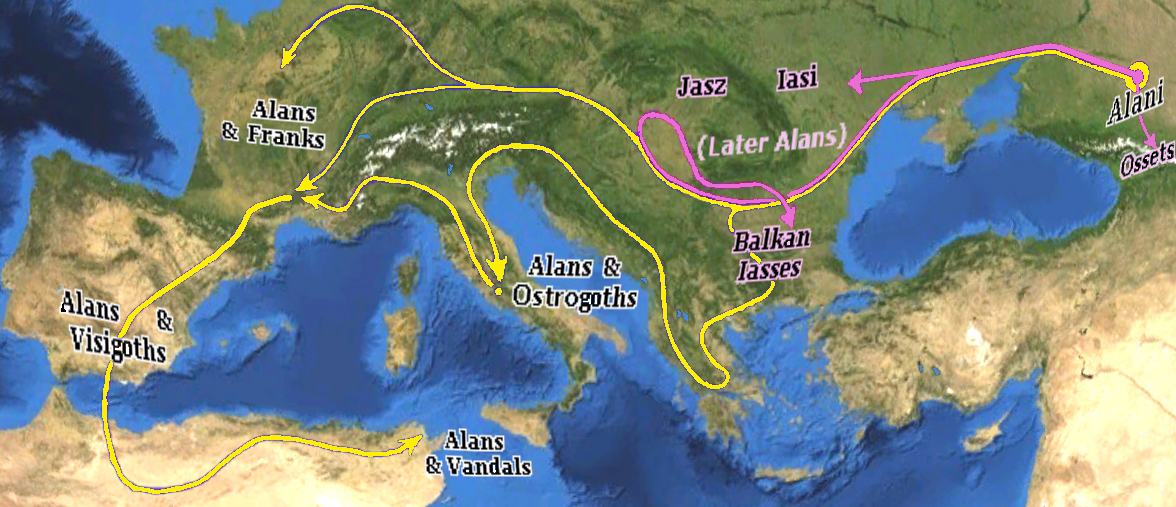
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Paganism
Modern paganism, also known as contemporary paganism and neopaganism, is a term for a religion or family of religions influenced by the various historical pre-Christian beliefs of pre-modern peoples in Europe and adjacent areas of North Africa and the Near East. Although they share similarities, contemporary pagan movements are diverse, and do not share a single set of beliefs, practices, or texts. Scholars of religion may characterise these traditions as new religious movements. Some academics who study the phenomenon treat it as a movement that is divided into different religions while others characterize it as a single religion of which different pagan faiths are denominations. Because of these different approaches there is disagreement on when or if the term ''pagan'' should be capitalized, though specialists in the field of pagan studies tend towards capitalisation. Prominent modern pagan religions include Wicca, Druidry, Heathenry, Rodnovery, and the Goddess movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Religious Movements
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in origin or they can be part of a wider religion, in which case they are distinct from pre-existing denominations. Some NRMs deal with the challenges which the modernizing world poses to them by embracing individualism, while other NRMs deal with them by embracing tightly knit collective means. Scholars have estimated that NRMs number in the tens of thousands worldwide, with most of their members living in Asia and Africa. Most NRMs only have a few members, some of them have thousands of members, and a few of them have more than a million members.Eileen Barker, 1999, "New Religious Movements: their incidence and significance", ''New Religious Movements: challenge and response'', Bryan Wilson and Jamie Cresswell editors, Routledge There is no single, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
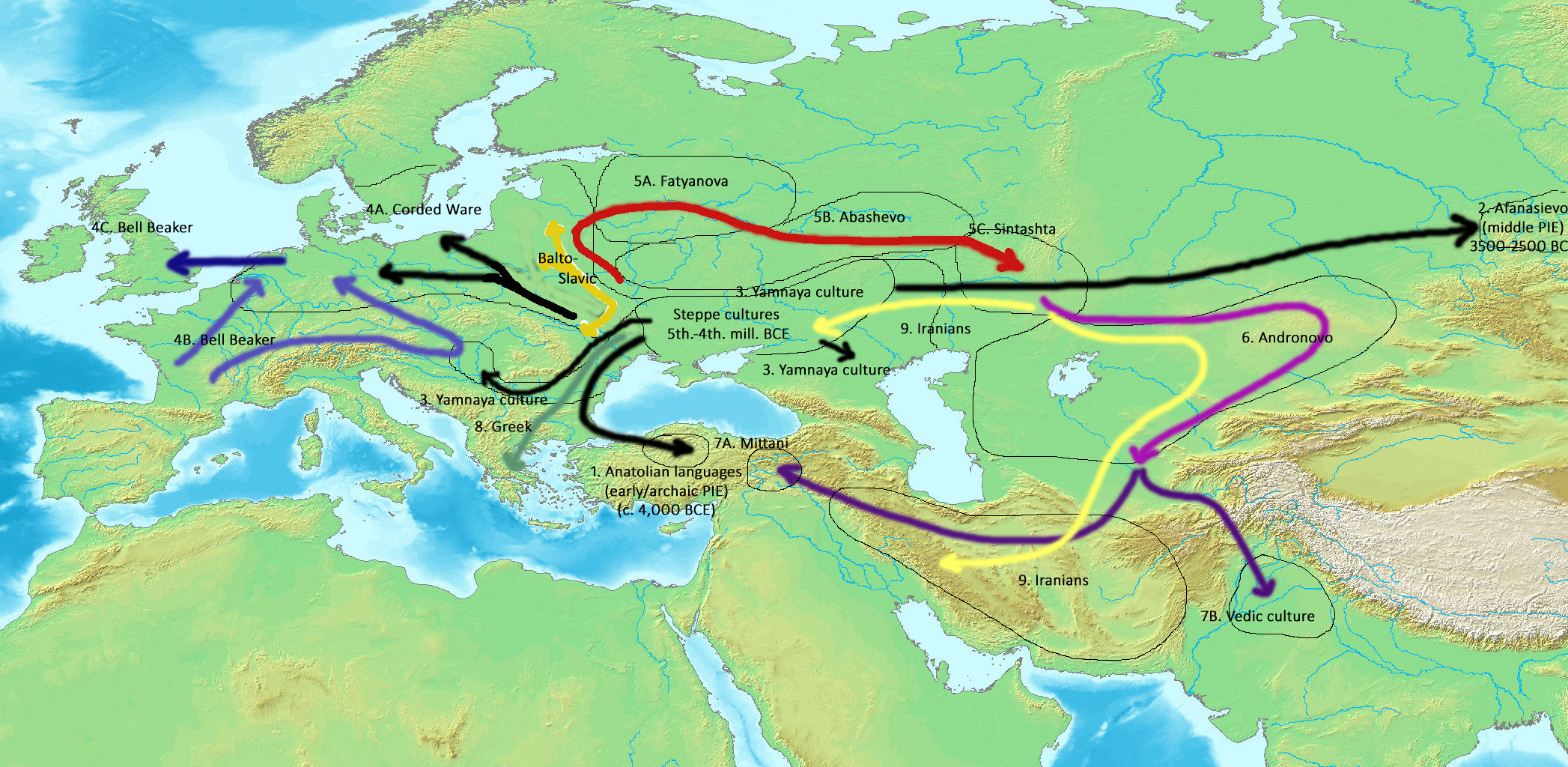
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranians
Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Indo-Iranic peoples by scholars, and sometimes as Arya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages, a major branch of the Indo-European language family, to major parts of Eurasia in the second part of the 3rd millennium BCE. They eventually branched out into Iranian peoples and Indo-Aryan peoples, predominantly in the geographical subregion of Southern Asia. Nomenclature The term '' Aryan'' has long been used to denote the ''Indo-Iranians'', because ''Arya'' is indeed the self-designation of the ancient speakers of the Indo-Iranian languages, specifically the Iranian and the Indo-Aryan peoples, collectively known as the Indo-Iranians. Despite this, some scholars use the term Indo-Iranian to refer to this group, though the term "Aryan" remains widely used by most scholars, such as Josef Wiesehofer, Will Durant, and Jaakko Häkkinen. Population geneticist Luigi Luca Cavall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Foltz
Richard Foltz is a Canadian scholar of American origin. He is a specialist in the history of Iranian civilization—what is sometimes referred to as "Greater Iran". He has also been active in the areas of environmental ethics and animal rights. Biography Foltz is a full professor in the Department of Religions and Cultures at Concordia University in Montreal, Quebec, and an affiliate professor at the Centre d'études du religieux contemporain, Université de Sherbrooke. He holds a Ph.D. in Middle Eastern History from Harvard University and degrees in Persian literature and applied linguistics from the University of Utah. He has taught at Kuwait University, Brown University, Columbia University, and the University of Florida. Prior to entering academia he worked for several years in Europe as a musician, film critic, and travel writer. The author of twelve books and over one hundred scholarly articles, his work has appeared in more than a dozen languages. Scholarly contributions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities. The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe, from the Great Hungarian Plain in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the steppes and the wooded steppes and even the semi-deserts from the Great Hungarian Plain to the Ordos in northern China." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |