|
Taxiles
Taxiles (in Greek language, Greek Tαξίλης or Ταξίλας; lived 4th century BC) was the Greece, Greek chroniclers' name for the ruler who reigned over the tract between the Indus River, Indus and the Jhelum River, Jhelum (Hydaspes) Rivers in the Punjab region at the time of Alexander the Great's expedition. His real name was Ambhi (Greek: Omphis), and the Greeks appear to have called him Taxiles or Taxilas, after the name of his capital city of Taxila, near the modern city of Attock, Pakistan.Diodorus Siculus, ''Bibliotheca''xvii. 86/ref> Life Ambhi ascended to throne of Taxila, Takshasila. He sent an embassy to Alexander the Great, Alexander along with presents consisting of 200 Talent (measurement), Talents of silver, 3,000 fat oxen and 10,000 sheep or more ( both are estimated around 600 talents of silver), 30 elephants and a force of 700 horsemen and offered for surrender. He appears to have been on hostile terms with his neighbour, Porus the Elder, Porus, who held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Hydaspes
The Battle of the Hydaspes was fought between Alexander the Great and king Porus in 326 BC. It took place on the banks of the Jhelum River (known to the ancient Greeks as Hydaspes) in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent (modern-day Punjab, Pakistan). The battle resulted in a Greek victory and the captivity of Porus. Large areas of Punjab were absorbed into the Macedonian Empire, and later Porus became reinstated by Alexander as a Satrap. Alexander's decision to cross the monsoon-swollen river—despite close Indian surveillance—in order to catch Porus's army in the flank has been referred to as one of his "masterpieces". Although victorious, it was also the most costly battle fought by the Macedonians. The fierce resistance put up by Porus and his men won the respect of Alexander who, after the battle, asked Porus to become one of his satraps. The battle is historically significant because it resulted in the exposure of ancient Greek political and cultural influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porus The Elder
Porus or Poros ( grc, Πῶρος ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Ancient India, Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. He is only mentioned in Greek sources. Credited to have been a legendary warrior with exceptional skills, Porus unsuccessfully fought against Alexander the Great in the Battle of the Hydaspes (326 BC).Fuller, pg 198 In the aftermath, an impressed Alexander not only reinstated him as his satrap but also granted him dominion over lands to the south-east extending until the Hyphasis (Beas River, Beas).p. xl, Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, J, Woronoff & I. SpenceArrian Anabasis of Alexander, V.29.2 Porus reportedly died sometime between 321 and 315 BC. Sources The only contemporary information available on Porus and his kingdom is from Greek sources, whereas Indian sources do not mention him. These Greek sources differ consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20, and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of thirty, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern Historical India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
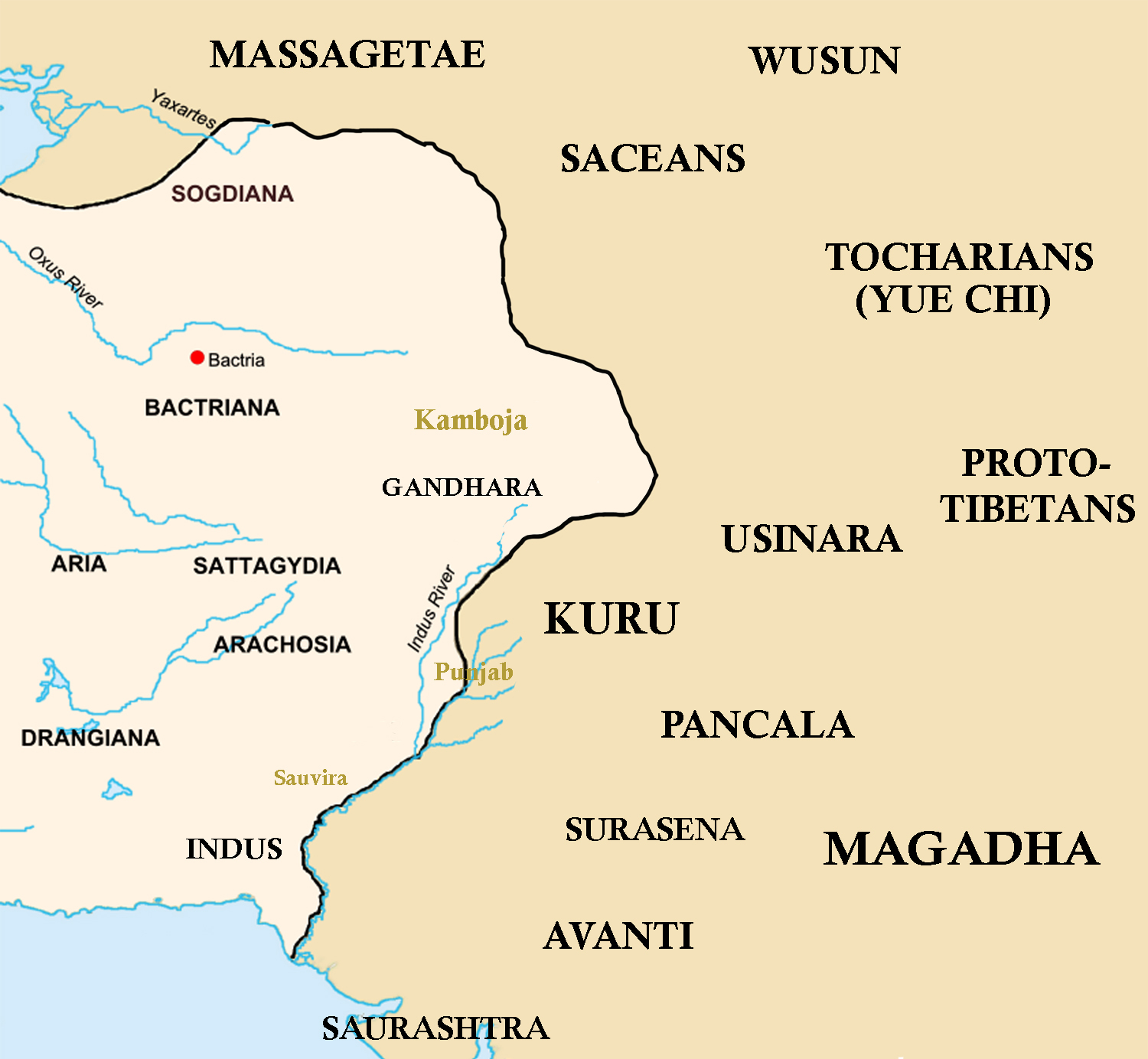
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. Punjab's capital and largest city and historical and cultural centre is Lahore. The other major cities include Faisalabad, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana, Amritsar, Sialkot, Chandigarh, Jalandhar, and Bahawalpur. Punjab grew out of the settlements along the five rivers, which served as an important route to the Near East as early as the ancient Indus Valley civilization, dating back to 3000 BCE, and had numerous migrations by the Indo-Aryan peoples. Agriculture has been the major economic feature of the Punjab and has therefore formed the foundation of Punjabi culture, with one's social status being determined by land ownership. The Punjab emerged as an important agricultura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleophis
Cleophis (Sanskrit: ''Kripa'' ) was an Assacani ruler and key figure in the war between the Assacani people and Alexander the Great. Cleophis was the mother of Assacanus, the Assacanis' war-leader at the time of Alexander's invasion in 326 BCE. After her son's death in battle, Cleophis assumed command and negotiated a settlement that allowed her to retain her status. Later accounts claim Cleophis had a son by Alexander, a notion dismissed by historians.Cf: ''The story of Cleophis' relations with the Macedonian king is heavily romanticized'' (Ref: The Greek World in the Fourth Century: From the Fall of the Athenian Empire to the Successors of..., 1997, p 211, Lawrence A. Tritle). The Assacani (called Ashvakas in Sanskrit, from the word Ashva, meaning "horse") were an independent people who lived in parts of what is now the Swat and Buner valleys in modern-day Pakistan. These highlanders were rebellious, fiercely independent clans who resisted subjugation. Alexander's war with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abisares
Abisares (or Abhisara; in Greek Ἀβισάρης), called Embisarus (Ἐμβίσαρος,) by Diodorus, was a king of Abhira descent whose territory lay in the river Hydaspes beyond the mountains. On his death in 325 Alexander appointed Abisares' son Curtis as his successor. Alexander the Great Abisares sent embassies of submission to Alexander the Great and Alexander allowed him to retain his kingdom with considerable additions. Onesicritus said that Abisares had two huge snakes and Alexander had a great desire to see them. Kingdom Hazara (country), the Abisares of the Greeks, forms the North-western district of the Peshawar division. It was conquered by Arjuna. However, Stein identifies the kingdom of Abhisara with the tract of the lower and middle hills between the Vitasta (Jhelum) and Chadrabhaga (Chenab) including the state of Rajapuri (Rajauri) in Kasmira. The kingdom of Abhisara finds reference in ancient Indian texts also. In epic times and Buddhist times, it had form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takshashila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great gained control of the city without a battle, as it was immediately surrendered to him by Omphis. Old Taxila was an important city of ancient India, situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was founded around 1000 BCE. Some ruins at Taxila date to the time of the Achaemenid Persian Empire, followed successively by the Maurya Empire, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the Indo-Scythians, and the Kushan Empire. Owing to its strategic location, Taxila has changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhara
Gandhāra is the name of an ancient region located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, more precisely in present-day north-west Pakistan and parts of south-east Afghanistan. The region centered around the Peshawar Valley and Swat river valley, though the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the Taxila region in Potohar Plateau and westwards into the Kabul Valley in Afghanistan, and northwards up to the Karakoram range. Gandhara has a deep rooted history of Hinduism mentioned in Indian scripts and epics including Rig Veda, Ramayana and Mahabharata. Famed for its unique Gandharan style of art which is influenced by the classical Hellenistic styles, Gandhara attained its height from the 1st century to the 5th century CE under the Kushan Empire, who had their capital at Peshawar (''Puruṣapura''). Gandhara "flourished at the crossroads of India, Central Asia, and the Middle East," connecting trade routes and absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great gained control of the city without a battle, as it was immediately surrendered to him by Omphis. Old Taxila was an important city of ancient India, situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was founded around 1000 BCE. Some ruins at Taxila date to the time of the Achaemenid Persian Empire, followed successively by the Maurya Empire, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the Indo-Scythians, and the Kushan Empire. Owing to its strategic location, Taxila has changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab, Pakistan
Punjab (; , ) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in central-eastern region of the country, Punjab is the second-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the largest province by population. It shares land borders with the Pakistani provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa to the north-west, Balochistan to the south-west and Sindh to the south, as well as Islamabad Capital Territory to the north-west and Autonomous Territory of AJK to the north. It shares an International border with the Indian states of Rajasthan and Punjab to the east and Indian-administered Kashmir to the north-east. Punjab is the most fertile province of the country as River Indus and its four major tributaries Ravi, Jhelum, Chenab and Sutlej flow through it. The province forms the bulk of the transnational Punjab region, now divided among Pakistan and India. The provincial capital is Lahore — a cultural, modern, historical, economic, and cosmopolitan centre of Pakistan. Other major cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhelum River
The Jhelum River (/dʒʰeːləm/) is a river in the northern Indian subcontinent. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian administered territory of Jammu and Kashmir, to the Pakistani-administered territory of Kashmir, and then into the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is the westernmost of the five rivers of the Punjab region, and flows through the Kashmir Valley. It is a tributary of the Chenab River and has a total length of about . Etymology Anjum Sultan Shahbaz, a Pakistani author, recorded some stories of the name Jhelum in his book ''Tareekh-e-Jhelum'' as:''Many writers have different opinions about the name of Jhelum. One suggestion is that in ancient days Jhelumabad was known as Jalham. The word Jhelum is reportedly derived from the words Jal (pure water) and Ham (snow). The name thus refers to the waters of a river (flowing beside the city) which have their origins in the snow-capped Himalayas.''However, some writers believe that when Mughal princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; ) was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period. ''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best source on the campaigns of Alexander the Great. Scholars have generally preferred Arrian to other extant primary sources; though this attitude is beginning to change in light of modern studies into Arrian's method. Arrian's life Arrian was born in Nicomedia (present-day İzmit), the provincial capital of Bithynia. Cassius Dio called him Flavius Arrianus Nicomediensis. In respect of his birth date, sources provide similar dates for his birth; within a few years prior to 90, 89, and 85–90 AD. The line of reasoning for dates belonging to 85–90 AD is from the fact of Arrian being made a consul around 130 AD, and the usual age for this, during this period, being forty-two years of age. (ref. pp. 312, & SYME 1958, ''same page''). Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |