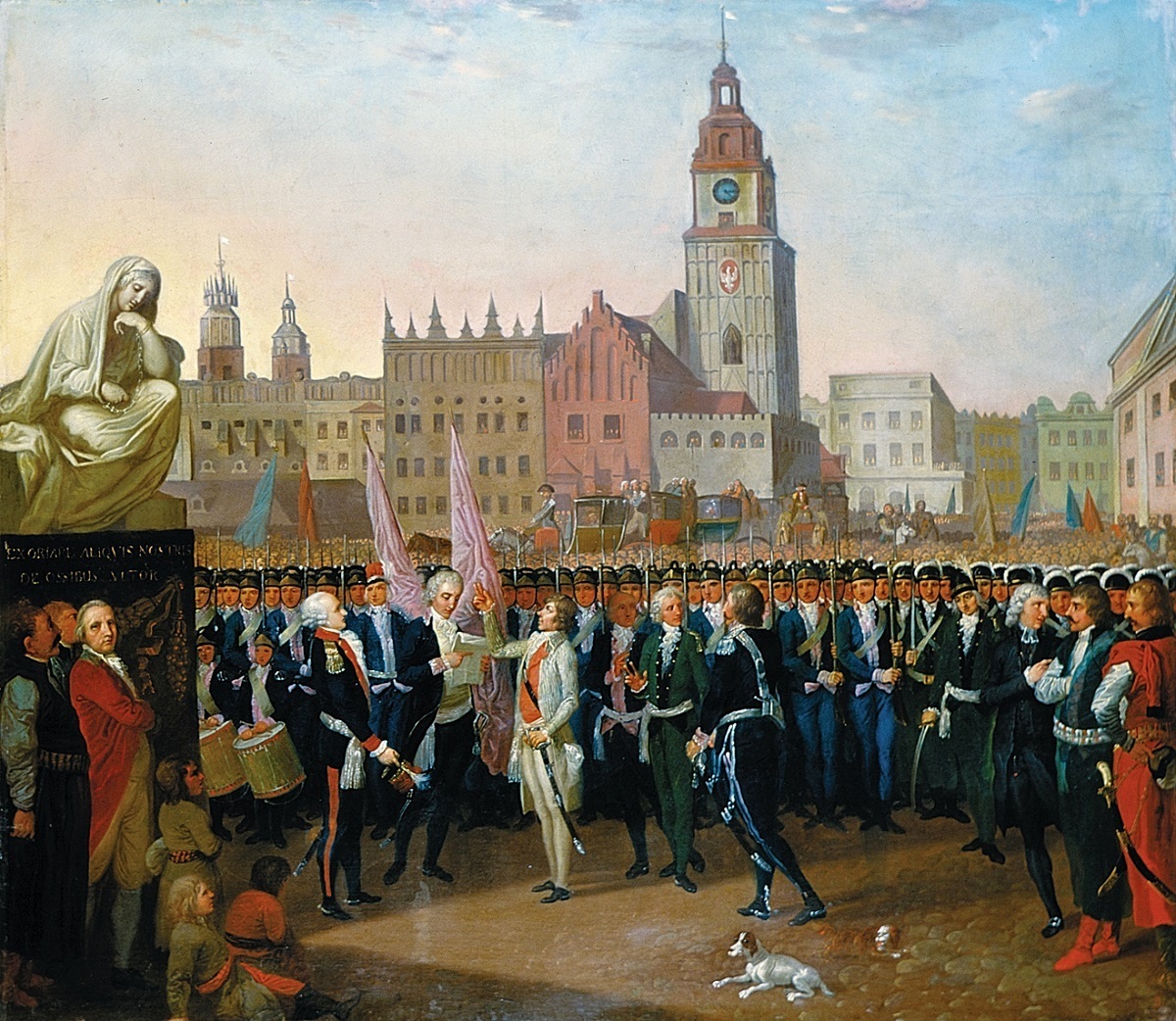|
Kościuszko Uprising
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794 and the Second Polish War, was an uprising against the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation. Background Decline of the Commonwealth By the early 18th century, the magnates of Poland and Lithuania controlled the state – or rather, they managed to ensure that no reforms would be carried out that might weaken their privileged status (the " Golden Freedoms"). Through the abuse of the '' liberum veto'' rule which enabled any deputy to paralyze the Sejm (Commonwealth's parliament) proceedings, deputies bribed by magnates or foreign powers or those simply content to believe they were living in an unprecedented "G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish-Russian War
Armed conflicts between Poland (including the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) and Russia (including the Soviet Union) include: Originally a Polish civil war that Russia, among others, became involved in. Originally a Hungarian revolution but was joined with Polish force on Hungarian side against Austria and Russia. Part of the broader Russian Revolution of 1905. See also * * * * * – in most of which Kingdom of Poland was allied with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ... * * * * * * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Polish-Russian War Lists of military conflicts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
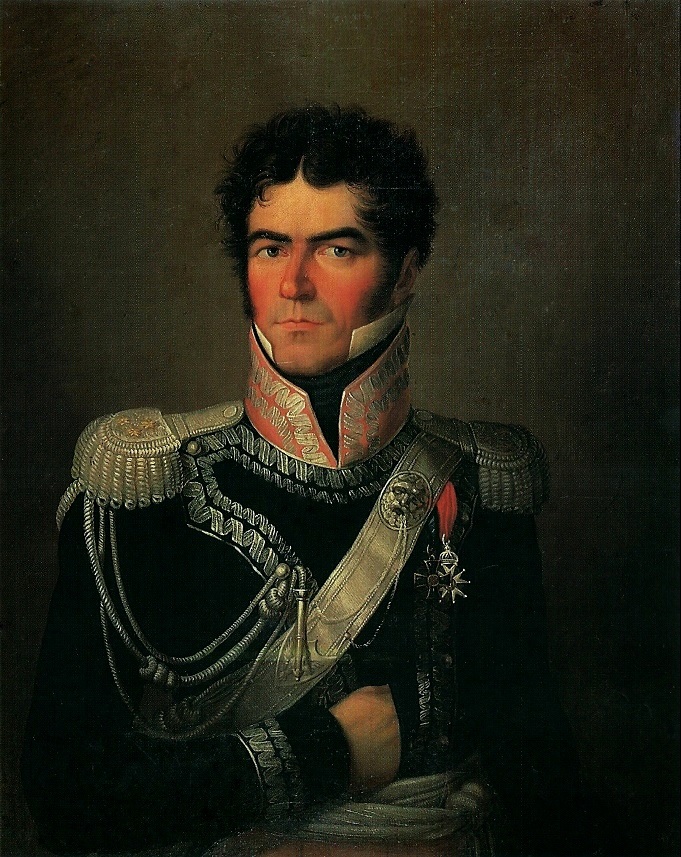
Stanisław Mokronowski
Stanisław Mokronowski (1761-1821) was a prominent member of the Polish landed gentry of Bogoria coat of arms. A general of the Polish Army and a royal Chamberlain Mokronowski took part in both the Polish–Russian War of 1792 (War in the Defence of the Constitution) and Kościuszko's Uprising of 1794. Early life Stanisław Mokronowski was born in 1761 to Ludwik Mokronowski and Józefa née Czosnowska. Educated by Jesuits, he later studied at the Szkoła Rycerska (Knight's School, also known as the Cadet Corps) in Warsaw, and later in Paris. He entered the military service in Poland, but for a few years he served in the French military. Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Four-Year Sejm He returned to Poland in 1788, and on the sejmik at Wyszogród land he was elected the deputy to the national Sejm (parliament), thus becoming a member of the famous [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Petrovich Saltykov
Count Ivan Petrovich Saltykov (russian: Иван Петрович Салтыков; 28 June 1730 – 14 November 1805) was a Russian Field Marshal, the Governor-General of Moscow from 1797 to 1804, and owner of the grand estate of Marfino. Biography Ivan was the only son of Field-Marshal Pyotr Semyonovich Saltykov. He began military service at the age of 15 in the Semenovsky Regiment at the rank of private. In 1758 he was inducted into the Imperial Court at the junior rank of Kamer-Junker. During the Seven Years' War Saltykov distinguished himself at the capture of both Königsberg and Elbing, and at the Battle of Zorndorf. After the onset of peace he received a promotion to major general and was decorated with the Order of St. Anna, 2nd class by Peter III. At Catherine the Great's coronation, he was awarded the Order of St. Alexander Nevsky. At the start of the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 the now Lieutenant-General Saltykov served under the command of Rumyantsev at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation born from several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. The Grand Duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Lithuania, Belarus and parts of Ukraine, Latvia, Poland, Russia and Moldova. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. The consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 13th century. Mindaugas, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in a religious crusad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Repnin
Prince Nikolai Vasilyevich Repnin (russian: Никола́й Васи́льевич Репни́н; – ) was an Imperial Russian statesman and general from the Repnin princely family who played a key role in the dissolution of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Rule of Poland Born in Saint Petersburg, Prince Repnin served in the Imperial Army under his father, Prince Vasily Anikitovich Repnin, during the Rhenish campaign of 1748, and subsequently resided for some time abroad, where he acquired "a thoroughly sound German education." He also participated, in a subordinate capacity, in the Seven Years' War. In 1763, Emperor Peter III sent him to Prussia as ambassador. The same year, Catherine transferred him to Poland as minister plenipotentiary; in Warsaw he was rumored to have had an affair with Izabela Fleming (and to have fathered Adam Jerzy Czartoryski).LeDonne, p.210 Due to the level of Russian control of the Polish government, Repnin was the effective ruler of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Suvorov
Alexander Vasilyevich Suvorov (russian: Алекса́ндр Васи́льевич Суво́ров, Aleksándr Vasíl'yevich Suvórov; or 1730) was a Russian general in service of the Russian Empire. He was Count of Rymnik, Count of the Holy Roman Empire, Prince of the Kingdom of Sardinia, Prince of the Russian Empire and the last Generalissimo of the Russian Empire. Suvorov is considered one of the greatest military commanders in Russian history and one of the great generals of the early modern period. He was awarded numerous medals, titles, and honors by Russia, as well as by other countries. Suvorov secured Russia's expanded borders and renewed military prestige and left a legacy of theories on warfare. He was the author of several military manuals, the most famous being ''The Science of Victory'', and was noted for several of his sayings. He never lost a single battle he commanded. Several military academies, monuments, villages, museums, and orders in Russia are dedica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romuald Giedroyć
Romuald Giedroyć (; ; 7 February 1750 – 15 October 1824) was a Polish-Lithuanian prince from the Lithuanian princely Giedraičiai family, who fought in the Bar Confederation, War of 1792 and the Uprising of 1794 as part of the Grand Ducal Lithuanian Army. From mid-1812 to early 1813, Giedroyć was also the commander of the Lithuanian regiments raised during the French invasion of Russia. In early 1813, he was captured by the Russians and exiled to Arkhangelsk. In 1815, Alexander I of Russia amnestied Giedroyć and made him a Lieutenant general of the Army of Congress Poland. Biography He came from a Lithuanian princely family. His father was Józef Giedroyć, starosta of , his mother was Józefa Kiełpsz. He was born on 7 February 1750 in . Bar Confederation From 1765, he was in the Corps of Cadets in Warsaw. Giedroyć began his military career in 1765 as a cadet in the 2nd Foot Regiment of the Grand Ducal Lithuanian Army, part of the Polish-Lithuanian military forces. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko
Prince Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko (1768–1844) was a Polish nobleman, general, military commander, diplomat and politician. Early life Eustachy Erazm Sanguszko was born in 1768 to Hieronim Janusz Sanguszko and Cecylia Usrzula Potocka. French Royal army In the years 1780–1786, Sanguszko graduated from the military school of Strasbourg and served in the Régiment Royal-Allemand (together with Stanisław Mokronowski) of the French Royal army. Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth Four-Year Sejm On 3 February 1789, Sanguszko began service in the Crown Army as a captain in the . On 5 October 1789, he was promoted to major, and on 28 April 1792, to vice-brigadier. He was a representative of the Lublin Voivodeship in the Great Sejm of 1788–1792. Sanguszko partook in the War of the Second Partition where he fought at the Battle of Zieleńce as a cavalry brigadier, receiving the Virtuti Militari in its wake on June 23. On 29 July 1792, the 24-year-old Sanguszko was pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Grabowski
{{Disambiguation ...
Stefan may refer to: * Stefan (given name) * Stefan (surname) * Ștefan, a Romanian given name and a surname * Štefan, a Slavic given name and surname * Stefan (footballer) (born 1988), Brazilian footballer * Stefan Heym, pseudonym of German writer Helmut Flieg (1913–2001) * Stefan (honorific), a Serbian title * ''Stefan'' (album), a 1987 album by Dennis González See also * Stefan number, a dimensionless number used in heat transfer * Sveti Stefan or Saint Stefan, a small islet in Montenegro * Stefanus (other) Stefanus may refer to: * A variation of the given name Stephen, particularly in regard to: ** Saint Stephen, first martyr of Christianity * St. Stefanus, Ghent, a Catholic church in Belgium dedicated to Saint Stephen * Stefanus Prize, a human righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Poniatowski
Prince Józef Antoni Poniatowski (; 7 May 1763 – 19 October 1813) was a Polish general, minister of war and army chief, who became a Marshal of the French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. A nephew of king Stanislaus Augustus of Poland (), Poniatowski began his military career in 1780 in the Austrian army, where he attained the rank of colonel. In 1789, after leaving Austrian service, he joined the Polish army at the request of his uncle. Poniatowski, now in the rank of major general and commander of the Royal Guards, took part in the Polish–Russian War of 1792, leading the crown forces at the victorious Battle of Zieleńce. After the king's support for the Targowica Confederation of 1792, Poniatowski felt compelled to resign. In 1794 he participated in the Kościuszko Uprising and took charge of defending Warsaw - for which the Russian authorities subsequently exiled him until 1798. In 1807, after Napoleon Bonaparte established the Duchy of Warsaw, Józef Poniatowsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michał Wielhorski (younger)
Michał Wielhorski (1755–1805) was a Polish-Lithuanian count. In 1789, he was a brigadier of the Polish Crown Army. In 1792, he was made a lieutenant general of that army and he fought in the War of 1792. During the Kościuszko Uprising, he was a lieutenant general of the Grand Ducal Lithuanian army. Son of Michał Wielhorski, brother of General Józef Wielhorski. He was an officer in the Habsburg army. He was in the same regiment as Józef Poniatowski, and was his friend. They fought together in the Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791) and were both wounded at Šabac in 1788. Together they entered service in the Polish Crown Army. Wielhorski was the brigadier of the 2nd Ukrainian National Cavalry Brigade with the rank of colonel. In 1792, he was a lieutenant general as the commander of the 2nd Ukrainian Division. He fought in the Volyn campaign. He was beaten at Boruszkowce. Poniatowski's right hand in the War of 1792, where he distinguished himself in the battle of Zieleńce (h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Henryk Dąbrowski
Jan Henryk Dąbrowski (; also known as Johann Heinrich Dąbrowski (Dombrowski) in German and Jean Henri Dombrowski in French; 2 August 1755 – 6 June 1818) was a Polish general and statesman, widely respected after his death for his patriotic attitude, and described as a national hero who spent his whole life restoring the legacy of Poland. Dąbrowski initially served in the Saxon Army and joined the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Army in 1792, shortly before the Second Partition of Poland. He was promoted to the rank of general in the Kościuszko Uprising of 1794. After the final Third Partition of Poland, which ended the existence of Poland as an independent country, he became actively involved in promoting the cause of Polish independence abroad. He was the founder of the Polish Legions in Italy serving under Napoleon from 1795, and as a general in Italian and French service he contributed to the brief restoration of the Polish state during the Greater Poland Upri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |