|
USNS Yukon (T-AO-202)
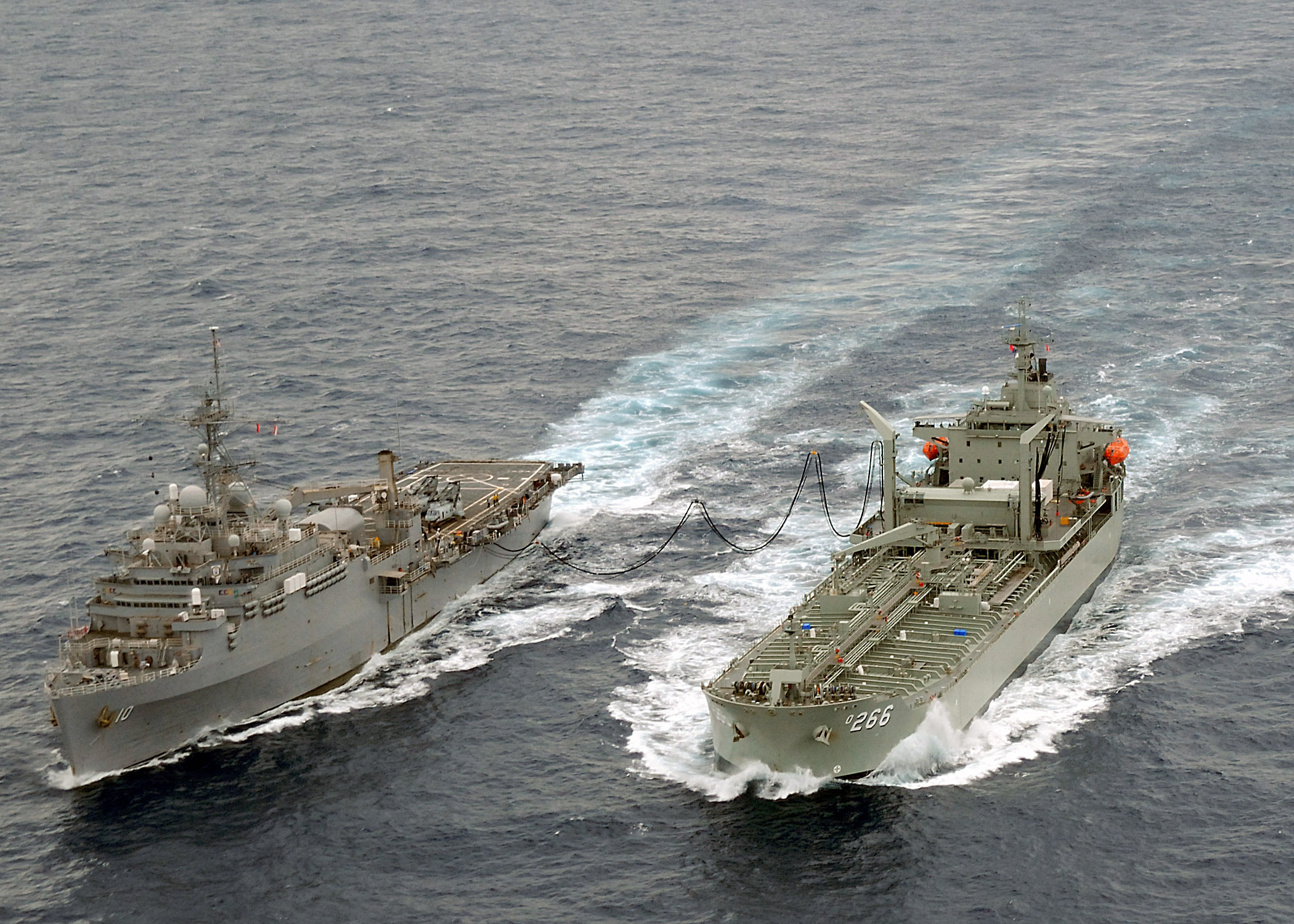
USNS ''Yukon'' (T-AO-202) is a underway replenishment oiler operated by the Military Sealift Command to support ships of the United States Navy. ''Yukon'', the sixteenth ship of the ''Henry J. Kaiser'' class, was laid down at Avondale Shipyard, Inc., at New Orleans, Louisiana, on 13 May 1991 and launched on 6 February 1993. She entered non-commissioned U.S. Navy service under the control of the Military Sealift Command with a primarily civilian crew on 25 March 1994. She serves in the United States Pacific Fleet. On 27 February 2000, ''Yukon'' collided with a smaller civilian cargo ship while entering the port of Dubai in the Persian Gulf. On 13 July 2000, ''Yukon'' collided with the amphibious transport dock USS ''Denver'' (LPD-9) during an underway replenishment about west of Hawaii. No one on either ship was injured, and there were no fuel leaks, but ''Yukon'' suffered major damage, including several large holes and dents above the water line on her starboard quarter, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Refrigeration
The term refrigeration refers to the process of removing heat from an enclosed space or substance for the purpose of lowering the temperature.International Dictionary of Refrigeration, http://dictionary.iifiir.org/search.phpASHRAE Terminology, https://www.ashrae.org/technical-resources/free-resources/ashrae-terminology Refrigeration can be considered an artificial, or human-made, cooling method. Refrigeration refers to the process by which energy, in the form of heat, is removed from a low-temperature medium and transferred to a high-temperature medium. This work of energy transfer is traditionally driven by mechanical means, but can also be driven by heat, magnetism, electricity, laser, or other means. Refrigeration has many applications, including household refrigerators, industrial freezers, cryogenics, and air conditioning. Heat pumps may use the heat output of the refrigeration process, and also may be designed to be reversible, but are otherwise similar to air conditioning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Denver (LPD-9)
USS ''Denver'' (LPD-9), an , was the third ship of United States Navy to bear this name. ''Denver''s keel was laid on 7 July 1964 at Lockheed Shipbuilding and Construction Company, Seattle, Washington. She was launched on 23 January 1965, christened by Mrs. Ann Daniels Love, wife of John A. Love, the former governor of Colorado, and commissioned on 26 October 1968. After 46 years of service, ''Denver'' was decommissioned at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam on 14 August 2014. At the time of her decommissioning, ''Denver'' was the oldest deployable warship in the U.S. Navy, and was one of the last active warships to have served in Vietnam. History Vietnam War In 1970, ''Denver'' played a key role in the SS ''Columbia Eagle'' incident. When ''Columbia Eagle'' was commandeered by two mutinous crew members on 14 March 1970, ''Denver'' was immediately dispatched to intercept and recapture ''Columbia Eagle''. ''Denver'' never really caught up with ''Columbian Eagle'', and sat out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
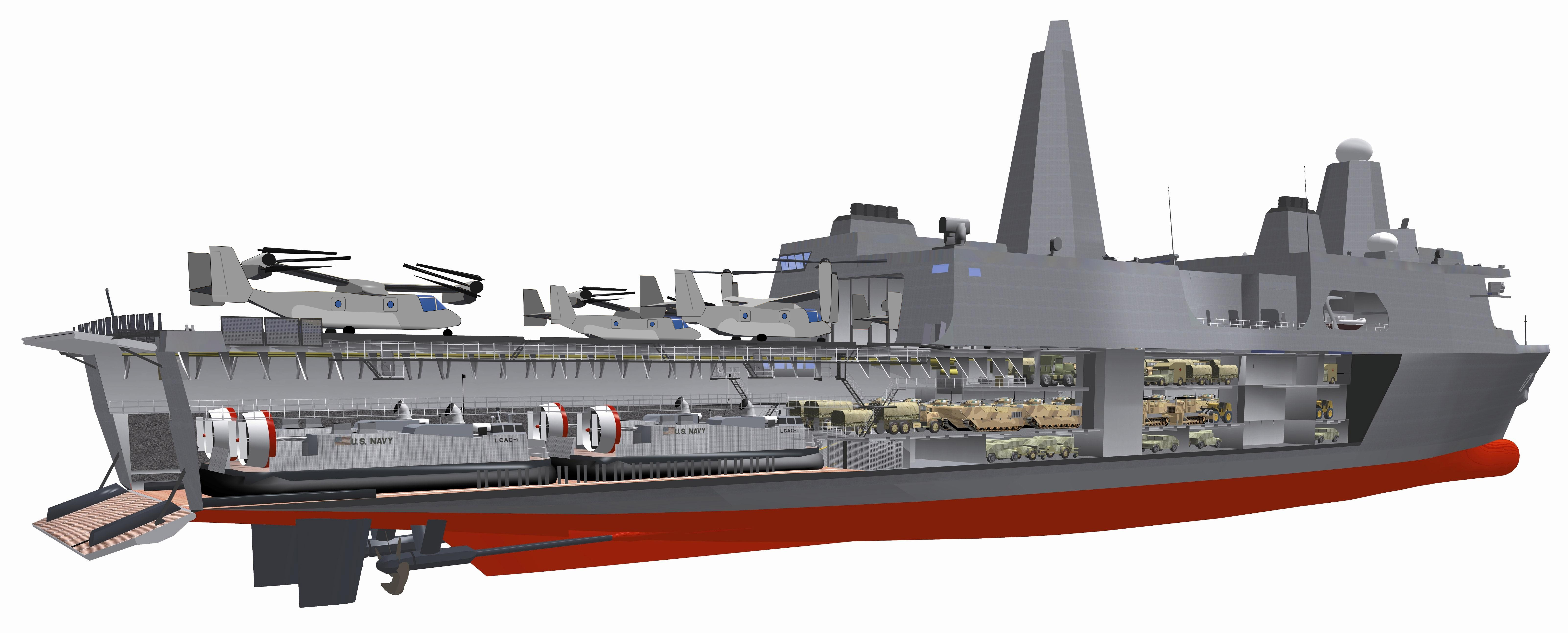
Amphibious Transport Dock
An amphibious transport dock, also called a landing platform dock (LPD), is an amphibious warfare ship, a warship that embarks, transports, and lands elements of a landing force for expeditionary warfare missions. Several navies currently operate this kind of ship. The ships are generally designed to transport troops into a war zone by sea, primarily using landing craft, although invariably they also have the capability to operate transport helicopters. Amphibious transport docks perform the mission of amphibious transports, amphibious cargo ships, and the older dock landing ships (LSD) by incorporating both a flight deck and a well deck that can be ballasted and deballasted to support landing craft or amphibious vehicles. The main difference between LSDs and LPDs is that while both have helicopter landing decks, the LPD also has hangar facilities for protection and maintenance. In the United States Navy, the newer class of LPD has succeeded the older classes of LSDs, and bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical NameWorking Paper No. 61, 23rd Session, Vienna, 28 March – 4 April 2006. accessed October 9, 2010 It is connected to the Gulf of Oman in the east by the Strait of Hormuz. The Shatt al-Arab river delta forms the northwest shoreline. The Persian Gulf has many fishing grounds, extensive reefs (mostly rocky, but also Coral reef, coral), and abundant pearl oysters, however its ecology has been damaged by industrialization and oil spills. The Persian Gulf is in the Persian Gulf Basin, which is of Cenozoic origin and related to the subduction of the Arabian Plate u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dubai
Dubai (, ; ar, دبي, translit=Dubayy, , ) is the most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, the most populated of the 7 emirates of the United Arab Emirates.The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa. D Long, B Reich. p.157 Established in the 18th century as a small fishing village, the city grew rapidly in the early 21st century with a focus on tourism and luxury, having the second most five-star hotels in the world, and the tallest building in the world, the Burj Khalifa, which is tall. In the eastern Arabian Peninsula on the coast of the Persian Gulf, it is also a major global transport hub for passengers and cargo. Oil revenue helped accelerate the development of the city, which was already a major mercantile hub. A centre for regional and international trade since the early 20th century, Dubai's economy relies on revenues from trade, tourism, aviation, real estate, and financial services. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cargo Ship
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. Cargo ships are usually specially designed for the task, often being equipped with crane (machine), cranes and other mechanisms to load and unload, and come in all sizes. Today, they are almost always built of welded steel, and with some exceptions generally have a life expectancy of 25 to 30 years before being scrapped. Definitions The words ''cargo'' and ''freight'' have become interchangeable in casual usage. Technically, "cargo" refers to the goods carried aboard the ship for hire, while "freight" refers to the act of carrying of such cargo, but the terms have been used interchangeably for centuries. Generally, the modern ocean shipping business is divided into two classes: # Liner business: typically (but not exclusively) container vessels (where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Pacific Fleet
The United States Pacific Fleet (USPACFLT) is a theater-level component command of the United States Navy, located in the Pacific Ocean. It provides naval forces to the Indo-Pacific Command. Fleet headquarters is at Joint Base Pearl Harbor–Hickam, Hawaii, with large secondary facilities at Naval Air Station North Island, California. Origins A Pacific Fleet was created in 1907 when the Asiatic Squadron and the Pacific Squadron were combined. In 1910, the ships of the First Squadron were organized back into a separate Asiatic Fleet. The General Order 94 of 6 December 1922 organized the United States Fleet, with the Battle Force as the Pacific presence. Until May 1940, the Battle Force was stationed on the West Coast of the United States. Headquarters, battleships, aircraft carriers and heavy cruisers were stationed at San Pedro close to the Long Beach Naval Shipyard. Light cruisers, destroyers and submarines were stationed at San Diego. During the summer of that year, as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underway Replenishment Oiler
A replenishment oiler or replenishment tanker is a naval auxiliary ship with fuel tanks and dry cargo holds which can supply both fuel and dry stores during underway replenishment (UNREP) at sea. Many countries have used replenishment oilers. The United States Navy's hull classification symbol for this type of ship was AOR. Replenishment oilers are slower and carry fewer dry stores than the U.S. Navy's modern fast combat support ships, which carry the classification AOE. History The development of the "oiler" paralleled the change from coal- to oil-fired boilers in warships. Prior to the adoption of oil fired machinery, navies could extend the range of their ships either by maintaining coaling stations or for warships to raft together with colliers and for coal to be manhandled aboard. Though arguments related to fuel security were made against such a change, the ease with which liquid fuel could be transferred led in part to its adoption by navies worldwide. One of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of STOL (Short TakeOff and Landing) or STOVL (Short TakeOff and Vertical Landing) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. In 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production.Munson 1968.Hirschberg, Michael J. and David K. Dailey"Sikorsky". ''US and Russian Helicopter Development in the 20th Century'', American Helicopter Society, International. 7 July 2000. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompanied by a vertical anti-torque tail rotor (i.e. unicopter, not to be confused with the single-blade monocopter) has become the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phalanx CIWS
The Phalanx CIWS (often spoken as "sea-wiz") is a gun-based close-in weapon system to defend military watercraft automatically against incoming threats such as aircraft, missiles, and small boats. It was designed and manufactured by the General Dynamics Corporation, Pomona Division,Thomas, Vincent C. ''The Almanac of Seapower 1987'' Navy League of the United States (1987) p.191 later a part of Raytheon. Consisting of a radar-guided Vulcan cannon mounted on a swiveling base, the Phalanx has been used by the United States Navy and the naval forces of 15 other countries. The US Navy deploys it on every class of surface combat ship, except the and . Other users include the British Royal Navy, the Royal Australian Navy, the Royal New Zealand Navy, the Royal Canadian Navy and the US Coast Guard (aboard its - and s). A land variant, the LPWS (Land Phalanx Weapon System), part of the C-RAM system, was developed. It was deployed to counter rocket, artillery and mortar attacks du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)