|
Tzykanisterion
The ''tzykanisterion'' ( el, τζυκανιστήριον) was a stadium for playing the ''tzykanion'' (, the Greek name for Chovgan, from Middle Persian ''čaukān'', ''čōkān''), a kind of polo adopted by the Byzantines from Sassanid Persia. History According to John Kinnamos (263.17–264.11), the ''tzykanion'' was played by two teams on horseback, equipped with long sticks topped by nets, with which they tried to push an apple-sized leather ball into the opposite team's goal.. The sport was very popular among the Byzantine nobility: Emperor Basil I (r. 867–886) excelled at it; his son, Emperor Alexander (r. 912–913), died from exhaustion while playing, Emperor Alexios I Komnenos (r. 1081–1118) was injured while playing with Tatikios, and John I of Trebizond (r. 1235–1238) died from an injury during a game. The Great Palace of Constantinople featured a ''tzykanisterion'', first built by Emperor Theodosius II (r. 408–450) on the southeastern part of the palace preci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chovgan
Chovgan, Chowgan or Chogan (Persian: چوگان ''čōwgan''), is a sporting team game with horses that originated in ancient Iran (Persia). It was considered an aristocratic game and held in a separate field, on specially trained horses. The game was widespread among the Asian peoples. It is played in Iran, Republic of Azerbaijan and among Tajiks and Uzbeks. In 2013, chovqan in the Republic of Azerbaijan, was included in the UNESCO list of Intangible Cultural Heritage in need of urgent safeguarding It was later adopted in the Western World, known today as polo. History Chovgan originated in ancient Iran (Persia) and was a Persian national sport played extensively by the nobility. Women played as well as men. Chovgan originated in the middle of the first millennium A.D., as a team game. It was very popular during the centuries in the Middle East. Fragments of the game were periodically portrayed in ancient miniatures, and also detailed descriptions and rules of the game wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nea Ekklesia
The Nea Ekklēsia ( gkm, Νέα Ἐκκλησία, "New Church"; known in English as "The Nea") was a church built by Byzantine Emperor Basil I the Macedonian in Constantinople between 876 and 880. It was the first monumental church built in the Byzantine capital after the Hagia Sophia in the 6th century, and marks the beginning of the middle period of Byzantine architecture. It continued in use until the Palaiologan period. Used as a gunpowder magazine by the Ottomans, the building was destroyed in 1490 after being struck by lightning. No traces of it survive, and information about it derives from historical accounts and depictions. History Emperor Basil I was the founder of the Macedonian dynasty, the most successful in Byzantine history. Basil regarded himself as a restorer of the empire, a new Justinian, and initiated a great building program in Constantinople in emulation his great predecessor. The ''Nea'' was to be Basil's Hagia Sophia, with its very name, "New Church", im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polo Venues
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ball through the opposing team's goal. Each team has four mounted riders, and the game usually lasts one to two hours, divided into periods called ''chukkas'' or "''chukkers''". Polo has been called "the sport of kings", and has become a spectator sport for equestrians and high society, often supported by sponsorship. The progenitor of the game and its variants existed from the to the as equestrian games played by nomadic Iranian and Turkic peoples. In Persia, where the sport evolved and developed, it was at first a training game for cavalry units, usually the royal guard or other elite troops. A notable example is Saladin, who was known for being a skilled polo player which contributed to his cavalry training. It is now popular around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polo In Europe
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ball through the opposing team's goal. Each team has four mounted riders, and the game usually lasts one to two hours, divided into periods called ''chukkas'' or "''chukkers''". Polo has been called "the sport of kings", and has become a spectator sport for equestrians and high society, often supported by sponsorship. The progenitor of the game and its variants existed from the to the as equestrian games played by nomadic Iranian and Turkic peoples. In Persia, where the sport evolved and developed, it was at first a training game for cavalry units, usually the royal guard or other elite troops. A notable example is Saladin, who was known for being a skilled polo player which contributed to his cavalry training. It is now popular around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polo
Polo is a ball game played on horseback, a traditional field sport and one of the world's oldest known team sports. The game is played by two opposing teams with the objective of scoring using a long-handled wooden mallet to hit a small hard ball through the opposing team's goal. Each team has four mounted riders, and the game usually lasts one to two hours, divided into periods called ''chukkas'' or "''chukkers''". Polo has been called "the sport of kings", and has become a spectator sport for equestrians and high society, often supported by sponsorship. The progenitor of the game and its variants existed from the to the as equestrian games played by nomadic Iranian and Turkic peoples. In Persia, where the sport evolved and developed, it was at first a training game for cavalry units, usually the royal guard or other elite troops. A notable example is Saladin, who was known for being a skilled polo player which contributed to his cavalry training. It is now popular around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
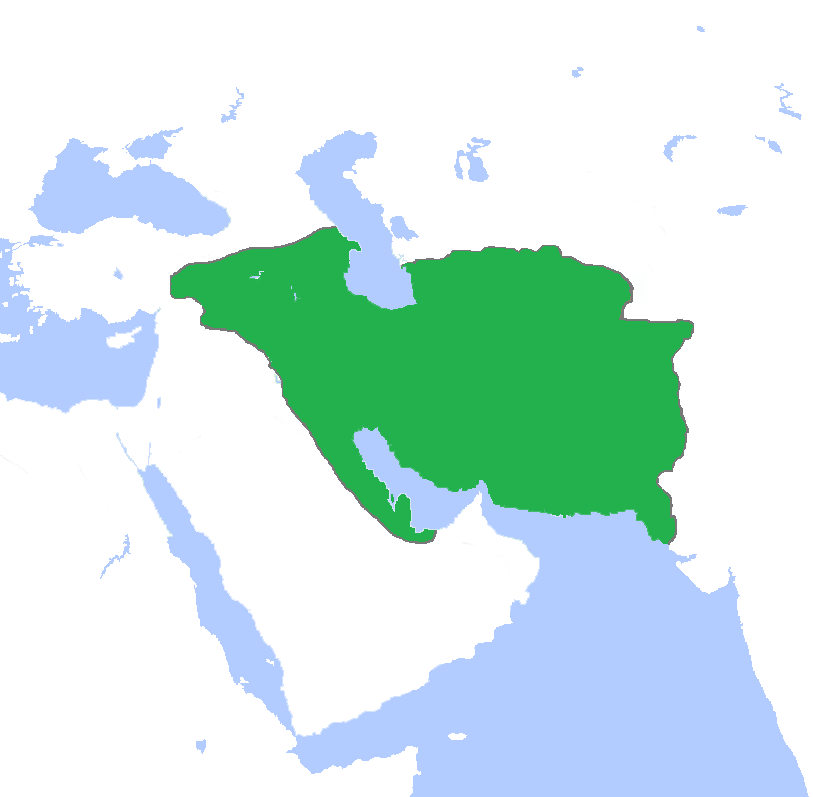
Sassanid Persia
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to power as Parthia weakened from internal strife and wars with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman–Iranian Relations
Relations between the Roman and Iranian states were established c. 92 BC. It was in 69 BC that the two states clashed for the first time; the political rivalry between the two empires would dominate much of Western Asia and Europe until 628. Initially commencing as a rivalry between the Parthians and Rome, from the 3rd to mid-7th centuries the Roman Empire (later the Byzantine Empire) and its rival Sassanid Persia were recognized as two of the leading powers in the world. Relations during the Republic The first direct contact between the Roman Republic and the Parthians was c. 92 BC, when Lucius Cornelius Sulla, while proconsul in Cilicia, met the Parthian ambassador Orobazus. Plutarch reports that he managed to take the central seat between the Parthian Ambassador and an ambassador from Pontus, and concluded a treaty that set the Euphrates as the boundary between the two powers. Orobazus was executed on his return to Parthia for allowing Sulla to outmaneuver him, and Sulla h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophanes The Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking up the religious life. Theophanes attended the Second Council of Nicaea in 787 and resisted the iconoclasm of Leo V the Armenian, for which he was imprisoned. He died shortly after his release. Theophanes the Confessor, venerated on 12 March in both the Eastern Orthodox and the Roman Catholic churches, should not be confused with Theophanes of Nicaea, whose feast is commemorated on 11 October. Biography Theophanes was born in Constantinople of wealthy and noble iconodule parents: Isaac, governor of the islands of the Aegean Sea, and Theodora, of whose family nothing is known. His father died when Theophanes was three years old, and the Byzantine Emperor Constantine V (740–775) subsequently saw to the boy's education and upbringing at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Alexiad/Book XV
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital, by Attica, Attic and Ionians, Ionian Greek colonists. During the Classical Greece, Classical Greek era, it was one of twelve cities that were members of the Ionian League. The city came under the control of the Roman Republic in 129 BC. The city was famous in its day for the nearby Temple of Artemis (completed around 550 BC), which has been designated one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Its many monumental buildings included the Library of Celsus and a theatre capable of holding 24,000 spectators. Ephesus was recipient city of one of the Pauline epistles; one of the seven churches of Asia addressed in the Book of Revelation; the Gospel of John may have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)

