|
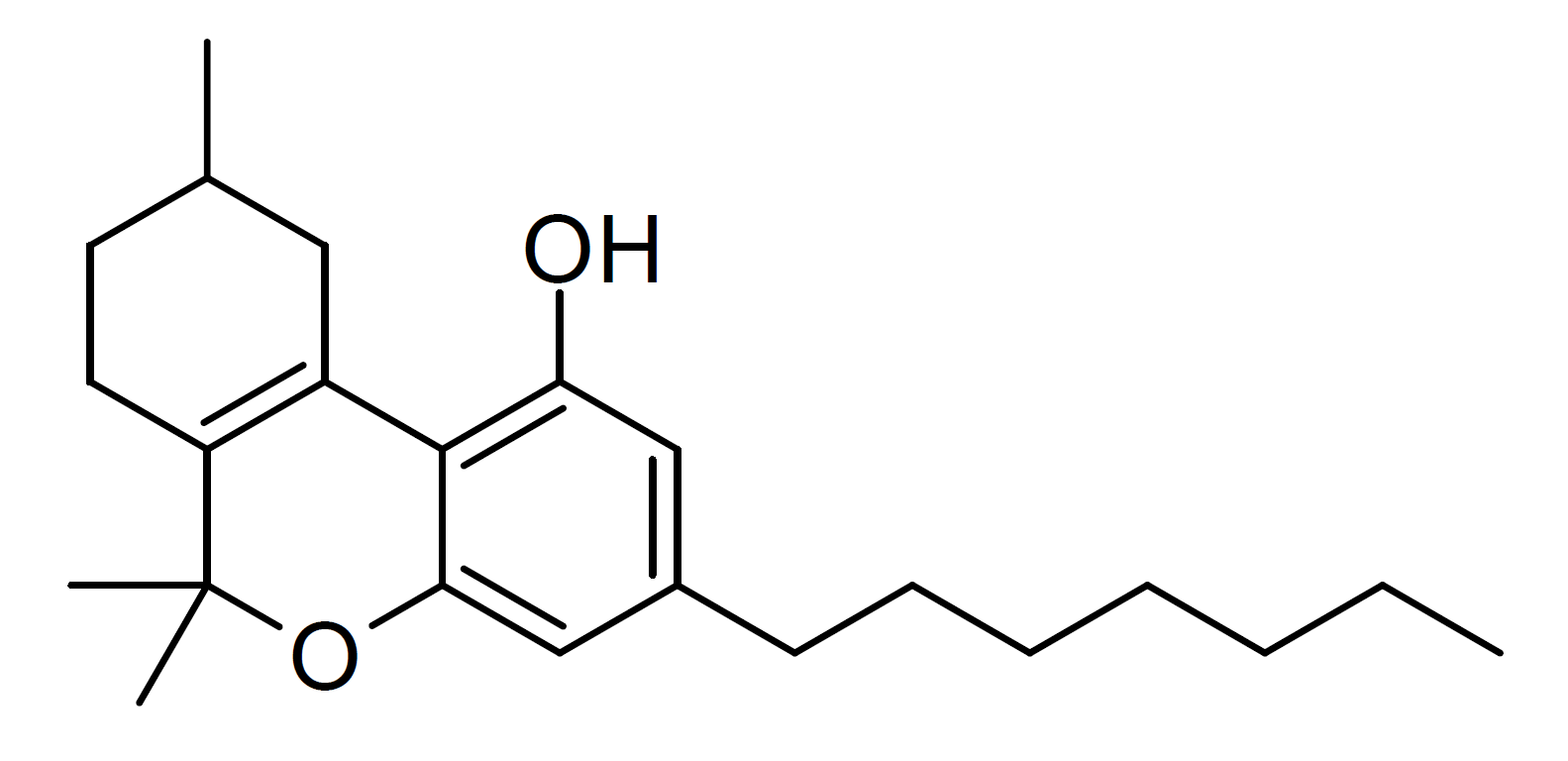
Tetrahydrocannabihexol
Tetrahydrocannabihexol (Δ9-THCH, Δ9-Parahexyl, n-Hexyl-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid, the hexyl homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which was first isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material in 2020 along with the corresponding hexyl homologue of cannabidiol, though it had been known for several decades prior to this as an isomer of the synthetic cannabinoid parahexyl. Another isomer Δ8-THCH is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code number JWH-124, though it is unclear whether this occurs naturally in ''Cannabis'', but likely is due to Delta-8-THC itself being a degraded form of Delta-9-THC. ] ] See also * Cannabidiphorol * Tetrahydrocannabiorcol * Tetrahydrocannabivarin * Tetrahydrocannabutol * Tetrahydrocannabiphorol Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from ''Cannabis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabidihexol Structure
Tetrahydrocannabihexol (Δ9-THCH, Δ9-Parahexyl, n-Hexyl-Δ9-THC) is a phytocannabinoid, the hexyl homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which was first isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material in 2020 along with the corresponding hexyl homologue of cannabidiol, though it had been known for several decades prior to this as an isomer of the synthetic cannabinoid parahexyl. Another isomer Δ8-THCH is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code number JWH-124, though it is unclear whether this occurs naturally in ''Cannabis'', but likely is due to Delta-8-THC itself being a degraded form of Delta-9-THC. ] ] See also * Cannabidiphorol * Tetrahydrocannabiorcol * Tetrahydrocannabivarin * Tetrahydrocannabutol * Tetrahydrocannabiphorol Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from ''Cannabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV, THV, O-4394, GWP42004) is a Homology (chemistry), homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) having a propyl (3-carbon) side chain instead of a pentyl (5-carbon) group on the molecule, which makes it produce very different effects from THC. Natural occurrence THCV is prevalent in certain central Asian and southern African strains of ''Cannabis''. Chemistry Similar to tetrahydrocannabinol, THC, THCV has 7 possible double bond isomers and 30 stereoisomers (see: Tetrahydrocannabinol#Isomerism). The alternative isomer Δ8-THCV is known as a synthetic compound with a code number of O-4395, but it is not known to have been isolated from ''Cannabis'' plant material. ] Description Plants with elevated levels of propyl cannabinoids (including THCV) have been found in populations of ''Cannabis sativa'' L. ssp. ''indica'' (= ''Cannabis indica'' Lam.) from China, India, Nepal, Thailand, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, as well as southern and western Africa. THCV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabutol
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabutol (tetrahydrocannabinol-C4, THC-C4, Δ9-THCB, (C4)-Δ9-THC, butyl-THC) is a phytocannabinoid found in cannabis that is a homologue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the main active component of Cannabis. Structurally, they are only different by the pentyl side chain being replaced by a butyl side chain. Pharmacology Δ9-THCB, showed an affinity for the human CB1 (''K''i = 15 nM) and CB2 receptors (''K''i = 51 nM) comparable to that of Δ9-THC. The formalin test in vivo was performed on Δ9-THCB in order to reveal possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The tetrad test in mice showed a partial agonistic activity of Δ9-THCB toward the CB1 receptor. THCB has rarely been isolated from cannabis samples, but appears to be less commonly present than THC or THCV. It is metabolized in a similar manner to THC. In an analysis by the University of Rhode Island on phytocannabinoids it was found that THC-Butyl had the highest 3C-like protease inhibitor a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) is a potent phytocannabinoid, a CB1 and CB2 agonist which was known as a synthetic homologue of THC, but for the first time in 2019 was isolated as a natural product in trace amounts from ''Cannabis sativa''. It is structurally similar to Δ9-THC, the main active component of cannabis, but with the pentyl side chain extended to heptyl. Since it has a longer side chain, its cannabinoid effects are "far higher than Δ9-THC itself." Tetrahydrocannabiphorol has a reported binding affinity approximately 33 times that of Delta-9-THC. Isomers Delta-3-THCP ] The Δ3/Δ6a(10a) isomer Δ3-THCP was synthesised in 1941, and was found to have around the same potency as Delta-3-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Δ3-THC, unlike the hexyl homologue parahexyl which was significantly stronger. Delta-8-THCP The Δ8 isomer is also known as a synthetic cannabinoid under the code name JWH-091, It's unconfirmed whether or not Delta-8-THCP is found naturally in cannabis plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytocannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (chemistry)
In chemistry, homology is the appearance of homologues. A homologue (also spelled as homolog) is a compound belonging to a series of compounds differing from each other by a repeating unit, such as a methylene bridge −−, a peptide residue, etc. A homolog is a special case of an analog. Examples are alkanes and compounds with alkyl side chains of different length (the repeating unit being a methylene group -CH2-). Periodic table On the periodic table, homologous elements share many electrochemical properties and appear in the same group (column) of the table. For example, all noble gases are colorless, monatomic gases with very low reactivity. These similarities are due to similar structure in their outer shells of valence electrons. Mendeleev used the prefix eka- for an unknown element below a known one in the same group. See also * Homologous series * Analog Analog or analogue may refer to: Computing and electronics * Analog signal, in which information is enco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-''trans''-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. THC is a lipid found in cannabis and, like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, it is assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress. THC was first discovered and isolated by Israeli chemist Raphael Mechoulam in Israel in 1964. It was found that, when smoked, THC is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, attaching itself to endocannabinoid receptors located in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and basal ganglia. These are the parts of the brain responsible for thinking, memory, pleasure, coordination a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively, ''C. ruderalis'' may be included within ''C. sativa'', all three may be treated as subspecies of ''C. sativa'', or ''C. sativa'' may be accepted as a single undivided species. The genus is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from Asia. The plant is also known as hemp, although this term is often used to refer only to varieties of ''Cannabis'' cultivated for non-drug use. Cannabis has long been used for hemp fibre, hemp seeds and their oils, hemp leaves for use as vegetables and as juice, medicinal purposes, and as a recreational drug. Industrial hemp products are made from cannabis plants selected to produce an abundance of fibre. Various cannabis strains have been bred, often selectively to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. , clinical research on CBD included studies related to anxiety, cognition, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions. Nevertheless, CBD is an herbal dietary supplement promoted with unproven claims of particular therapeutic effects. The global market size for CBD was predicted to exceed billion by 2028. Cannabidiol can be taken internally in multiple ways, including by inhaling cannabis smoke or vapor, oral, and as an aerosol spray into the cheek. It may be supplied as CBD oil containing only CBD as the active ingredient (excluding tetrahydrocannabinol HCor terpenes), CBD-dominant hemp extract oil, capsules, dried cannabis, or prescription liquid solution. CBD does not have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Cannabinoid
Synthetic cannabinoids are a class of designer drug molecules that bind to the same receptors to which cannabinoids (THC, CBD and many others) in cannabis plants attach. These novel psychoactive substances should not be confused with synthetic phytocannabinoids (THC or CBD obtained by chemical synthesis) or synthetic endocannabinoids from which they are in many aspects distinct. Typically, synthetic cannabinoids are sprayed onto plant matter and are usually smoked, although they have also been ingested as a concentrated liquid form in the US and UK since 2016. They have been marketed as herbal incense, or "herbal smoking blends", and sold under common names like K2, spice, and synthetic marijuana. They are often labeled "not for human consumption" for liability defense. A large and complex variety of synthetic cannabinoids are designed in an attempt to avoid legal restrictions on cannabis, making synthetic cannabinoids designer drugs. Most synthetic cannabinoids are agonists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parahexyl
Parahexyl (Synhexyl, n-hexyl-Δ3-THC, (C6)-Δ6a(10a)-THC) is a synthetic homologue of THC which was invented in 1941 during attempts to elucidate the structure of Δ9-THC, one of the active components of cannabis. Parahexyl is similar in both structure and activity to THC, differing only in the position of one double bond and the lengthening of the chain by one CH2 group to . Parahexyl produces effects typical of other cannabinoid receptor agonists in animals. It has a somewhat higher oral bioavailability than THC itself but is otherwise very similar. Presumably, it acts as a CB1 agonist in the same way as THC, but as there has been no research published using parahexyl since the discovery of the CB1 receptor, this has not been definitively confirmed. Parahexyl was occasionally used as an anxiolytic in the mid-20th century, the dosage ranging from 5 mg to 90 mg. Parahexyl was made illegal under UN convention in 1982 on the basis of its structural similarity and simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |