Grand Duchy Of Lithuania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the

 The first written reference to Lithuania is found in the
The first written reference to Lithuania is found in the

 From 1263 to 1269, Lithuania had three grand dukes –
From 1263 to 1269, Lithuania had three grand dukes – 
 Lithuania was in a good position to conquer the western and the southern parts of former
Lithuania was in a good position to conquer the western and the southern parts of former 

 Lithuania was Christianized in 1387, led by Jogaila, who personally translated Christian prayers into the Lithuanian language and his cousin Vytautas the Great who founded many Catholic churches and allocated lands for parishes in Lithuania. The state reached a peak under
Lithuania was Christianized in 1387, led by Jogaila, who personally translated Christian prayers into the Lithuanian language and his cousin Vytautas the Great who founded many Catholic churches and allocated lands for parishes in Lithuania. The state reached a peak under  The rapid expansion of the influence of Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow soon put it into a comparable position to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and after the annexation of Novgorod in 1478, Muscovy was among the preeminent states in Baltic states, northeastern Europe. Between 1492 and 1508, Ivan III further consolidated Muscovy, winning the key Battle of Vedrosha and regaining such ancient lands of
The rapid expansion of the influence of Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow soon put it into a comparable position to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and after the annexation of Novgorod in 1478, Muscovy was among the preeminent states in Baltic states, northeastern Europe. Between 1492 and 1508, Ivan III further consolidated Muscovy, winning the key Battle of Vedrosha and regaining such ancient lands of
 The wars with the Teutonic Order, the loss of land to Moscow, and the continued pressure threatened the survival of the state of Lithuania, so it was forced to ally more closely with
The wars with the Teutonic Order, the loss of land to Moscow, and the continued pressure threatened the survival of the state of Lithuania, so it was forced to ally more closely with
 Administrative structure of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1413–1564).
Administrative structure of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1413–1564).
 In the 13th century, the Lithuania Proper, centre of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was inhabited by a majority that spoke Lithuanian, though it was not a written language until the 16th century. In the other parts of the duchy, the majority of the population, including Ruthenian nobility, Ruthenian nobles and ordinary people, used both spoken and written Ruthenian. Nobles who migrated from one place to another would adapt to a new locality and adopt the local religion and culture and those Lithuanian nobility, Lithuanian noble families that moved to Slavic areas often took up the local culture quickly over subsequent generations. Ruthenians were native to the east-central and south-eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Ruthenian, also called Chancery Slavonic in its written form, was used to write laws alongside Polish, Latin and German, but its use varied between regions. From the time of Vytautas, there are fewer remaining documents written in Ruthenian than there are in Latin and German, but later Ruthenian became the main language of documentation and writings, especially in eastern and southern parts of the Duchy. In the 16th century at the time of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Lithuanian lands became partially polonization, polonized over time and started to use Polish language, Polish for writing much more often than the Lithuanian and Ruthenian languages. Polish finally became the official chancellery language of the Commonwealth in 1697.
The voivodeships with a predominantly ethnic Lithuanian population, Vilnius voivodeship, Vilnius, Trakai voivodeship, Trakai, and Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitian voivodeships, remained almost wholly Lithuanian-speaking, both colloquially and by ruling nobility. Ruthenian communities were also present in the extreme southern parts of Trakai voivodeship and south-eastern parts of Vilnius Voivodeship. In addition to Lithuanians and Ruthenians, other important ethnic groups throughout the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were Lithuanian Jews, Jews and Lipka Tatars, Tatars.
In the 13th century, the Lithuania Proper, centre of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was inhabited by a majority that spoke Lithuanian, though it was not a written language until the 16th century. In the other parts of the duchy, the majority of the population, including Ruthenian nobility, Ruthenian nobles and ordinary people, used both spoken and written Ruthenian. Nobles who migrated from one place to another would adapt to a new locality and adopt the local religion and culture and those Lithuanian nobility, Lithuanian noble families that moved to Slavic areas often took up the local culture quickly over subsequent generations. Ruthenians were native to the east-central and south-eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Ruthenian, also called Chancery Slavonic in its written form, was used to write laws alongside Polish, Latin and German, but its use varied between regions. From the time of Vytautas, there are fewer remaining documents written in Ruthenian than there are in Latin and German, but later Ruthenian became the main language of documentation and writings, especially in eastern and southern parts of the Duchy. In the 16th century at the time of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Lithuanian lands became partially polonization, polonized over time and started to use Polish language, Polish for writing much more often than the Lithuanian and Ruthenian languages. Polish finally became the official chancellery language of the Commonwealth in 1697.
The voivodeships with a predominantly ethnic Lithuanian population, Vilnius voivodeship, Vilnius, Trakai voivodeship, Trakai, and Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitian voivodeships, remained almost wholly Lithuanian-speaking, both colloquially and by ruling nobility. Ruthenian communities were also present in the extreme southern parts of Trakai voivodeship and south-eastern parts of Vilnius Voivodeship. In addition to Lithuanians and Ruthenians, other important ethnic groups throughout the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were Lithuanian Jews, Jews and Lipka Tatars, Tatars.
 Numerous languages were used in state documents depending on which period in history and for what purpose. These languages included Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Ruthenian, Polish and, to a lesser extent (mostly in early diplomatic communication), Latin and German.
The Court used Ruthenian to correspond with Eastern countries while Latin and German were used in foreign affairs with Western countries. During the latter part of the history of the Grand Duchy, Polish was increasingly used in State documents, especially after the Union of Lublin. By 1697, Polish had largely replaced Ruthenian as the "official" language at Court, although Ruthenian continued to be used on a few official documents until the second half of the 18th century.
It is known that Jogaila, being Lithuanians, ethnic Lithuanian by the man's line, himself knew and spoke in the Lithuanian language with
Numerous languages were used in state documents depending on which period in history and for what purpose. These languages included Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Ruthenian, Polish and, to a lesser extent (mostly in early diplomatic communication), Latin and German.
The Court used Ruthenian to correspond with Eastern countries while Latin and German were used in foreign affairs with Western countries. During the latter part of the history of the Grand Duchy, Polish was increasingly used in State documents, especially after the Union of Lublin. By 1697, Polish had largely replaced Ruthenian as the "official" language at Court, although Ruthenian continued to be used on a few official documents until the second half of the 18th century.
It is known that Jogaila, being Lithuanians, ethnic Lithuanian by the man's line, himself knew and spoke in the Lithuanian language with
 Ruthenian and Polish were used as state languages of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, besides Latin and German in diplomatic correspondence. However, Lithuanian was dominant in parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania like Samogitia, where the Samogitian nobility, local nobility's reliance on Lithuanian resulted in Stanisław Radziwiłł, Stanislovas Radvila remarking in a letter to his brother Mikalojus Kristupas Radvila Našlaitėlis immediately after becoming the Elder of Samogitia that: "While learning various languages, I forgot Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, and now I see, I have to go to school again, because that language, as I see, God willing, will be needed." Vilnius, Trakai and Samogitia were the core voivodeships of the state, being part of Lithuania Proper, as evidenced by the privileged position of their governors in state authorities, such as the Council of Lords. Peasants in ethnic Lithuanian territories spoke exclusively Lithuanian, except in transitional border regions, but the Statutes of Lithuania and other laws and documentation were written in Ruthenian, Latin and Polish. Following the example of the royal court, there was a tendency to replace Lithuanian language, Lithuanian with Polish in the ethnic Lithuanian areas, whereas Ruthenian was stronger in ethnic Belarusian and Ukrainian territories. A note written by Sigismund von Herberstein's states that, in an ocean of Ruthenian in this part of Europe, there were two non-Ruthenian regions: Lithuania and Samogitia.
Ruthenian and Polish were used as state languages of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, besides Latin and German in diplomatic correspondence. However, Lithuanian was dominant in parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania like Samogitia, where the Samogitian nobility, local nobility's reliance on Lithuanian resulted in Stanisław Radziwiłł, Stanislovas Radvila remarking in a letter to his brother Mikalojus Kristupas Radvila Našlaitėlis immediately after becoming the Elder of Samogitia that: "While learning various languages, I forgot Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, and now I see, I have to go to school again, because that language, as I see, God willing, will be needed." Vilnius, Trakai and Samogitia were the core voivodeships of the state, being part of Lithuania Proper, as evidenced by the privileged position of their governors in state authorities, such as the Council of Lords. Peasants in ethnic Lithuanian territories spoke exclusively Lithuanian, except in transitional border regions, but the Statutes of Lithuania and other laws and documentation were written in Ruthenian, Latin and Polish. Following the example of the royal court, there was a tendency to replace Lithuanian language, Lithuanian with Polish in the ethnic Lithuanian areas, whereas Ruthenian was stronger in ethnic Belarusian and Ukrainian territories. A note written by Sigismund von Herberstein's states that, in an ocean of Ruthenian in this part of Europe, there were two non-Ruthenian regions: Lithuania and Samogitia.
 Since the founding of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the higher strata of Lithuanian society from ethnic Lithuania spoke Lithuanian, although from the later 16th century gradually began using Polish, and those from Ruthenia – Ruthenian. Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitia was unique because of its economic situation – it lay near sea ports and there were fewer people under corvee, instead of that, many commoners were taxpayers. As a result, the stratification of society was not as sharp as in other areas. Being more similar to a commoner population, the local szlachta spoke Lithuanian to a bigger extent than in the areas close to the capital Vilnius, which itself had become the starting point of intensive linguistic Polonization of the surrounding areas since the 18th century.
In Vilnius University, there are preserved texts written in the Lithuanian language of the Vilnius area, a dialect of Eastern Aukštaitian, which was spoken in a territory located south-eastwards from Vilnius. The sources are preserved in works of graduates from Stanislovas Rapolionis-based Lithuanian language schools, graduate Martynas Mažvydas and Rapalionis relative Abraomas Kulvietis.
One of the main sources of Lithuanian written in the Eastern Aukštaitian dialect (Vilnius dialect) was preserved by Konstantinas Sirvydas in a trilingual (Polish-Latin-Lithuanian) 17th-century dictionary, ''Dictionarium trium linguarum in usum studiosæ juventutis'', which was the main Lithuanian dictionary used until the late 19th century.
''Universitas lingvarum Litvaniae, Universitas lingvarum Litvaniæ'', published in Vilnius, 1737, is the oldest surviving grammar of the Lithuanian language published in the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Since the founding of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the higher strata of Lithuanian society from ethnic Lithuania spoke Lithuanian, although from the later 16th century gradually began using Polish, and those from Ruthenia – Ruthenian. Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitia was unique because of its economic situation – it lay near sea ports and there were fewer people under corvee, instead of that, many commoners were taxpayers. As a result, the stratification of society was not as sharp as in other areas. Being more similar to a commoner population, the local szlachta spoke Lithuanian to a bigger extent than in the areas close to the capital Vilnius, which itself had become the starting point of intensive linguistic Polonization of the surrounding areas since the 18th century.
In Vilnius University, there are preserved texts written in the Lithuanian language of the Vilnius area, a dialect of Eastern Aukštaitian, which was spoken in a territory located south-eastwards from Vilnius. The sources are preserved in works of graduates from Stanislovas Rapolionis-based Lithuanian language schools, graduate Martynas Mažvydas and Rapalionis relative Abraomas Kulvietis.
One of the main sources of Lithuanian written in the Eastern Aukštaitian dialect (Vilnius dialect) was preserved by Konstantinas Sirvydas in a trilingual (Polish-Latin-Lithuanian) 17th-century dictionary, ''Dictionarium trium linguarum in usum studiosæ juventutis'', which was the main Lithuanian dictionary used until the late 19th century.
''Universitas lingvarum Litvaniae, Universitas lingvarum Litvaniæ'', published in Vilnius, 1737, is the oldest surviving grammar of the Lithuanian language published in the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
 Old Prussians, Prussian tribes (of Balts, Baltic origin) were the subject of Polish expansion, which was largely unsuccessful, so Duke Konrad of Masovia invited the
Old Prussians, Prussian tribes (of Balts, Baltic origin) were the subject of Polish expansion, which was largely unsuccessful, so Duke Konrad of Masovia invited the
File:Rudamina hill fort (09-06-13)1.jpg, Lithuanian ancient Hillfort#Lithuania, hill fort in Rudamina (Lazdijai), Rudamina
File:Kernavė - Hill forts 01.jpg, Lithuanian ancient Hillfort#Lithuania, hill fort mounds in
Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Encyclopedia in Three Volumes, Volume I
2nd edition, 2007. 688 pages, illustrated,
Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Encyclopedia in Three Volumes, Volume II
2nd edition, 2007. 792 pages, illustrated,
Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Encyclopedia in Three Volumes, Volume III
1st edition, 2010. 696 pages, illustrated, * Norman Davies. ''God's Playground''. Columbia University Press; 2nd edition (2002), . * * Robert Frost. ''The Oxford History of Poland-Lithuania: Volume I: The Making of the Polish-Lithuanian Union, 1385–1569''. Oxford University Press, 2015, * Alan V. Murray. ''Crusade and Conversion on the Baltic Frontier 1150–1500'' (Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Fourth Series). Routledge, 2001. . * Alan V. Murray. ''The Clash of Cultures on the Medieval Baltic Frontier'' Routledge, 2016. . * Zenonas Norkus. ''An Unproclaimed Empire: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania: From the Viewpoint of Comparative Historical Sociology of Empires'', Routledge, 2017, 426 p. * S. C. Rowell. ''Chartularium Lithuaniae res gestas magni ducis Gedeminne illustrans. Gedimino laiškai''. Vilnius, 2003,
e-copy
* S. C. Rowell. ''Lithuania Ascending: A Pagan Empire within East-Central Europe, 1295–1345'' (Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Fourth Series). Cambridge University Press, 2014. . * S. C. Rowell, D. Baronas. ''The conversion of Lithuania. From pagan barbarians to late medieval Christians''. Vilnius, 2015, . * Daniel Z. Stone. ''The Polish-Lithuanian State, 1386–1795''. University of Washington Press. 2014. pp. xii, 374. * A. Dubonis, D. Antanavičius, R. Ragauskiene, R. Šmigelskytė-Štukienė. ''The Lithuanian Metrica : History and Research''. Academic Studies Press. Brighton, United States, 2020. * Jūratė Kiaupienė. ''Between Rome and Byzantium: The Golden Age of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania's Political Culture. Second half of the fifteenth century to first half of the seventeenth century''. Academic Studies Press. Brighton, United States, 2020.
History of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
Zenonas Norkus. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the Retrospective of Comparative Historical Sociology of Empires
{{Authority control Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Medieval Lithuania Medieval Belarus Medieval Ukraine Medieval Poland Medieval Russia Early Modern history of Lithuania Early Modern history of Belarus Early Modern history of Ukraine Early Modern history of Poland Early Modern history of Russia Former grand duchies, Lithuania Former empires in Europe, Lithuania, Grand Duchy Former Slavic countries, Lithuania, Grand Duchy Polish–Lithuanian union Subdivisions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 1230s establishments in Europe 1795 disestablishments in Europe 1795 disestablishments in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth States and territories established in the 13th century States and territories disestablished in the 18th century Former countries Former monarchies of Europe
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
nation born from several united Baltic tribes
The Balts or Baltic peoples ( lt, baltai, lv, balti) are an ethno-linguistic group of peoples who speak the Baltic languages of the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages.
One of the features of Baltic languages is the number ...
from Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija (; literally in Lithuanian: ''Upper lands'') is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from lands being in upper basin of Nemunas River or being relative to Lowlands up to Šiauliai.
Geography
Au ...
.
The Grand Duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
and other neighbouring states, including what is now Lithuania, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and parts of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Latvia, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
and Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-eth ...
and multiconfessional
Multiconfessional countries have a power sharing arrangement between people of different faiths, usually three or more significant confessional groups within the same jurisdiction. Examples of modern countries deemed multiconfessional are Leban ...
state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage.
The consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 13th century. Mindaugas
Mindaugas (german: Myndowen, la, Mindowe, orv, Мендог, be, Міндоўг, pl, Mendog, c. 1203–1263) is the first known Grand Duke of Lithuania and the only crowned King of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or ...
, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
King of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Kingdom of Lithuania, Lithuania, which was established as an Absolute monarchy, absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three Duke, ducal D ...
in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in a religious crusade by the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
and the Livonian Order, but survived. Its rapid territorial expansion started late in the reign of Gediminas
Gediminas ( la, Gedeminne, ; – December 1341) was the king or Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1315 or 1316 until his death. He is credited with founding this political entity and expanding its territory which later spanned the area ranging from t ...
, and continued under the diarchy
Diarchy (from ancient Greek, Greek , ''di-'', "double", and , ''-arkhía'', "ruled"),Occasionally misspelled ''dyarchy'', as in the ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' article on the colonial British institution duarchy, or duumvirate (from Latin ', ...
and co-leadership of his sons Algirdas and Kęstutis
Kęstutis ( la, Kinstut, ; – 3 or 15 August 1382) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania. He was the Duke of Trakai and governed the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, 1342–1382, together with his brother Algirdas (until 1377), and with his nephew Jogaila ...
. Algirdas's son Jogaila signed the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; be, Крэўская унія, translit=Kreŭskaja unija; pl, unia w Krewie; lt, Krėvos sutartis) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made ...
in 1386, bringing two major changes in the history of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania: conversion to Christianity of Europe's last pagan state, and establishment of a dynastic union
A dynastic union is a type of union with only two different states that are governed under the same dynasty, with their boundaries, their laws, and their interests remaining distinct from each other.
Historical examples
Union of Kingdom of Arag ...
between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland.
The reign of Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
, son of Kęstutis, marked both the greatest territorial expansion of the Grand Duchy and the defeat of the Teutonic Knights in the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
in 1410. It also marked the rise of the Lithuanian nobility
The Lithuanian nobility or szlachta ( Lithuanian: ''bajorija, šlėkta'') was historically a legally privileged hereditary elite class in the Kingdom of Lithuania and Grand Duchy of Lithuania (including during period of foreign rule 1795–191 ...
. After Vytautas's death, Lithuania's relationship with the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
greatly deteriorated. Lithuanian noblemen, including the Radvila family, attempted to break the personal union with Poland. However, unsuccessful wars
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
with the Grand Duchy of Moscow forced the union to remain intact.
Eventually, the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
of 1569 created a new state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
. In the Federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania maintained its political distinctiveness and had separate ministries, laws, army, and treasury. The federation was terminated by the passing of the Constitution of 3 May 1791
The Constitution of 3 May 1791,; lt, Gegužės trečiosios konstitucija titled the Governance Act, was a constitution adopted by the Great Sejm ("Four-Year Sejm", meeting in 1788–1792) for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, a dual mo ...
, when it was supposed to become a single country, the Commonwealth, under one monarch, one parliament and no Lithuanian autonomy. Shortly afterward, the unitary character of the state was confirmed by adopting the Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations
The Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations ( pl, Zaręczenie Wzajemne Obojga Narodów;Michał Rozbicki, ''European and American Constitutionalism in the Eighteenth Century'', Uniwersytet Warszawski Ośrodek Studiów Amerykańskich, 1990, p.109-110Ke ...
.
However, the newly reformed Commonwealth was invaded by Russia in 1792 and partitioned between neighbouring states. A truncated state (whose principal cities were Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
, Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
and Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
) remained that was nominally independent. After the Kościuszko Uprising, the territory was completely partitioned among the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
and Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
in 1795.
Etymology
The name of Lithuania (''Litua'') was first mentioned in 1009 in Annals of Quedlinburg. Some older etymological theories relate the name to a small river not far fromKernavė
Kernavė was a medieval capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and today is a tourist attraction and an archeological site (population 272, 2011). It is located in the Širvintos district municipality located in southeast Lithuania. A Lithuania ...
, the core area of the early Lithuanian state and a possible first capital of the would-be Grand Duchy of Lithuania, is usually credited as the source of the name. This river's original name is Lietava
Lietava ( hu, Zsolnalitva) is a village and municipality in Žilina District in the Žilina Region of northern Slovakia. Lietava Castle, the third largest castle in Slovakia, is in the village.
History
In historical records the village was firs ...
.Zigmas Zinkevičius. Kelios mintys, kurios kyla skaitant Alfredo Bumblausko Senosios Lietuvos istoriją 1009-1795m. Voruta, 2005. As time passed, the suffix -''ava'' could have changed into -''uva'', as the two are from the same suffix branch. The river flows in the lowlands and easily spills over its banks, therefore the traditional Lithuanian form ''liet''- could be directly translated as ''lietis'' (to spill), of the root derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''leyǝ-''. However, the river is very small and some find it improbable that such a small and local object could have lent its name to an entire nation. On the other hand, such a fact is not unprecedented in world history. The most credible modern theory of etymology of the name of Lithuania (Lithuanian: ''Lietuva'') is Artūras Dubonis's hypothesis, that Lietuva relates to the word ''leičiai
Leičiai (singular: leitis) were a distinct social group of the Lithuanian society in the early Grand Duchy of Lithuania subordinate to the Lithuanian ruler or the state itself. Leičiai were native to the Lietuva Land and formed the core of th ...
'' (plural of ''leitis'', a social group of warriors-knights in the early Grand Duchy of Lithuania). The title of the ''Grand Duchy'' was consistently applied to Lithuania from the 14th century onward.
In other languages, the grand duchy is referred to as:
* be, Вялікае Княства Літоўскае
*german: Großfürstentum Litauen
* et, Leedu Suurvürstiriik
* la, Magnus Ducatus Lituaniæ
* lv, Lieitija or
* lt, Lietuvos Didžioji Kunigaikštystė
*Old literary Lithuanian: Didi Kunigystė Lietuvos (''didi Kunigiſte Lietuwos'')
* pl, Wielkie Księstwo Litewskie
* ro, Marele Ducat al Lituaniei
*russian: Великое княжество Литовское
* Ruthenian: Великое кнѧзство Литовское
* uk, Велике князiвство Литовське
Naming convention of both title of ruler (hospodar
Hospodar or gospodar is a term of Slavonic origin, meaning "lord" or " master".
Etymology and Slavic usage
In the Slavonic language, ''hospodar'' is usually applied to the master/owner of a house or other properties and also the head of a family. ...
) and the state changed as it expanded its territory. Following the decline of the Kingdom of Ruthenia
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
and incorporation of its lands into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Gediminas
Gediminas ( la, Gedeminne, ; – December 1341) was the king or Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1315 or 1316 until his death. He is credited with founding this political entity and expanding its territory which later spanned the area ranging from t ...
started to title himself as "King of Lithuanians and many Ruthenians", while the name of the state became the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Ruthenia. Similarly the title changed to "King of Lithuanians and Ruthenians, ruler and duke of Semigallia" when Semigallia
Semigallia, also spelt Semigalia, ( lv, Zemgale; german: Semgallen; lt, Žiemgala; pl, Semigalia; liv, Zemgāl) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands located in the south of the Daugava river and the north of the Saule region of Samogitia. ...
became part of the state. The 1529 edition of the Statute of Lithuania
The Statutes of Lithuania, originally known as the Statutes of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, were a 16th-century codification of all the legislation of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and its successor, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Stat ...
described the titles of Sigismund I the Old as "King of Poland, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, Ruthenia, Prussia, Samogitia, Mazovia, and other lands
Land is the solid surface of the Earth that is not covered by water.
Land, lands, The Land, or the Lands may also refer to:
Entertainment and media Film
*Land (1987 film), ''Land'' (1987 film), a British television film by Barry Collins
*Land ( ...
. When southern and western Ruthenian lands were transferred to the Crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
after the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
, the titles of the Grand Duke of Lithuania were transferred to the titles of the rulers of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
The country was also called the Republic of Lithuania ( la, Respublica Lituana) since at least the mid-16th century, already before the Union of Lublin in 1569.
History
Establishment of the state

Quedlinburg Chronicle
The ''Annals of Quedlinburg'' ( lat, Annales Quedlinburgenses; german: Quedlinburger Annalen) were written between 1008 and 1030 in the convent of Quedlinburg Abbey. In recent years a consensus has emerged that it is likely that the annalist was ...
, which dates from 1009. In the 12th century, Slavic chronicles refer to Lithuania as one of the areas attacked by the Rus'. Pagan Lithuanians initially paid tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
to Polotsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
, but they soon grew in strength and organized their own small-scale raids. At some point between 1180 and 1183 the situation began to change, and the Lithuanians started to organize sustainable military raids on the Slavic provinces, raiding the Principality of Polotsk
The Principality of Polotsk ( be, По́лацкае кня́ства, ''Polackaje kniastva''; la, Polocensis Ducatus), also known as the Duchy of Polotsk or Polotskian Rus', was a medieval principality of the Early East Slavs. The origin and ...
as well as Pskov, and even threatening Novgorod. The sudden spark of military raids marked consolidation of the Lithuanian lands in Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija (; literally in Lithuanian: ''Upper lands'') is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from lands being in upper basin of Nemunas River or being relative to Lowlands up to Šiauliai.
Geography
Au ...
. The Lithuanians are the only branch within the Baltic group that managed to create a state entity in premodern times.
The Lithuanian Crusade
The Lithuanian Crusade was a series of economic Christian colonization campaigns by the Teutonic Order and the Livonian Order under the pretext of forcibly Christianizing the pagan Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The Livonian Order occupied Riga in ...
began after the Livonian Order and Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
, crusading military orders, were established in Riga and in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
in 1202 and 1226 respectively. The Christian orders posed a significant threat to pagan Baltic tribes, and further galvanized the formation of the Lithuanian state. The peace treaty with Galicia–Volhynia of 1219 provides evidence of cooperation between Lithuanians and Samogitia
Samogitia or Žemaitija ( Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
ns. This treaty lists 21 Lithuanian dukes, including five senior Lithuanian dukes from Aukštaitija (Živinbudas
Živinbudas was one of the five senior Lithuanian dukes mentioned in the treaty with Halych-Volhynia in 1219. The treaty lists a total of 21 dukes, five of them being elder or superior. Since Živinbudas is mentioned first in the list, it is pre ...
, Daujotas Daujotas was one of the 5 elder Lithuanian duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sover ...
, Vilikaila
Vilikaila or Viligaila was one of the five elder Lithuanian duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, gran ...
, Dausprungas Dausprungas (also ''Dovsprunk'' in Russian sources, died before 1238) was the older brother of Mindaugas, the first King of Lithuania. Dausprungas is mentioned in the peace treaty with Galicia–Volhynia in 1219 among the 21 early dukes of Lithuan ...
and Mindaugas
Mindaugas (german: Myndowen, la, Mindowe, orv, Мендог, be, Міндоўг, pl, Mendog, c. 1203–1263) is the first known Grand Duke of Lithuania and the only crowned King of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or ...
) and several dukes from Žemaitija
Samogitia or Žemaitija ( Samogitian: ''Žemaitėjė''; see below for alternative and historical names) is one of the five cultural regions of Lithuania and formerly one of the two core administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuani ...
. Although they had battled in the past, the Lithuanians and the Žemaičiai now faced a common enemy. Likely Živinbudas had the most authority and at least several dukes were from the same families. The formal acknowledgement of common interests and the establishment of a hierarchy among the signatories of the treaty foreshadowed the emergence of the state.
Kingdom of Lithuania
Mindaugas, the duke of southern Lithuania, was among the five senior dukes mentioned in the treaty with Galicia–Volhynia. TheLivonian Rhymed Chronicle
The ''Livonian Rhymed Chronicle'' (german: Livländische Reimchronik) is a chronicle written in Middle High German by an anonymous author. It covers the period 1180 – 1343 and contains a wealth of detail about Livonia — modern South Estonia a ...
, reports that by the mid-1230s, Mindaugas had acquired supreme power in the whole of Lithuania. In 1236, the Samogitians, led by Vykintas
200 px, Monument to Duke Vykintas in Tverai
Vykintas (died ) was Duke of Samogitia and a rival to the future King of Lithuania, Mindaugas. In 1236 he probably led the Samogitian forces in the Battle of Saule against the Livonian Order. The Order ...
, defeated the Livonian Order in the Battle of Saule
The Battle of Saule ( lt, Saulės mūšis / Šiaulių mūšis; german: Schlacht von Schaulen; lv, Saules kauja) was fought on 22 September 1236, between the Livonian Brothers of the Sword and pagan troops of Samogitians and Semigallians. Betwe ...
. The Order was forced to become a branch of the Teutonic Knights in Prussia, making Samogitia, a strip of land that separated Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
from Prussia, the main target of both orders. The battle provided a break in the wars with the Knights, and Lithuania exploited this situation, arranging attacks on the Ruthenian provinces and annexing Navahrudak
Novogrudok ( be, Навагрудак, Navahrudak; lt, Naugardukas; pl, Nowogródek; russian: Новогрудок, Novogrudok; yi, נאַוואַראַדאָק, Novhardok, Navaradok) is a town in the Grodno Region, Belarus.
In the Middle ...
and Hrodna
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
.
In 1248, a civil war broke out between Mindaugas and his nephews Tautvilas
Tautvilas (or Tautvila; died 1263) was Duke of Polotsk and one of Dausprungas' sons and nephews of King of Lithuania Mindaugas. Tautvilas together with his brother Gedvydas and uncle Vykintas waged a civil war against Mindaugas. The war resulted ...
and Edivydas Gedvydas (or Edivid) (believed to have died ca. 1253) was one of the sons of Dausprungas and nephews of King of Lithuania Mindaugas. Gedvydas together with his brother Tautvilas and uncle Vykintas waged a civil war against Mindaugas. Gedvydas' broth ...
. The powerful coalition against Mindaugas included Vykintas, the Livonian Order, Daniel of Galicia
Daniel of Galicia ( uk, Данило Романович (Галицький), Danylo Romanovych (Halytskyi); Old Ruthenian: Данило Романовичъ, ''Danylo Romanovyčъ''; pl, Daniel I Romanowicz Halicki; 1201 – 1264) was a King ...
and Vasilko of Volhynia
Vasylko Romanovych (1203–1269), Prince of Belz (1207–1269), Prince of Brest (1231–1269), and Prince of Volhynia (1231–1269).
He was the son of Roman the Great, the younger brother of Daniel of Galicia.
Family
Father
*Roman the Great
Bro ...
. Taking advantage of internal conflicts, Mindaugas allied with the Livonian Order. He promised to convert to Christianity and exchange some lands in western Lithuania in return for military assistance against his nephews and the royal crown. In 1251, Mindaugas was baptized and Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV ( la, Innocentius IV; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universitie ...
issued a papal bull proclaiming the creation of the Kingdom of Lithuania
The Kingdom of Lithuania was a Lithuanian state, which existed roughly from 1251 to 1263. King Mindaugas was the first and only Lithuanian monarch crowned King of Lithuania with the assent of the Pope. The formation of the Kingdom of Lithuani ...
. After the civil war ended, Mindaugas was crowned as King of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Kingdom of Lithuania, Lithuania, which was established as an Absolute monarchy, absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three Duke, ducal D ...
on 6 July 1253, starting a decade of relative peace. Mindaugas later renounced Christianity and converted back to paganism. Mindaugas tried to expand his influence in Polatsk
Polotsk (russian: По́лоцк; be, По́лацк, translit=Polatsk (BGN/PCGN), Polack (official transliteration); lt, Polockas; pl, Połock) is a historical city in Belarus, situated on the Dvina River. It is the center of the Polotsk Dist ...
, a major centre of commerce in the Daugava River
, be, Заходняя Дзвіна (), liv, Vēna, et, Väina, german: Düna
, image = Fluss-lv-Düna.png
, image_caption = The drainage basin of the Daugava
, source1_location = Valdai Hills, Russia
, mouth_location = Gulf of Riga, Baltic S ...
basin, and Pinsk
Pinsk ( be, Пі́нск; russian: Пи́нск ; Polish: Pińsk; ) is a city located in the Brest Region of Belarus, in the Polesia region, at the confluence of the Pina River and the Pripyat River. The region was known as the Marsh of Pinsk ...
. The Teutonic Knights used this period to strengthen their position in parts of Samogitia and Livonia, but they lost the Battle of Skuodas
The Battle of Skuodas or Schoden was a medieval battle fought in ca. 1259 near Skuodas in present-day Lithuania during the Lithuanian Crusade. The Samogitian army of 3,000 invaded Courland and on their way back defeated the Livonian Order, kil ...
in 1259 and the Battle of Durbe in 1260. This encouraged the conquered Semigallians and Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians ( Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that ...
to rebel against the Knights.
Encouraged by Treniota
Treniota ( be, Транята; ''Troniata''; c. 1210–1264) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania (1263–1264).
Treniota was the nephew of Mindaugas, the first and only king of Lithuania. While Mindaugas had converted to Christianity in order to di ...
, Mindaugas broke the peace with the Order, possibly reverted to pagan beliefs. He hoped to unite all Baltic tribes under the Lithuanian leadership. As military campaigns were not successful, the relationships between Mindaugas and Treniota deteriorated. Treniota, together with Daumantas of Pskov
Daumantas or Dovmont ( Russian: Довмонт, Belarusian: Даўмонт, Christian name Timothy (russian: Тимофей), ; c. 1240? – 17 May 1299), was a Lithuanian prince best remembered as a military leader of the Principality of ...
, assassinated Mindaugas and his two sons, Ruklys and Rupeikis, in 1263. The state lapsed into years of internal fighting.Rise of the Gediminids
 From 1263 to 1269, Lithuania had three grand dukes –
From 1263 to 1269, Lithuania had three grand dukes – Treniota
Treniota ( be, Транята; ''Troniata''; c. 1210–1264) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania (1263–1264).
Treniota was the nephew of Mindaugas, the first and only king of Lithuania. While Mindaugas had converted to Christianity in order to di ...
, Vaišvilkas
Vaišvilkas or Vaišelga (also spelled as ''Vaišvila'', ''Vojszalak'', ''Vojšalk'', ''Vaišalgas''; killed on 18 April 1267) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania (1264–1267). He was son of Mindaugas, the first and only Christian King of Lithu ...
, and Svarn, Švarnas. The state did not disintegrate, however, and Traidenis came to power in 1269. He strengthened Lithuanian control in Black Ruthenia and fought with the Livonian Order, winning the Battle of Karuse in 1270 and the Battle of Aizkraukle in 1279. There is considerable uncertainty about the identities of the grand dukes of Lithuania between his death in 1282 and the assumption of power by Vytenis in 1295. During this time the Orders finalized their conquests. In 1274, the Great Prussian Rebellion ended, and the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
proceeded to conquer other Baltic tribes: the Nadruvians and Skalvians in 1274–1277, and the Yotvingians in 1283; the Livonian Order completed its conquest of Semigalia, the last Baltic ally of Lithuania, in 1291. The Orders could now turn their full attention to Lithuania. The "buffer zone" composed of other Baltic tribes had disappeared, and Grand Duchy of Lithuania was left to battle the Orders on its own.
The Gediminids, Gediminid dynasty ruled the grand duchy for over a century, and Vytenis was the first ruler of the dynasty. During his reign Lithuania was in constant war with the Order, the Kingdom of Poland, and Ruthenia. Vytenis was involved in succession disputes in Poland, supporting Boleslaus II of Masovia, who was married to a Lithuanian duchess, Gaudemunda of Lithuania, Gaudemunda. In Ruthenia, Vytenis managed to recapture lands lost after the assassination of Mindaugas and to capture the principalities of and Principality of Turov, Turov. In the struggle against the Order, Vytenis allied with Riga's citizens; securing positions in Riga strengthened trade routes and provided a base for further military campaigns. Around 1307, Polotsk, an important trading centre, was annexed by military force. Vytenis also began constructing a defensive castle network along Nemunas. Gradually this network developed into the main defensive line against the Teutonic Order.
Territorial expansion
The expansion of the state reached its height under Grand DukeGediminas
Gediminas ( la, Gedeminne, ; – December 1341) was the king or Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1315 or 1316 until his death. He is credited with founding this political entity and expanding its territory which later spanned the area ranging from t ...
, also titled by some contemporaneous German sources as ''Rex de Owsteiten'' ( en, King of Aukštaitija
Aukštaitija (; literally in Lithuanian: ''Upper lands'') is the name of one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. The name comes from lands being in upper basin of Nemunas River or being relative to Lowlands up to Šiauliai.
Geography
Au ...
), who created a strong central government and established an empire that later spread from the Black Sea to the Baltic Sea. In 1320, most of the principalities of western Rus' were either vassalized or annexed by Lithuania. In 1321, Gediminas Battle on the Irpen' River, captured Kiev, sending Stanislav of Kiev, Stanislav, the last Rurikid to rule Kiev, into exile. Gediminas also re-established the permanent capital of the Grand Duchy in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urb ...
, presumably moving it from Senieji Trakai, Old Trakai in 1323. The state continued to expand its territory under the reign of Grand Duke Algirdas and his brother Kęstutis
Kęstutis ( la, Kinstut, ; – 3 or 15 August 1382) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania. He was the Duke of Trakai and governed the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, 1342–1382, together with his brother Algirdas (until 1377), and with his nephew Jogaila ...
, who both ruled the state harmonically.
 Lithuania was in a good position to conquer the western and the southern parts of former
Lithuania was in a good position to conquer the western and the southern parts of former Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
. While almost every other state around it had been Mongol invasion of Rus', plundered or defeated by the Mongols, the hordes stopped at the modern borders of Belarus, and the core territory of the Grand Duchy was left mostly untouched. The weak control of the Mongols over the areas they had conquered allowed the expansion of Lithuania to accelerate. Rus' principalities were never incorporated directly into the Golden Horde, maintaining vassal relationships with a fair degree of independence. Lithuania annexed some of these areas as vassals through diplomacy, as they exchanged rule by the Mongols or the Grand Prince of Moscow with rule by the Grand Duchy. An example is Novgorod, which was often in the Lithuanian sphere of influence and became an occasional dependency of the Grand Duchy. Lithuanian control resulted from internal frictions within the city, which attempted to escape submission to Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow. Such relationships could be tenuous, however, as changes in a city's internal politics could disrupt Lithuanian control, as happened on a number of occasions with Novgorod and other East-Slavic cities.
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania managed to hold off Mongol incursions and eventually secured gains. In 1333 and 1339, Lithuanians defeated large Mongol forces attempting to regain Smolensk from the Lithuanian sphere of influence. By about 1355, the State of Moldavia had formed, and the Golden Horde did little to re-vassalize the area. In 1362, regiments of the Grand Duchy army defeated the Golden Horde at the Battle at Blue Waters (1362), Battle at Blue Waters. In 1380, a Lithuanian army allied with Russian forces to defeat the Golden Horde in the Battle of Kulikovo, and though the rule of the Mongols did not end, their influence in the region waned thereafter. In 1387, Moldavia became a vassal of Poland and, in a broader sense, of Lithuania. By this time, Lithuania had conquered the territory of the Golden Horde all the way to the Dnieper River. In a crusade against the Golden Horde in 1398 (in an alliance with Tokhtamysh), Lithuania invaded northern Crimea and won a decisive victory. In an attempt to place Tokhtamish on the Golden Horde throne in 1399, Lithuania moved against the Horde but was defeated in the Battle of the Vorskla River, losing the steppe region.
Personal Union with Poland

 Lithuania was Christianized in 1387, led by Jogaila, who personally translated Christian prayers into the Lithuanian language and his cousin Vytautas the Great who founded many Catholic churches and allocated lands for parishes in Lithuania. The state reached a peak under
Lithuania was Christianized in 1387, led by Jogaila, who personally translated Christian prayers into the Lithuanian language and his cousin Vytautas the Great who founded many Catholic churches and allocated lands for parishes in Lithuania. The state reached a peak under Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
, who reigned from 1392 to 1430. Vytautas was one of the most famous rulers of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, serving as the Grand Duke from 1401 to 1430, and as the Prince of Hrodna
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
(1370–1382) and the Prince of Lutsk (1387–1389). Vytautas was the son of Kęstutis
Kęstutis ( la, Kinstut, ; – 3 or 15 August 1382) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania. He was the Duke of Trakai and governed the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, 1342–1382, together with his brother Algirdas (until 1377), and with his nephew Jogaila ...
, uncle of Jogaila, who became King of Poland in 1386, and he was the grandfather of Vasili II of Moscow.
In 1410, Vytautas commanded the forces of the Grand Duchy in the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
. The battle ended in a decisive Polish-Lithuanian victory against the Teutonic Order. The Lithuanian Crusade, war of Lithuania against military Orders, which lasted for more than 200 years, and was one of the longest wars in the history of Europe, was finally ended. Vytautas backed the economic development of the state and introduced many reforms. Under his rule, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania slowly became more centralized, as the governours loyal to Vytautas replaced local princes with dynastic ties to the throne. The governours were rich landowners who formed the basis for the nobility of the Grand Duchy. During Vytautas' rule, the Radziwiłł and Goštautas families started to gain influence.
 The rapid expansion of the influence of Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow soon put it into a comparable position to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and after the annexation of Novgorod in 1478, Muscovy was among the preeminent states in Baltic states, northeastern Europe. Between 1492 and 1508, Ivan III further consolidated Muscovy, winning the key Battle of Vedrosha and regaining such ancient lands of
The rapid expansion of the influence of Grand Duchy of Moscow, Moscow soon put it into a comparable position to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and after the annexation of Novgorod in 1478, Muscovy was among the preeminent states in Baltic states, northeastern Europe. Between 1492 and 1508, Ivan III further consolidated Muscovy, winning the key Battle of Vedrosha and regaining such ancient lands of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
as Chernihiv and Bryansk.
On 8 September 1514, the allied forces of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland, under the command of Hetman Konstanty Ostrogski, fought the Battle of Orsha against the army of the Grand Duchy of Moscow, under Konyushy Ivan Chelyadnin and Kniaz Mikhail Golitsin. The battle was part of a long series of Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars conducted by Russian rulers striving to gather all the former lands of Kievan Rus' under their rule. According to ''Rerum Moscoviticarum Commentarii'' by Sigismund von Herberstein, the primary source for the information on the battle, the much smaller army of Poland–Lithuania (under 30,000 men) defeated the 80,000 Muscovite soldiers, capturing their camp and commander. The Muscovites lost about 30,000 men, while the losses of the Poland–Lithuania army totalled only 500. While the battle is remembered as one of the greatest Lithuanian victories, Muscovy ultimately prevailed in the war. Under the 1522 peace treaty, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania made large territorial concessions.
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
 The wars with the Teutonic Order, the loss of land to Moscow, and the continued pressure threatened the survival of the state of Lithuania, so it was forced to ally more closely with
The wars with the Teutonic Order, the loss of land to Moscow, and the continued pressure threatened the survival of the state of Lithuania, so it was forced to ally more closely with Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, uniting with its western neighbour as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
(Commonwealth of Two Nations) in the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
of 1569. During the period of the Union, many of the territories formerly controlled by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were transferred to the Crown of the Polish Kingdom, while the gradual process of Polonization slowly drew Lithuania itself under Polish domination. The Grand Duchy retained many rights in the federation (including separate ministries, laws, army, and treasury) until the May Constitution of Poland and Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations
The Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations ( pl, Zaręczenie Wzajemne Obojga Narodów;Michał Rozbicki, ''European and American Constitutionalism in the Eighteenth Century'', Uniwersytet Warszawski Ośrodek Studiów Amerykańskich, 1990, p.109-110Ke ...
were passed in 1791.
Partitions and the Napoleonic period
Following the Partitions of Poland, partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, most of the lands of the former Grand Duchy were directly annexed by theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, the rest by Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
. In 1812, just prior to the French invasion of Russia, the former Grand Duchy revolted against the Russians. Soon after his arrival in Vilnius, Napoleon proclaimed the creation of a Commissary Provisional Government of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania which, in turn, renewed the Polish-Lithuanian Union. The union was never formalized, however, as only half a year later Napoleon's ''Grande Armée'' was pushed out of Russia and forced to retreat further westwards. In December 1812, Vilnius was recaptured by Russian forces, bringing all plans of recreation of the Grand Duchy to an end. Most of the lands of the former Grand Duchy were re-annexed by Russia. The Augustów Voivodeship (later Augustów Governorate), including the counties of Marijampolė and Kalvarija, Lithuania, Kalvarija, was attached to the Congress Poland, Kingdom of Poland, a rump state in personal union with Russia.
Administrative division
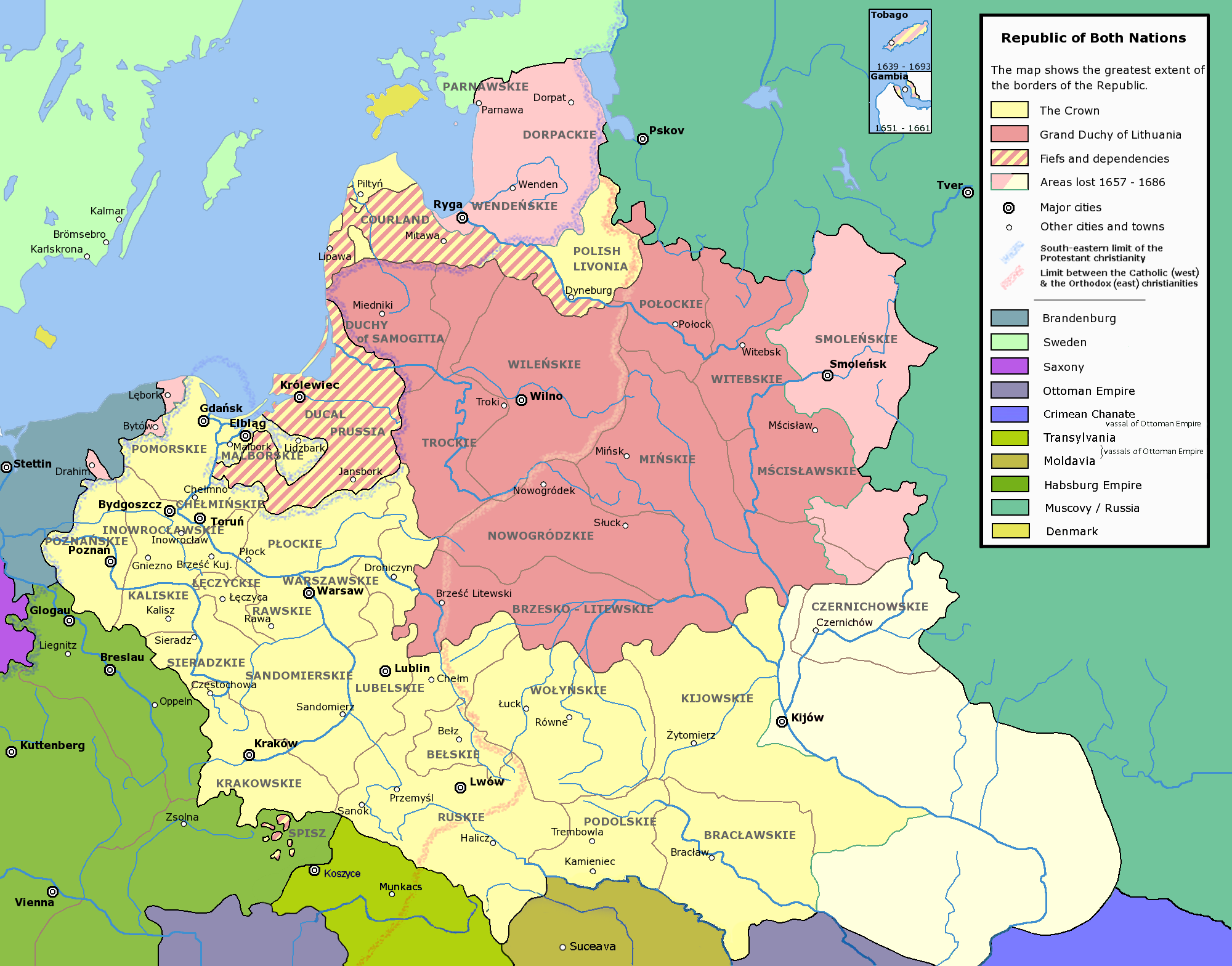
 Administrative structure of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1413–1564).
Administrative structure of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1413–1564).
Religion and culture
Christianity and paganism
After the baptism in 1252 and coronation of KingMindaugas
Mindaugas (german: Myndowen, la, Mindowe, orv, Мендог, be, Міндоўг, pl, Mendog, c. 1203–1263) is the first known Grand Duke of Lithuania and the only crowned King of Lithuania. Little is known of his origins, early life, or ...
in 1253, Lithuania was recognized as a Christian state until 1260, when Mindaugas supported an uprising in Courland and (according to the German order) renounced Christianity. Up until 1387, Lithuanian nobles professed their own religion, which was polytheistic. Ethnic Lithuanians were very dedicated to their faith. The pagan beliefs needed to be deeply entrenched to survive strong pressure from missionaries and foreign powers. Until the 17th century, there were relics of old faith reported by counter-reformation active Society of Jesus, Jesuit priests, like feeding žaltys with milk or bringing food to graves of ancestors. The lands of modern-day Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, as well as local dukes (princes) in these regions, were firmly Eastern Orthodox, Orthodox Christian (Greek Catholic after the Union of Brest), though. While pagan beliefs in Lithuania were strong enough to survive centuries of pressure from military orders and missionaries, they did eventually succumb. A separate Metropolitanate of Lithuania, Eastern Orthodox metropolitan eparchy was created sometime between 1315 and 1317 by the Constantinople Patriarch John XIII of Constantinople, John XIII. Following the Galicia–Volhynia Wars which divided the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland, in 1355 the Halych metropoly was liquidated and its eparchies transferred to the metropoles of Lithuania and Volhynia.
In 1387, Lithuania Christianization of Lithuania, converted to Catholicism, while most of the Ruthenian lands stayed Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox, however, on 22 February 1387, Supreme Duke Jogaila banned Catholics marriages with Orthodox, and demanded those Orthodox who previously married with the Catholics to convert to Catholicism. At one point, though, Pope Alexander VI reprimanded the Grand Duke for keeping non-Catholics as advisers. Consequently, only in 1563 did Grand Duke Sigismund II Augustus issue a privilege that equalized the rights of Orthodox and Catholics in Lithuania and abolished all previous restrictions on Orthodox. There was an effort to polarise Orthodox Christians after the Union of Brest in 1596, by which some Orthodox Christians acknowledged papal authority and Catholic catechism, but preserved their liturgy. The country also became one of the major centres of the Reformation.
In the second half of the 16th century, Calvinism spread in Lithuania, supported by the families of Radziwiłł, Chodkiewicz, Sapieha, Dorohostajski and others. By the 1580s the majority of the senators from Lithuania were Calvinist or Socinianism, Socinian Unitarians (Jan Kiszka).
In 1579, Stephen Báthory, King of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and Grand Duke of Lithuania, founded Vilnius University, one of the oldest universities in Northern Europe. Due to the work of the Jesuits during the Counter-Reformation the university soon developed into one of the most important scientific and cultural centres of the region and the most notable scientific centre of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The work of the Jesuits as well as conversions from among the Lithuanian senatorial families turned the tide and by the 1670s Polish Reformed Church, Calvinism lost its former importance though it still retained some influence among the ethnically Lithuanian peasants and some middle nobility.
Islam
Islam in Lithuania, unlike many other northern and western European countries, has a long history starting from 14th century. Small groups of Muslim Lipka Tatars migrated to ethnically Lithuanian lands, mainly under the rule of Grand Duke Vytautas the Great, Vytautas (early 15th century). In Lithuania, unlike many other European societies at the time, there was religious freedom. Lithuanian Tatars were allowed to settle in certain places, such as Trakai and Kaunas. Keturiasdešimt Totorių is one of the oldest Tatar settlements in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. After a successful military campaign of the Crimean Peninsula in 1397, Vytautas brought the first Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar prisoners of war to Trakai and various places in the Duchy of Trakai, including localities near Vokė river just south of Vilnius. The first mosque in this village was mentioned for the first time in 1558. There were 42 Tatar families in the village in 1630.Judaism
Languages
 In the 13th century, the Lithuania Proper, centre of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was inhabited by a majority that spoke Lithuanian, though it was not a written language until the 16th century. In the other parts of the duchy, the majority of the population, including Ruthenian nobility, Ruthenian nobles and ordinary people, used both spoken and written Ruthenian. Nobles who migrated from one place to another would adapt to a new locality and adopt the local religion and culture and those Lithuanian nobility, Lithuanian noble families that moved to Slavic areas often took up the local culture quickly over subsequent generations. Ruthenians were native to the east-central and south-eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Ruthenian, also called Chancery Slavonic in its written form, was used to write laws alongside Polish, Latin and German, but its use varied between regions. From the time of Vytautas, there are fewer remaining documents written in Ruthenian than there are in Latin and German, but later Ruthenian became the main language of documentation and writings, especially in eastern and southern parts of the Duchy. In the 16th century at the time of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Lithuanian lands became partially polonization, polonized over time and started to use Polish language, Polish for writing much more often than the Lithuanian and Ruthenian languages. Polish finally became the official chancellery language of the Commonwealth in 1697.
The voivodeships with a predominantly ethnic Lithuanian population, Vilnius voivodeship, Vilnius, Trakai voivodeship, Trakai, and Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitian voivodeships, remained almost wholly Lithuanian-speaking, both colloquially and by ruling nobility. Ruthenian communities were also present in the extreme southern parts of Trakai voivodeship and south-eastern parts of Vilnius Voivodeship. In addition to Lithuanians and Ruthenians, other important ethnic groups throughout the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were Lithuanian Jews, Jews and Lipka Tatars, Tatars.
In the 13th century, the Lithuania Proper, centre of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was inhabited by a majority that spoke Lithuanian, though it was not a written language until the 16th century. In the other parts of the duchy, the majority of the population, including Ruthenian nobility, Ruthenian nobles and ordinary people, used both spoken and written Ruthenian. Nobles who migrated from one place to another would adapt to a new locality and adopt the local religion and culture and those Lithuanian nobility, Lithuanian noble families that moved to Slavic areas often took up the local culture quickly over subsequent generations. Ruthenians were native to the east-central and south-eastern parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Ruthenian, also called Chancery Slavonic in its written form, was used to write laws alongside Polish, Latin and German, but its use varied between regions. From the time of Vytautas, there are fewer remaining documents written in Ruthenian than there are in Latin and German, but later Ruthenian became the main language of documentation and writings, especially in eastern and southern parts of the Duchy. In the 16th century at the time of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Lithuanian lands became partially polonization, polonized over time and started to use Polish language, Polish for writing much more often than the Lithuanian and Ruthenian languages. Polish finally became the official chancellery language of the Commonwealth in 1697.
The voivodeships with a predominantly ethnic Lithuanian population, Vilnius voivodeship, Vilnius, Trakai voivodeship, Trakai, and Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitian voivodeships, remained almost wholly Lithuanian-speaking, both colloquially and by ruling nobility. Ruthenian communities were also present in the extreme southern parts of Trakai voivodeship and south-eastern parts of Vilnius Voivodeship. In addition to Lithuanians and Ruthenians, other important ethnic groups throughout the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were Lithuanian Jews, Jews and Lipka Tatars, Tatars.
Languages for state and academic purposes
 Numerous languages were used in state documents depending on which period in history and for what purpose. These languages included Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Ruthenian, Polish and, to a lesser extent (mostly in early diplomatic communication), Latin and German.
The Court used Ruthenian to correspond with Eastern countries while Latin and German were used in foreign affairs with Western countries. During the latter part of the history of the Grand Duchy, Polish was increasingly used in State documents, especially after the Union of Lublin. By 1697, Polish had largely replaced Ruthenian as the "official" language at Court, although Ruthenian continued to be used on a few official documents until the second half of the 18th century.
It is known that Jogaila, being Lithuanians, ethnic Lithuanian by the man's line, himself knew and spoke in the Lithuanian language with
Numerous languages were used in state documents depending on which period in history and for what purpose. These languages included Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, Ruthenian, Polish and, to a lesser extent (mostly in early diplomatic communication), Latin and German.
The Court used Ruthenian to correspond with Eastern countries while Latin and German were used in foreign affairs with Western countries. During the latter part of the history of the Grand Duchy, Polish was increasingly used in State documents, especially after the Union of Lublin. By 1697, Polish had largely replaced Ruthenian as the "official" language at Court, although Ruthenian continued to be used on a few official documents until the second half of the 18th century.
It is known that Jogaila, being Lithuanians, ethnic Lithuanian by the man's line, himself knew and spoke in the Lithuanian language with Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
, his cousin from the Gediminids dynasty. Also, during the Christianization of Lithuania#Christianization by Jogaila and Vytautas, Christianization of Samogitia, none of the clergy, who came to Duchy of Samogitia, Samogitia with Jogaila, were able to communicate with the natives, therefore Jogaila himself taught the Samogitians about the Catholic Church, Catholicism, thus he was able to communicate in the Samogitian dialect of the Lithuanian language. Use of Lithuanian still continued at the Court after the death of Vytautas and Jogaila. Since the young Grand Duke Casimir IV Jagiellon was underage, the supreme control over the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was in the hands of the Lithuanian Council of Lords, presided by Jonas Goštautas, while Casimir was taught Lithuanian language and the customs of Lithuania by appointed court officials. Grand Duke Alexander Jagiellon also could understand and speak Lithuanian. While Grand Duke Sigismund II Augustus maintained both Polish-speaking and Lithuanian-speaking courts.
From the beginning of the 16th century, and especially after a Glinski rebellion, rebellion led by Michael Glinski in 1508, there were attempts by the Court to replace the usage of Ruthenian with Latin. The use of Ruthenian by academics in areas formerly part of Rus' and even in Lithuania proper was widespread. kanclerz, Court Chancellor of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania Lew Sapieha noted in the preface of the Statutes of Lithuania, Third Statute of Lithuania (1588) that all state documents to be written exclusively in Ruthenian. The same was stated in part 4 of the Statute: Despite that, Polish-language editions stated the same in Polish. Statutes of the Grand Duchy were translated into Latin and Polish. One of the main reasons for translations into Latin was that Ruthenian had no well defined and codified law concepts and definitions, which caused many disputes in courts. Another reason to use Latin was a popular idea that Lithuanians were descendants of Romans – the mythical house of Palemonids. Augustinus Rotundus translated the Second Statute into Latin.
According to scientist Rita Regina Trimonienė, the Lithuanians surnames are not Slavicism, slavified and are written as they were pronounced by parishioners in the registers of baptism of Cathedral of Saints Peter and Paul, Šiauliai, Šiauliai Church (dated in the 17th century).
In 1552, Grand Duke Sigismund II Augustus ordered that orders of the Magistrate of Vilnius be announced in Lithuanian, Polish, and Ruthenian. The same requirement was valid for the Magistrate of Kaunas.
Mikalojus Daukša, writing in the introduction to his Postil of Mikalojus Daukša, ''Postil'' (1599) (which was written in Lithuanian) in Polish, advocated the promotion of Lithuanian in the Grand Duchy, noting in the introduction that many people, especially szlachta, preferred to speak Polish rather than Lithuanian, but spoke Polish poorly. Such were the linguistic trends in the Grand Duchy that, by the political reforms of 1564–1566, sejmik, parliaments, local land courts, appellate courts and other State functions were recorded in Polish, and Polish became increasingly spoken across all social classes.
Lithuanian language situation
 Ruthenian and Polish were used as state languages of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, besides Latin and German in diplomatic correspondence. However, Lithuanian was dominant in parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania like Samogitia, where the Samogitian nobility, local nobility's reliance on Lithuanian resulted in Stanisław Radziwiłł, Stanislovas Radvila remarking in a letter to his brother Mikalojus Kristupas Radvila Našlaitėlis immediately after becoming the Elder of Samogitia that: "While learning various languages, I forgot Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, and now I see, I have to go to school again, because that language, as I see, God willing, will be needed." Vilnius, Trakai and Samogitia were the core voivodeships of the state, being part of Lithuania Proper, as evidenced by the privileged position of their governors in state authorities, such as the Council of Lords. Peasants in ethnic Lithuanian territories spoke exclusively Lithuanian, except in transitional border regions, but the Statutes of Lithuania and other laws and documentation were written in Ruthenian, Latin and Polish. Following the example of the royal court, there was a tendency to replace Lithuanian language, Lithuanian with Polish in the ethnic Lithuanian areas, whereas Ruthenian was stronger in ethnic Belarusian and Ukrainian territories. A note written by Sigismund von Herberstein's states that, in an ocean of Ruthenian in this part of Europe, there were two non-Ruthenian regions: Lithuania and Samogitia.
Ruthenian and Polish were used as state languages of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, besides Latin and German in diplomatic correspondence. However, Lithuanian was dominant in parts of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania like Samogitia, where the Samogitian nobility, local nobility's reliance on Lithuanian resulted in Stanisław Radziwiłł, Stanislovas Radvila remarking in a letter to his brother Mikalojus Kristupas Radvila Našlaitėlis immediately after becoming the Elder of Samogitia that: "While learning various languages, I forgot Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, and now I see, I have to go to school again, because that language, as I see, God willing, will be needed." Vilnius, Trakai and Samogitia were the core voivodeships of the state, being part of Lithuania Proper, as evidenced by the privileged position of their governors in state authorities, such as the Council of Lords. Peasants in ethnic Lithuanian territories spoke exclusively Lithuanian, except in transitional border regions, but the Statutes of Lithuania and other laws and documentation were written in Ruthenian, Latin and Polish. Following the example of the royal court, there was a tendency to replace Lithuanian language, Lithuanian with Polish in the ethnic Lithuanian areas, whereas Ruthenian was stronger in ethnic Belarusian and Ukrainian territories. A note written by Sigismund von Herberstein's states that, in an ocean of Ruthenian in this part of Europe, there were two non-Ruthenian regions: Lithuania and Samogitia.
 Since the founding of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the higher strata of Lithuanian society from ethnic Lithuania spoke Lithuanian, although from the later 16th century gradually began using Polish, and those from Ruthenia – Ruthenian. Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitia was unique because of its economic situation – it lay near sea ports and there were fewer people under corvee, instead of that, many commoners were taxpayers. As a result, the stratification of society was not as sharp as in other areas. Being more similar to a commoner population, the local szlachta spoke Lithuanian to a bigger extent than in the areas close to the capital Vilnius, which itself had become the starting point of intensive linguistic Polonization of the surrounding areas since the 18th century.
In Vilnius University, there are preserved texts written in the Lithuanian language of the Vilnius area, a dialect of Eastern Aukštaitian, which was spoken in a territory located south-eastwards from Vilnius. The sources are preserved in works of graduates from Stanislovas Rapolionis-based Lithuanian language schools, graduate Martynas Mažvydas and Rapalionis relative Abraomas Kulvietis.
One of the main sources of Lithuanian written in the Eastern Aukštaitian dialect (Vilnius dialect) was preserved by Konstantinas Sirvydas in a trilingual (Polish-Latin-Lithuanian) 17th-century dictionary, ''Dictionarium trium linguarum in usum studiosæ juventutis'', which was the main Lithuanian dictionary used until the late 19th century.
''Universitas lingvarum Litvaniae, Universitas lingvarum Litvaniæ'', published in Vilnius, 1737, is the oldest surviving grammar of the Lithuanian language published in the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Since the founding of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the higher strata of Lithuanian society from ethnic Lithuania spoke Lithuanian, although from the later 16th century gradually began using Polish, and those from Ruthenia – Ruthenian. Eldership of Samogitia, Samogitia was unique because of its economic situation – it lay near sea ports and there were fewer people under corvee, instead of that, many commoners were taxpayers. As a result, the stratification of society was not as sharp as in other areas. Being more similar to a commoner population, the local szlachta spoke Lithuanian to a bigger extent than in the areas close to the capital Vilnius, which itself had become the starting point of intensive linguistic Polonization of the surrounding areas since the 18th century.
In Vilnius University, there are preserved texts written in the Lithuanian language of the Vilnius area, a dialect of Eastern Aukštaitian, which was spoken in a territory located south-eastwards from Vilnius. The sources are preserved in works of graduates from Stanislovas Rapolionis-based Lithuanian language schools, graduate Martynas Mažvydas and Rapalionis relative Abraomas Kulvietis.
One of the main sources of Lithuanian written in the Eastern Aukštaitian dialect (Vilnius dialect) was preserved by Konstantinas Sirvydas in a trilingual (Polish-Latin-Lithuanian) 17th-century dictionary, ''Dictionarium trium linguarum in usum studiosæ juventutis'', which was the main Lithuanian dictionary used until the late 19th century.
''Universitas lingvarum Litvaniae, Universitas lingvarum Litvaniæ'', published in Vilnius, 1737, is the oldest surviving grammar of the Lithuanian language published in the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Demographics
In 1260, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was the land of Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania, and ethnic Lithuanians formed the majority (67.5%) of its 400,000 people. With the acquisition of new Ruthenian territories, in 1340 this portion decreased to 30%. By the time of the largest expansion towards Kievan Rus', Rus' lands, which came at the end of the 13th and during the 14th century, the territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was 800 to 930 thousand km2, just 10% to 14% of which was ethnically Lithuanian. On 6 May 1434, Grand Duke Sigismund Kęstutaitis released his privilege which tied the Orthodox and Catholic Lithuanian nobles rights in order to attract the Ruthenian nobility, Slavic nobles of the eastern regions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania who supported the former Grand Duke Švitrigaila. An estimate of the population in the territory of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania together gives a population at 7.5 million for 1493, breaking them down by ethnicity at 3.75 million Ruthenians (ethnic Ukrainians, Belarusians), 3.25 million Poles and 0.5 million Lithuanians. With theUnion of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
, 1569, Lithuanian Grand Duchy lost large part of lands to the Polish Crown.
According to an analysis of the tax registers in 1572, Lithuania proper had 850,000 residents of which 680,000 were Lithuanians.
In the mid and late 17th century, due to Russian and Swedish invasions, there was much devastation and population loss on throughout the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, including ethnic Lithuanian population in Vilnius voivodeship, Vilnius surroundings. Besides devastation, the Ruthenian population declined proportionally after the territorial losses to Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. By 1770 there were about 4.84 million inhabitants in the territory of 320 thousand km2, the biggest part of whom were inhabitants of Ruthenia and about 1.39 million or 29% – of ethnic Lithuania. During the following decades, the population decreased in a result of Partitions of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, partitions.
Legacy
 Old Prussians, Prussian tribes (of Balts, Baltic origin) were the subject of Polish expansion, which was largely unsuccessful, so Duke Konrad of Masovia invited the
Old Prussians, Prussian tribes (of Balts, Baltic origin) were the subject of Polish expansion, which was largely unsuccessful, so Duke Konrad of Masovia invited the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
to settle near the Prussian area of settlement. The fighting between Prussians and the Teutonic Knights gave the more distant Lithuanian tribes time to unite. Because of strong enemies in the south and north, the newly formed Lithuanian state concentrated most of its military and diplomatic efforts on expansion eastward.
The rest of the former Ruthenian lands were conquered by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Some other lands in Ukraine were vassalized by Lithuania later. The subjugation of Eastern Slavs by two powers created substantial differences between them that persist to this day. While there were certainly substantial regional differences in Kievan Rus', it was the Lithuanian annexation of much of southern and western Ruthenia that led to the permanent division between Ukrainians, Belarusians, and Russians. And even four Grand Dukes of Lithuania are appeared on the Millennium of Russia monument.
In the 19th century, the romantic references to the times of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania were an inspiration and a substantial part of both the Lithuanian national revival, Lithuanian and Belarusian national revival, Belarusian national revival movements and Romanticism in Poland.
Notwithstanding the above, Lithuania was a kingdom under Mindaugas, who was crowned by the authority of Pope Innocent IV in 1253. Vytenis, Gediminas and Vytautas the Great also assumed the title of King, although uncrowned by the Pope. A failed attempt was made in 1918 to revive the Kingdom under a German Prince, Wilhelm Karl, Duke of Urach, who would have reigned as Mindaugas II of Lithuania.
In the first half of the 20th century, the memory of the multiethnic history of the Grand Duchy was revived by the Krajowcy movement, which included Ludwik Abramowicz (1879–1939), Ludwik Abramowicz (Liudvikas Abramovičius), Konstancja Skirmuntt, Mykolas Römeris (Michał Pius Römer), Józef Albin Herbaczewski (Juozapas Albinas Herbačiauskas), Józef Mackiewicz and Stanisław Mackiewicz. This feeling was expressed in poetry by Czesław Miłosz.
Pseudoscience, Pseudoscientific theory of litvinism was developed since the 1990s.
According to the 10th article of the ''Law on the State Flag and Other Flags of the Republic of Lithuania'' ( lt, Lietuvos Respublikos valstybės vėliavos ir kitų vėliavų įstatymas), adopted by the Seimas, the Flag of Lithuania#State (historical) flag, historical Lithuanian state flag (with horseback knight on a red field, which initial design dates back to the reign of Grand Duke Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
) must be constantly raised over the most important governmental buildings (e.g. Seimas Palace, Government of Lithuania and its Government of Lithuania#Ministries, ministries, Lithuanian courts, municipal council buildings) and significant historical buildings (e.g. Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania, Trakai Island Castle), also in Kernavė
Kernavė was a medieval capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and today is a tourist attraction and an archeological site (population 272, 2011). It is located in the Širvintos district municipality located in southeast Lithuania. A Lithuania ...
and in the site of the Senieji Trakai Castle.
Gallery
Kernavė
Kernavė was a medieval capital of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and today is a tourist attraction and an archeological site (population 272, 2011). It is located in the Širvintos district municipality located in southeast Lithuania. A Lithuania ...
, now listed as a UNESCO World Heritage List, World Heritage Site
File:VILLINUS OLD TOWN LITHUANIA SEP 2013 (9851246475).jpg, Vilnius Old Town - the political and cultural center of the Grand Duchy, today a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
File:Kaunas castle 20160603.jpg, Kaunas Castle
File:Ліда. Лідскі замак.jpg, Lida Castle
File:Novogrudok ruin.jpg, Ruins of Navahrudak Castle. Current state (2004)
File:Kreva Castle Panorama.jpg, Ruins of Kreva Castle
File:MirCastle1.JPG, Mir Castle Complex, Mir Castle - a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Belarus.
File:Кам'янецька фортеця. Кам'янець-Подільський.jpg, Kamianets-Podilskyi Castle in Ukraine.
File:Medininkų pilis iš dangaus - www.aerialmedia.tv 02.jpg, Medininkai Castle
File:Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania 2019 2.jpg, Palace of the Grand Dukes of Lithuania in Vilnius
File:GreatCourtyard.jpg, Vilnius University and the Church of St. John
File:Kauno Šv. Jurgio kankinio bažnyčia.jpg, St. George the Martyr Church, Kaunas, St. George Church (1487) in Kaunas
File:Vytautas church.jpg, Church of Vytautas the Great in Kaunas
File:PerkūnoNamasUlAleksotoKn.JPG, House of Perkūnas in Kaunas
File:Pažaislis Monastery interior 1, Kaunas, Lithuania - Diliff.jpg, Pažaislis Monastery church, decorated with expensive marble
File:St. Peter and St. Paul's Church 1, Vilnius, Lithuania - Diliff.jpg, Church of St. Peter and St. Paul, Vilnius, St. Peter and St. Paul's Church - a masterpiece of Lithuanian Baroque architecture.
File:Royal insignias of the rulers of Lithuania in the Vilnius Cathedral, 1931.jpg, Royal insignias of the List of rulers of Lithuania, rulers of Lithuania in the Vilnius Cathedral, 1931
File:Lithuanian National Museum 14.jpg, Coins of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
File:Lithuanian National Museum 13.jpg, Coins of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
File:Coins of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.jpg, Coins of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
File:Lithuanian double-Denar of Zigmantas Vaza with his monogram and Lithuanian Vytis (Waykimas), 1621.jpg, Lithuanian double-Denar of Grand Duke Sigismund III Vasa with his monogram and Lithuanian Vytis (Waykimas), minted in Vilnius, 1621.
File:Lithuanian soldiers during the Battle of Žalgiris reconstruction 3.jpg, Recreation of the Lithuanian soldiers
File:Crimean Karaites traditional clothes.jpg, Showcase of the Crimean Karaites traditional lifestyle in Trakai, Lithuania
File:Zemaitukai.jpg, Žemaitukas, a historic horse breed from Lithuania, known from the 6–7th centuries, used as a warhorse by the Lithuanians
File:Chrzest Litwy 1387 Matejko.JPG, "Christianization of Lithuania#Christianization by Jogaila and Vytautas, Christianization of Lithuania in 1387", oil on canvas by Jan Matejko, 1889, Royal Castle in Warsaw
File:Lithuanian soldiers of XVI century.PNG, Lithuanian soldiers of the 16th century.
File:Konstanty Szyrwid.PNG, Priest, lexicographer Konstantinas Sirvydas, the cherisher of the Lithuanian language in the 17th century
File:Lithuanian national coats of arms – Columns of Gediminas, Double Cross of the Jagiellonians (Jogaila) and Samogitian bear, painted in 1875.jpg, Lithuanian national coats of arms: w:Columns of Gediminas, Columns of Gediminas, Double Cross of the w:Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonians (w:Jogaila, Jogaila) and w:Duchy of Samogitia, Samogitian bear
File:Vytis (Waykimas) of the Grand Chancellor of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with the Double Cross of the Jagiellonian dynasty.jpg, Coat of arms of the Grand Chancellors of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
File:Vytis (Waikymas) of the Grand Marshal of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with the Double Cross of the Jagiellonian dynasty.jpg, Coat of arms of the Grand Marshals of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
File:Magni Ducatus Lithuaniae Main.jpg, A detailed 1613 map of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania by Mikołaj Krzysztof "the Orphan" Radziwiłł. The map is considered to be one of the best cartographic works of the Renaissance. Kept in the Uppsala Museum.
File:First page of Giesmes tikieimuy katholickam pridiarancias, o per metu szwietes giedamas Kuriup priliduoda Pfalmay Dowida. s. (in Lithuanian language) by S. M. Slavočinskis, Vilnius, 1646.jpg, Saliamonas Mozerka Slavočinskis' book named ''Giesmes tikieimuy katholickam pridiarancias, o per metu szwietes giedamas: Kuriup priliduoda Pfalmay Dowida. s.'' in the Lithuanian language, published in Vilnius, 1646.
File:Metryka litewska.jpg, Lithuanian Metrica
File:Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations which distinguishes Poles, Lithuanians, Ruthenians, and others (20 October 1791).jpg, Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations
The Reciprocal Guarantee of Two Nations ( pl, Zaręczenie Wzajemne Obojga Narodów;Michał Rozbicki, ''European and American Constitutionalism in the Eighteenth Century'', Uniwersytet Warszawski Ośrodek Studiów Amerykańskich, 1990, p.109-110Ke ...
which distinguishes Poles, Lithuanians, Ruthenians, and others, adopted on 20 October 1791
See also
References
Sources
Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Encyclopedia in Three Volumes, Volume I
2nd edition, 2007. 688 pages, illustrated,
Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Encyclopedia in Three Volumes, Volume II
2nd edition, 2007. 792 pages, illustrated,
Grand Duchy of Lithuania: Encyclopedia in Three Volumes, Volume III
1st edition, 2010. 696 pages, illustrated, * Norman Davies. ''God's Playground''. Columbia University Press; 2nd edition (2002), . * * Robert Frost. ''The Oxford History of Poland-Lithuania: Volume I: The Making of the Polish-Lithuanian Union, 1385–1569''. Oxford University Press, 2015, * Alan V. Murray. ''Crusade and Conversion on the Baltic Frontier 1150–1500'' (Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Fourth Series). Routledge, 2001. . * Alan V. Murray. ''The Clash of Cultures on the Medieval Baltic Frontier'' Routledge, 2016. . * Zenonas Norkus. ''An Unproclaimed Empire: The Grand Duchy of Lithuania: From the Viewpoint of Comparative Historical Sociology of Empires'', Routledge, 2017, 426 p. * S. C. Rowell. ''Chartularium Lithuaniae res gestas magni ducis Gedeminne illustrans. Gedimino laiškai''. Vilnius, 2003,
e-copy
* S. C. Rowell. ''Lithuania Ascending: A Pagan Empire within East-Central Europe, 1295–1345'' (Cambridge Studies in Medieval Life and Thought: Fourth Series). Cambridge University Press, 2014. . * S. C. Rowell, D. Baronas. ''The conversion of Lithuania. From pagan barbarians to late medieval Christians''. Vilnius, 2015, . * Daniel Z. Stone. ''The Polish-Lithuanian State, 1386–1795''. University of Washington Press. 2014. pp. xii, 374. * A. Dubonis, D. Antanavičius, R. Ragauskiene, R. Šmigelskytė-Štukienė. ''The Lithuanian Metrica : History and Research''. Academic Studies Press. Brighton, United States, 2020. * Jūratė Kiaupienė. ''Between Rome and Byzantium: The Golden Age of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania's Political Culture. Second half of the fifteenth century to first half of the seventeenth century''. Academic Studies Press. Brighton, United States, 2020.
External links
History of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
Zenonas Norkus. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the Retrospective of Comparative Historical Sociology of Empires
{{Authority control Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Medieval Lithuania Medieval Belarus Medieval Ukraine Medieval Poland Medieval Russia Early Modern history of Lithuania Early Modern history of Belarus Early Modern history of Ukraine Early Modern history of Poland Early Modern history of Russia Former grand duchies, Lithuania Former empires in Europe, Lithuania, Grand Duchy Former Slavic countries, Lithuania, Grand Duchy Polish–Lithuanian union Subdivisions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 1230s establishments in Europe 1795 disestablishments in Europe 1795 disestablishments in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth States and territories established in the 13th century States and territories disestablished in the 18th century Former countries Former monarchies of Europe