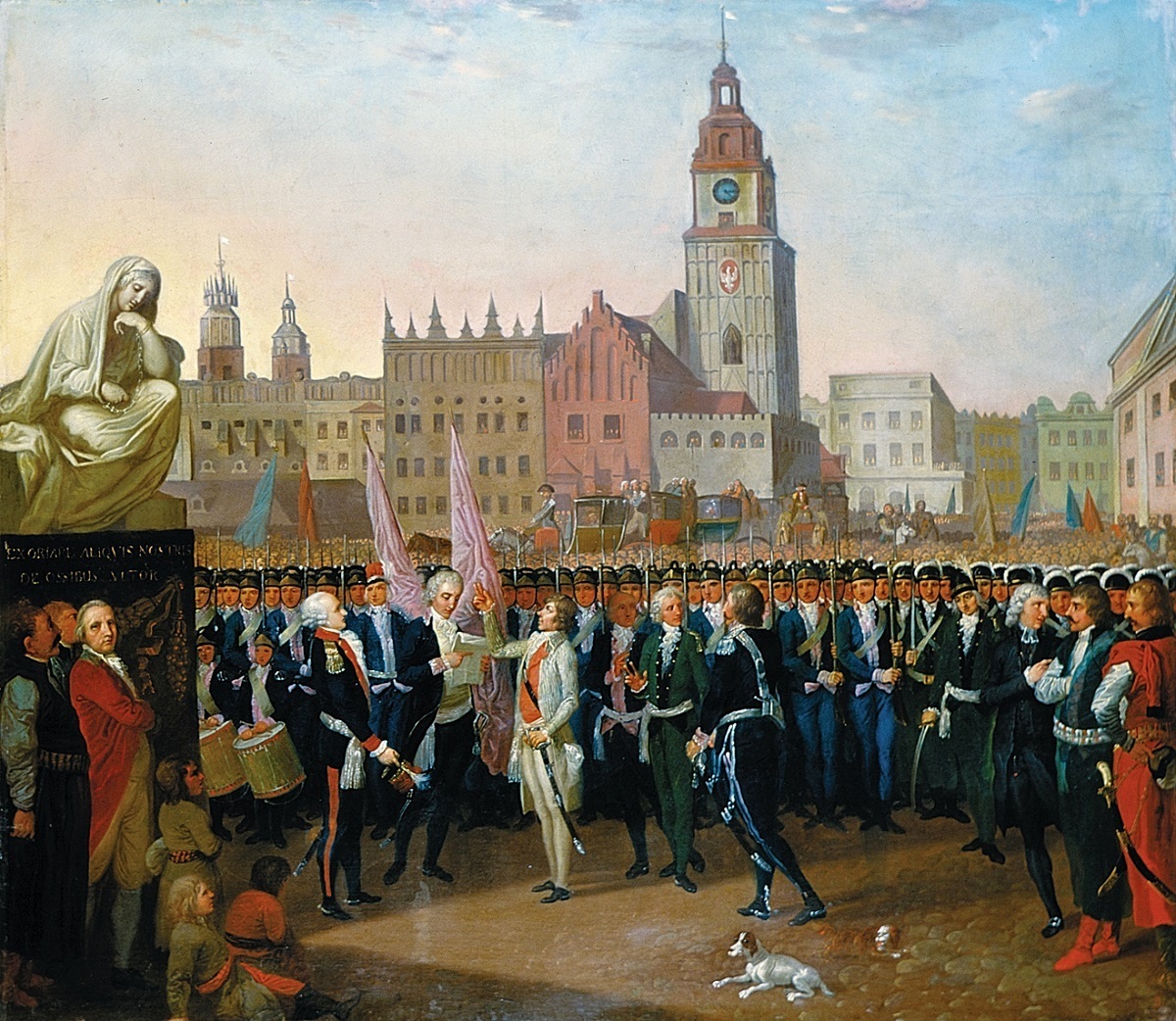|
Tomasz Maruszewski
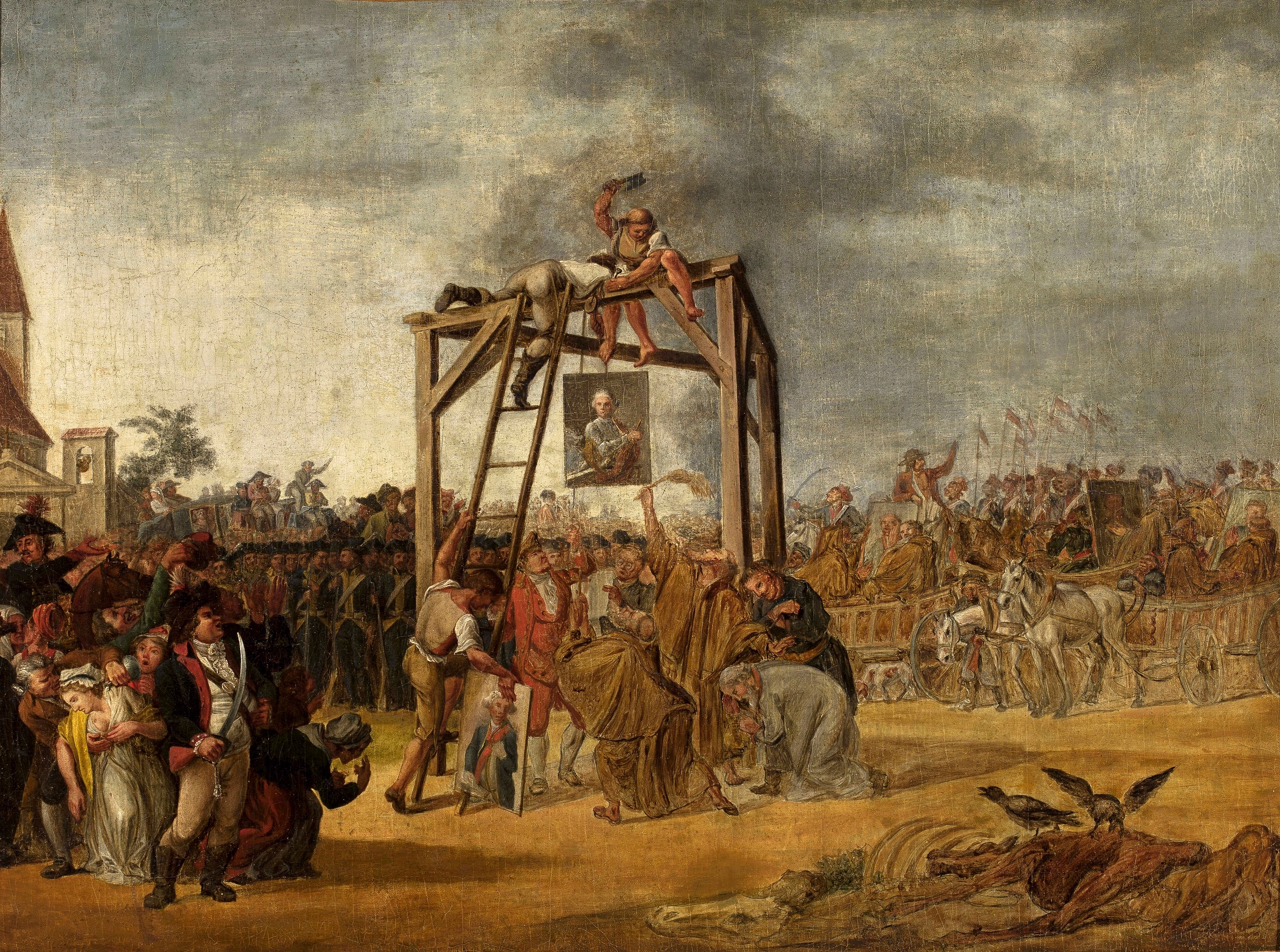
Tomasz Maruszewski (1769–1834) was a prominent participant in the Kościuszko Uprising. A burgher and Polish Jacobin, he was a member of Kołłątaj's Forge and was ennobled by the Great Sejm in 1790. After pro-reform forces were defeated in the 1792 War in Defense of the Constitution, together with Hugo Kołłątaj he emigrated to Saxony, but in 1793 he returned to Poland. On behalf of Tadeusz Kościuszko he went to Warsaw, where he helped organize the Warsaw Uprising. When the Uprising had succeeded, he was likely responsible for the subsequent execution of Targowica Confederation The Targowica Confederation ( pl, konfederacja targowicka, , lt, Targovicos konfederacija) was a Confederation (Poland), confederation established by Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Polish and Lithuanian magnates on 27 April 1792, in Saint Pe ... members. He left Poland again after the defeat of the Kościuszko Uprising and the Third Partition of Poland (1795). To the end he worked clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the "Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those simply content to believe they were living in an unprecedented "Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadeusz Kościuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko ( be, Andréj Tadévuš Banavientúra Kasciúška, en, Andrew Thaddeus Bonaventure Kosciuszko; 4 or 12 February 174615 October 1817) was a Polish Military engineering, military engineer, statesman, and military leader who became a national hero in Belarus, France, Lithuania, Poland and the United States. He fought in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth's struggles against Russian Empire, Russia and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, and on the US side in the American Revolutionary War. As Supreme Commander of the Polish National Armed Forces, he led the 1794 Kościuszko Uprising. Kościuszko was born in February 1746, in a manor house on the Mieračoŭščyna, Mereczowszczyzna estate in Brest Litovsk Voivodeship, then Grand Duchy of Lithuania, a part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (now Ivatsevichy District of Belarus). At age 20, he graduated from the Corps of Cadets (Warsaw), Corps of Cadets in Warsaw, Poland. After the start of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1834 Deaths
Events January–March * January – The Wilmington and Raleigh Railroad is chartered in Wilmington, North Carolina. * January 1 – Zollverein (Germany): Customs charges are abolished at borders within its member states. * January 3 – The government of Mexico imprisons Stephen F. Austin in Mexico City. * February 13 – Robert Owen organizes the Grand National Consolidated Trades Union in the United Kingdom. * March 6 – York, Upper Canada, is incorporated as Toronto. * March 11 – The United States Survey of the Coast is transferred to the Department of the Navy. * March 14 – John Herschel discovers the open cluster of stars now known as NGC 3603, observing from the Cape of Good Hope. * March 28 – Andrew Jackson is censured by the United States Congress (expunged in 1837). April–June * April 10 – The LaLaurie mansion in New Orleans burns, and Madame Marie Delphine LaLaurie flees to France. * April 14 – The Whig Party is officially named by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1769 Births
Events January–March * February 2 – Pope Clement XIII dies, the night before preparing an order to dissolve the Jesuits.Denis De Lucca, ''Jesuits and Fortifications: The Contribution of the Jesuits to Military Architecture in the Baroque Age'' (BRILL, 2012) pp315-316 * February 17 – The British House of Commons votes to not allow MP John Wilkes to take his seat after he wins a by-election. * March 4 – Mozart departs Italy, after the last of his three tours there. * March 16 – Louis Antoine de Bougainville returns to Saint-Malo, following a three-year circumnavigation of the world with the ships '' La Boudeuse'' and '' Étoile'', with the loss of only seven out of 330 men; among the members of the expedition is Jeanne Baré, the first woman known to have circumnavigated the globe. She returns to France some time after Bougainville and his ships. April–June * April 13 – James Cook arrives in Tahiti, on the ship HM Bark ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Partition Of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland (1795) was the last in a series of the Partitions of Poland–Lithuania and the land of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth among Prussia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Russian Empire which effectively ended Polish–Lithuanian national sovereignty until 1918. The partition was the result of the Kościuszko Uprising and was followed by a number of Polish uprisings during the period. Background Following the First Partition of Poland in 1772, in an attempt to strengthen the significantly weakened Commonwealth, King Stanisław August Poniatowski put into effect a series of reforms to enhance Poland's military, political system, economy, and society. These reforms reached their climax with the enactment of the May Constitution in 1791, which established a constitutional monarchy with separation into three branches of government, strengthened the bourgeoisie and abolished many of the nobility's privileges as well as many of the old laws of serfdom. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Targowica Confederation
The Targowica Confederation ( pl, konfederacja targowicka, , lt, Targovicos konfederacija) was a Confederation (Poland), confederation established by Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Polish and Lithuanian magnates on 27 April 1792, in Saint Petersburg, with the backing of the Russian Empress Catherine II of Russia, Catherine II. The confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791 and fought in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, which led to the Second Partition of Poland, Second and Third Partition of Poland, Third Partitions of Poland. History The Targowica confederation opposed the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which had been adopted by the Great Sejm, especially the provisions limiting the privileges of the nobility. The text of the founding act of the confederation was drafted by the Russian general Vasili Stepanovich Popov, Chief of Staff of Prince Grigori Alexandrovich Potemkin. Its purpose was proclaimed in the small town of Targowica and the Potocki's estate (now in H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw Uprising (1794)
The Warsaw Uprising of 1794 or Warsaw Insurrection ( pl, insurekcja warszawska) was an armed insurrection by the people of Warsaw early in the Kościuszko Uprising. Supported by the Polish Army, the uprising aimed to throw off control by the Russian Empire of the Polish capital city (Warsaw). It began on 17 April 1794, soon after Tadeusz Kościuszko's victory at the Battle of Racławice. Although the Russian forces had more soldiers and better equipment, the Polish regular forces and militia, armed with rifles and sabres from the Warsaw Arsenal, inflicted heavy losses on the surprised enemy garrison. Russian soldiers found themselves under crossfire from all sides and from buildings, and several units broke early and suffered heavy casualties in their retreat. Kościuszko's envoy, Tomasz Maruszewski, and Ignacy Działyński and others had been laying the groundwork for the uprising since early 1793. They succeeded in winning popular support: the majority of Polish units sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of , and the sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants. The term Saxony has been in use for more than a millennium. It was used for the medieval Duchy of Saxony, the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Saxony, and twice for a republic. The first Free State of Saxony was established in 1918 as a constituent state of the Weimar Republic. After World War II, it was under Soviet occupation before it became part of the communist East Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They are sometimes divided into a petty (), middle (), large (), upper (), and ancient () bourgeoisie and collectively designated as "the bourgeoisie". The bourgeoisie in its original sense is intimately linked to the existence of cities, recognized as such by their urban charters (e.g., municipal charters, town privileges, German town law), so there was no bourgeoisie apart from the citizenry of the cities. Rural peasants came under a different legal system. In Marxist philosophy, the bourgeoisie is the social class that came to own the means of production during modern industrialization and whose societal concerns are the value of property and the preservation of capital to ensure the perpetuation of their economic supremacy in society. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Kołłątaj
Hugo Stumberg Kołłątaj, also spelled ''Kołłątay'' (pronounced , 1 April 1750 – 28 February 1812), was a prominent Polish constitutional reformer and educationalist, and one of the most prominent figures of the Polish Enlightenment. He served as Deputy Chancellor of the Crown, 1791–92. He was a Roman Catholic priest, social and political activist, political thinker, historian, philosopher, and polymath. Biography Early life Hugo Kołłątaj was born 1 April 1750 in Dederkały Wielkie (now in Western Ukraine) in Volhynia into a family of Polish nobility. Soon after, his family moved to Nieciesławice, near Sandomierz, where he spent his childhood. He attended school in Pińczów. He began his studies at the Kraków Academy, subsequently, Jagiellonian University, where he studied law and gained a doctorate. Afterwards, around 1775 he took holy orders. He studied in Vienna and Italy (Naples and Rome , established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Russian War Of 1792
The Polish–Russian War of 1792 (also, War of the Second Partition, and in Polish sources, War in Defence of the Constitution ) was fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth on one side, and the Targowica Confederation (conservative nobility of the Commonwealth opposed to the new Constitution of 3 May 1791) and the Russian Empire under Catherine the Great on the other. The war took place in two theaters: a northern in Lithuania and a southern in what is now Ukraine. In both, the Polish forces retreated before the numerically superior Russian forces, though they offered significantly more resistance in the south, thanks to the effective leadership of Polish commanders Prince Józef Poniatowski and Tadeusz Kościuszko. During the three-month-long struggle several battles were fought, but no side scored a decisive victory. The largest success of the Polish forces was the defeat of one of the Russian formations at the Battle of Zieleńce on 18 June; in the aftermath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |