|
The Crystal Palace Dinosaurs
The Crystal Palace Dinosaurs are a series of sculptures of dinosaurs and other extinct animals, incorrect by modern standards, in the London borough of Bromley's Crystal Palace Park. Commissioned in 1852 to accompany the Crystal Palace after its move from the Great Exhibition in Hyde Park, they were unveiled in 1854 as the first dinosaur sculptures in the world. The models were designed and sculpted by Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins under the scientific direction of Sir Richard Owen, representing the latest scientific knowledge at the time. The models, also known as Dinosaur Court, were classed as Grade II listed buildings from 1973, extensively restored in 2002, and upgraded to Grade I listed in 2007. The models represent 15 genera of extinct animals, only three of which are true dinosaurs. They are from a wide range of geological ages, and include true dinosaurs, ichthyosaurs, and plesiosaurs mainly from the Mesozoic era, and some mammals from the more recent Cenozoic era. Today ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantellodon In Crystal Palace Park
''Mantellisaurus'' is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur that lived in the Barremian and early Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous Period of Europe. Its remains are known from Belgium (Bernissart), England, Spain and Germany. The type and only species is ''M. atherfieldensis''. Formerly known as ''Iguanodon atherfieldensis'', the new genus ''Mantellisaurus'' was erected for the species by Gregory Paul in 2007. According to Paul, ''Mantellisaurus'' was more lightly built than ''Iguanodon'' and more closely related to ''Ouranosaurus'', making ''Iguanodon'' in its traditional sense paraphyletic. It is known from many complete and almost complete skeletons. The genus name honours Gideon Mantell, the discoverer of ''Iguanodon''. History of discovery Discovery and naming of the holotype The holotype fossil, NHMUK R5764, was originally discovered by Reginald Walter Hooley in 1914 in the upper Vectis Formation of southern England and reported upon in 1917. He posthumously named it ''Ig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalosaurus
''Megalosaurus'' (meaning "great lizard", from Greek , ', meaning 'big', 'tall' or 'great' and , ', meaning 'lizard') is an extinct genus of large carnivorous theropod dinosaurs of the Middle Jurassic period (Bathonian stage, 166 million years ago) of Southern England. Although fossils from other areas have been assigned to the genus, the only certain remains of ''Megalosaurus'' come from Oxfordshire and date to the late Middle Jurassic. ''Megalosaurus'' was, in 1824, the first genus of non-avian dinosaur to be validly named. The type species is ''Megalosaurus bucklandii'', named in 1827. In 1842, ''Megalosaurus'' was one of three genera on which Richard Owen based his Dinosauria. On Owen's directions a model was made as one of the Crystal Palace Dinosaurs, which greatly increased the public interest for prehistoric reptiles. Over fifty other species would eventually be classified under the genus; at first, this was because so few types of dinosaur had been identified, but the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Observer
''The Observer'' is a British newspaper published on Sundays. It is a sister paper to ''The Guardian'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', whose parent company Guardian Media Group Limited acquired it in 1993. First published in 1791, it is the world's oldest Sunday newspaper. History Origins The first issue, published on 4 December 1791 by W.S. Bourne, was the world's first Sunday newspaper. Believing that the paper would be a means of wealth, Bourne instead soon found himself facing debts of nearly £1,600. Though early editions purported editorial independence, Bourne attempted to cut his losses and sell the title to the government. When this failed, Bourne's brother (a wealthy businessman) made an offer to the government, which also refused to buy the paper but agreed to subsidise it in return for influence over its editorial content. As a result, the paper soon took a strong line against radicals such as Thomas Paine, Francis Burdett and Joseph Priestley. 19th century In 180 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Palace Iguanodon
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838 by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''zōḗ'' (), "life", meaning "ancient life" ). It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from , and is subdivided into six geologic periods (from oldest to youngest): # Cambrian # Ordovician # Silurian # Devonian # Carboniferous # Permian The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic was a time of dramatic geological, climatic, and evolutionary change. The Cambrian witnessed the most rapid and widespread diversification of life in Earth's history, known as the Cambrian explosion, in which most modern phyla first appeared. Arthropods, molluscs, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and synapsids all evolved during the Paleozoic. Life began in the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, (gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineering. Us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together with Saur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
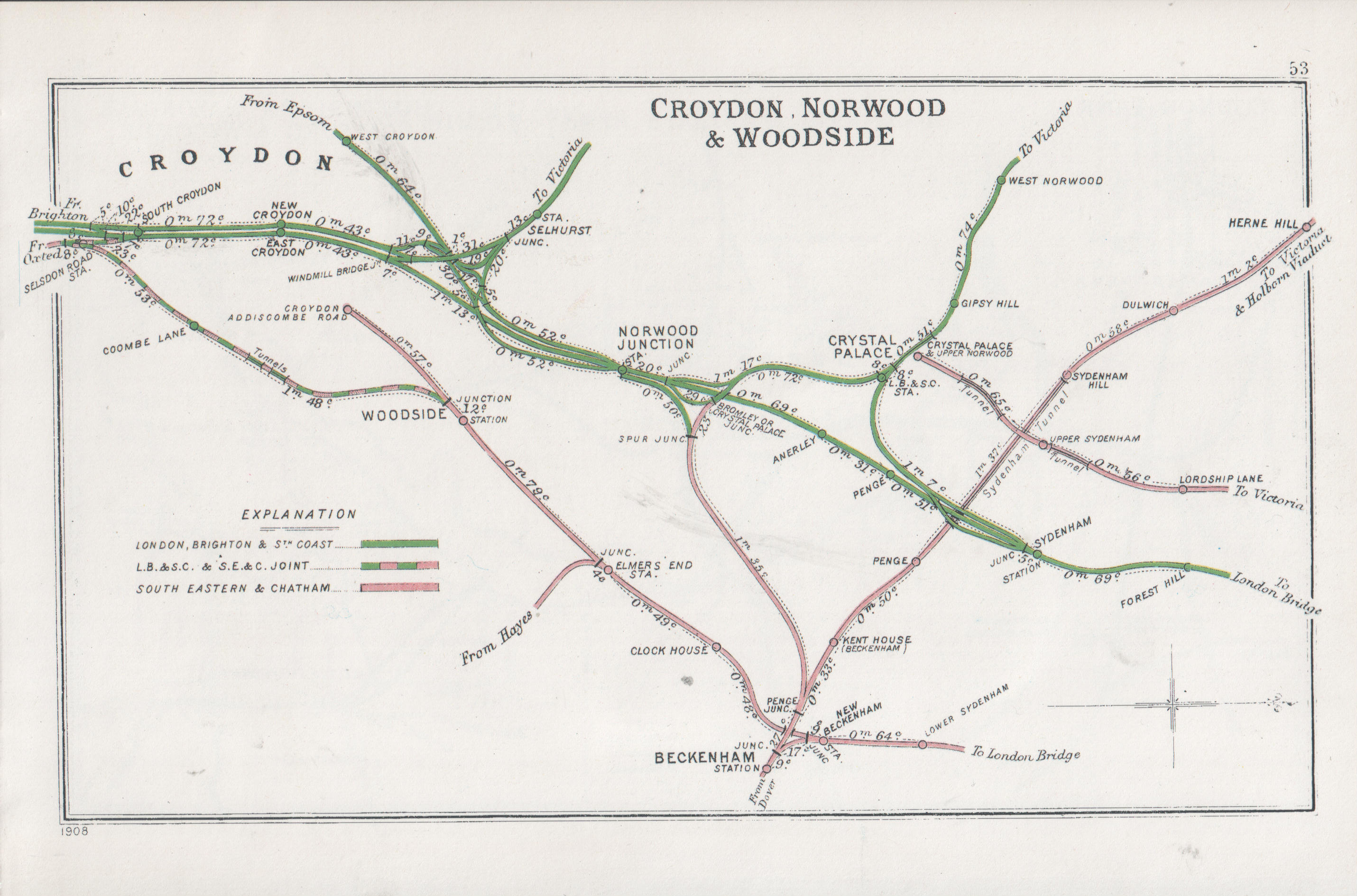
Penge West Railway Station
Penge West railway station is located in Penge, a district of the London Borough of Bromley in south London. The station is operated by London Overground, with Overground and Southern trains serving the station. Thameslink and some Southern services pass through the station. It is down the line from , in Travelcard Zone 4. station is a short walk away and has services to London Victoria, Bromley South and Orpington. station is also within walking distance and has more frequent trains to London Bridge. Penge West station forms part of the new southbound route of the London Overground East London line that opened on 23 May 2010. Penge West station provides convenient access to The Dinosaur Park via the south gate of the Crystal Palace Park. History The original Penge station was opened by the London and Croydon Railway in 1839, probably more for logistical reasons than anything else: the railway crossed the nearby High Street by a level crossing, and the station would h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydenham Hill
Sydenham Hill forms part of a longer ridge and is an affluent locality in southeast London. It is also the name of a road which runs along the northeastern part of the ridge, demarcating the London Boroughs of Southwark, Bromley, and Lewisham. Its highest part is the apex of the Boroughs of Southwark and Lewisham and the 15th-highest peak in London, at . The road connects the A205 road in the northeast at Forest Hill with the A212 road to the southwest at Crystal Palace. Sydenham Hill railway station, Sydenham Hill Wood nature reserve and ''Dulwich and Sydenham Hill Golf course'' are on its west slopes thus in the Borough of Southwark. The London boroughs of Lambeth and Croydon have part of the hill within their jurisdiction. Geography Sydenham Hill is approximately 5.6 miles to the southeast of Charing Cross. It is also at the centre of many of south London's major shopping districts being 3.6 miles south of Lewisham, 4.6 miles northwest of Bromley and 4 miles nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penge
Penge () is a suburb of South East London, England, now in the London Borough of Bromley, west of Bromley, north east of Croydon and south east of Charing Cross. History Penge was once a small hamlet, which was recorded under the name Penceat in an Anglo-Saxon deed dating from 957. Most historians believe the name of the town is derived from the Celtic word ''Penceat'', which means 'edge of wood' and refers to the fact that the surrounding area was once covered in a dense forest. The original Celtic words of which the name was composed referred to 'pen' ('head'), as in the Welsh 'pen', and 'ceat' ('wood'), similar to the Welsh 'coed', as in the name of the town of Pencoed in Wales. The largest amosite mine in the world, in South Africa, was named Penge apparently because one of the British directors thought the two areas were similar in appearance. Pensgreene and the Crooked Billet Penge was an inconspicuous area with few residents before the arrival of the railways. A trav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)