|
Tang Feifan
Tang Feifan (; July 23, 1897 – September 30, 1958) was a Chinese medical microbiologist best known for culturing the ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' agent in the yolk sacs of eggs. Tang was persecuted during the "Pulling Out Bourgeois White Flag Movement" and committed suicide in 1958. Biography Early life Tang was born Tang Ruizhao () in Tangjiaping Village of Liling, Hunan, on July 23, 1897, to a relatively poor gentry family, during the Qing Empire. He was the second of three children. He had a younger brother, Tang Qiufan (). His father Tang Luquan () taught at a family friend He Zhongshan's () old-style private school, in which Tang Feifan studied poetry, history, philosophy, mathematics, and natural science. His son, He Jian, became Tang Feifan's close friend. "Learning from the West with its advanced science and technology;Invigorating the Chinese nation", Tang had often heard the hometown folks talk about reform and revolution in his childhood. When China was often cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tāng (surname)
Tāng (; ) is a Chinese surname. It is 72nd surname in the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' or ''Baijiaxing'' of the Song dynasty and 101st in modern popularity. The Tang (湯) family name comes from Tang of Shang, the first ruler of the Shang dynasty. Ancestry.ca In modern times the character can also mean "" or "". Notable people * (; 1550–1616), Chinese playwright * |
Sick Man Of Asia
The phrase "Sick man of Asia" (), or "Sick man of East Asia" () when referring specifically to China, is a term denoting a country in Asia undergoing economic or political strife. It originally referred to Qing China in the late 19th and early 20th centuries which, experiencing internal divisions and social upheaval at the time, was taken advantage of by the great powers. Early usage The term "sick man of Europe" was initially coined in 1853 by Tsar Nicholas I to refer to the Ottoman Empire, which was then in a state of decline. After World War I the phrase was applied to various European countries including France, Italy, the United Kingdom, Spain and Germany. One of the earliest instances of the term "sick man" being applied to China was in the January 5, 1863 edition of the '' Daily News'' in an article about the ongoing Taiping Rebellion. That article was reprinted in the January 7, 1863 edition of the ''Belfast Morning News'' under the title "The Supposed 'Sick Man' in Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Denmark
The Danish Realm ( da, Danmarks Rige; fo, Danmarkar Ríki; kl, Danmarkip Naalagaaffik), officially the Kingdom of Denmark (; ; ), is a sovereign state located in Northern Europe and Northern North America. It consists of Denmark, metropolitan Denmark, the kingdom's territory in continental Europe and sometimes called "Denmark proper" ( da, egentlige Danmark, links=no), and the realm's two autonomous regions: the Faroe Islands and Greenland.Administrative divisions – Denmark The World Factbook. Access date: 14 April 2012 The relationship between the three parts of the Kingdom is also known as The unity of the Realm (; fo, ríkisfelagsskapurin, links=no; kl, naalagaaffeqatigiinneq, links=no). The Kingdom of Denmark is not a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Microbiological Societies
The International Union of Microbiological Societies (IUMS), founded in 1927 as the International Society of Microbiology, is one of 40 member unions and associations of the International Science Council (ISC), and was formerly under ISC's predecessor, the International Council for Science. The union's objectives are to promote the study of microbiological sciences internationally: initiate, facilitate and coordinate research and other scientific activities which involve international cooperation; ensure the discussion and dissemination of the results of international conferences, symposia and meetings and assist in the publication of their reports; represent microbiological sciences in ISC and maintain contact with other international organizations. IUMS activities include the classification and nomenclature of bacteria, fungi and viruses, food microbiology, medical microbiology and diagnostics, culture collections, education, and biological standardization. The president-ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCG Vaccine
Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) vaccine is a vaccine primarily used against tuberculosis (TB). It is named after its inventors Albert Calmette and Camille Guérin. In countries where tuberculosis or leprosy is common, one dose is recommended in healthy babies as soon after birth as possible. In areas where tuberculosis is not common, only children at high risk are typically immunized, while suspected cases of tuberculosis are individually tested for and treated. Adults who do not have tuberculosis and have not been previously immunized, but are frequently exposed, may be immunized, as well. BCG also has some effectiveness against Buruli ulcer infection and other nontuberculous mycobacterial infections. Additionally, it is sometimes used as part of the treatment of bladder cancer. Rates of protection against tuberculosis infection vary widely and protection lasts up to 20 years. Among children, it prevents about 20% from getting infected and among those who do get infected, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet as well as Southeast Asian countries: Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys by as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
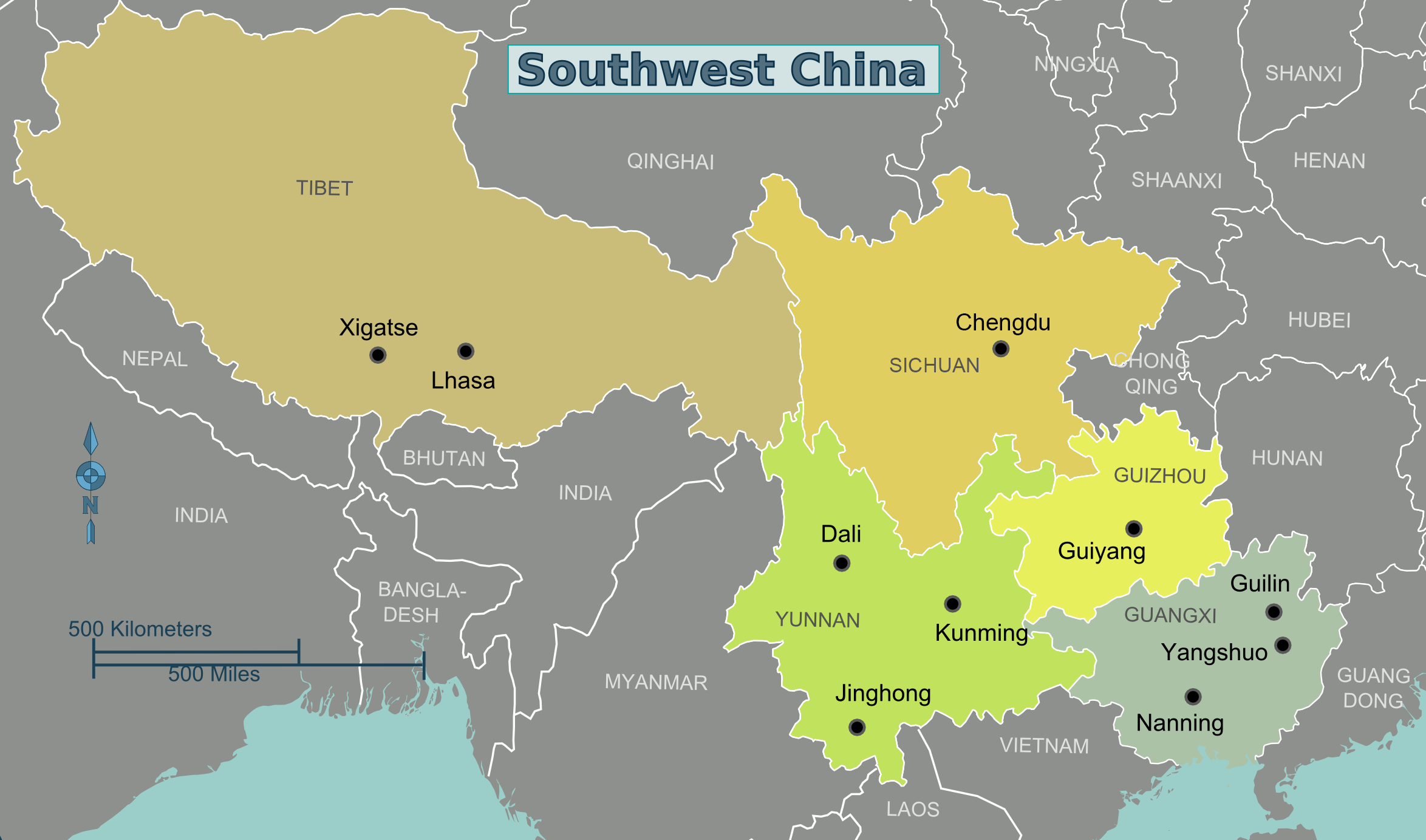
Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China. Geography Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and plains to the east. Key geographic features in the region include the Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Sichuan Basin in the northeast, and the karstic Yungui Plateau in the east. The majority of the region is drained by the Yangtze River which forms the Three Gorges in the northeast of the region. The narrowest concept of Southwest China consists of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, while wider definitions often include Guangxi and western portions of Hunan. The official government definition of Southwest China includes the core provinces of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, in addition to the Tibet Autonomous Region. History Portions of Southwest China were incorporated in the 3nd century BCE into the Qin dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunming
Kunming (; ), also known as Yunnan-Fu, is the capital and largest city of Yunnan province, China. It is the political, economic, communications and cultural centre of the province as well as the seat of the provincial government. The headquarters of many of Yunnan's large businesses are in Kunming. It was important during World War II as a Chinese military center, American air base, and transport terminus for the Burma Road. In the middle of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, Kunming is at an altitude of above sea level and a latitude just north of the Tropic of Cancer. As of 2020 census, Kunming had a total population of 8,460,088 inhabitants, of whom 5,604,310 lived in its built-up (or metro) area made of all urban districts but Jinning, not conurbated yet. It is at the northern edge of Dian Lake, surrounded by temples and lake-and-limestone hill landscapes. Kunming consists of an old, previously walled city, a modern commercial district, residential zones and university areas. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) or War of Resistance (Chinese term) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident on 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking escalated into a full-scale invasion. Some Chinese historians believe that the Japanese invasion of Manchuria on 18 September 1931 marks the start of the war. This full-scale war between the Chinese and the Empire of Japan is often regarded as the beginning of World War II in Asia. China fought Japan with aid from Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, United Kingdom and the United States. After the Japanese attacks on Malaya and Pearl Harbor in 1941, the war merged with other conflicts which are generally categorized under those conflicts of World War II a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Fei-fan And Joseph Needham In 1944
Tang or TANG most often refers to: * Tang dynasty * Tang (drink mix) Tang or TANG may also refer to: Chinese states and dynasties * Jin (Chinese state) (11th century – 376 BC), a state during the Spring and Autumn period, called Tang (唐) before 8th century BC * Tang dynasty (唐; 618–907), a major Chinese dynasty * Later Tang (唐; 923–937), a state during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period * Southern Tang (唐; 937–975), a state during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period Food * Tang (drink mix), a brand name of instant fruit flavored drinks, produced by Mondelēz International * Guk, soup or stew in Korean cuisine, sometimes known as "tang" Places Europe * Tang, County Westmeath, a village in Ireland * Tang, North Yorkshire, a settlement in England Asia * Tang, Ardabil, a village in Ardabil Province, Iran * Tang, Badakhshan, a village in Afghanistan * Tang, a village in Bumthang District, Bhutan * Tang (唐镇), a town in Pudong, Shanghai, China * T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |