|
Tyrrhena Terra
Tyrrhena Terra is a large area on Mars, centered south of the Martian equator and immediately northeast of the Hellas basin. Its coordinates are , and it covers 2300 km at its broadest extent. It was named for a classic albedo feature of the planet and is in the Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle of Mars. Tyrrhena Terra is typical of the southern Martian terrae, with heavily cratered highlands and other rugged terrain. It contains the large volcano Tyrrhena Patera, one of the oldest volcanoes on Mars. Its largest crater is Herschel. Licus Vallis and the Ausonia Montes are other major features in the region. Some channels and dunes are visible in Tyrrhena Terra, as shown in the images below. Wikiesp 035761 1520layers.jpg, Layers in a valley East of Terby Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location is Iapygia quadrangle. Wikiterracimmeriaboundaries.jpg, MOLA map showing boundaries of Tyrrhena Terra and other nearby regions Image:25897ausoniachannel.jpg, Channel in Auson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellas Basin
Hellas Planitia is a plain located within the huge, roughly circular impact basin Hellas located in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. Hellas is the third- or fourth-largest known impact crater in the Solar System. The basin floor is about deep, deeper than the Moon's South Pole-Aitken basin, and extends about east to west.The part below zero datum, see Geography of Mars#Zero elevation It is centered at Hellas Planitia spans the boundary between the Hellas quadrangle and the Noachis quadrangle. Description With a diameter of about , it is the largest unambiguous impact structure on the planet; the obscured Utopia Planitia is slightly larger (the Borealis Basin, if it proves to be an impact crater, is considerably larger). Hellas Planitia is thought to have been formed during the Late Heavy Bombardment period of the Solar System, approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago, when a protoplanet or large asteroid hit the surface. The altitude difference between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Briault Crater , an impact crater in the Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle of Mars
{{disambiguation, surname ...
Briault may refer to: * Jean-Claude Briault (born 1947), New Caledonian politician * P. Briault (died 1922), French astronomer * Briault (crater) Briault may refer to: * Jean-Claude Briault (born 1947), New Caledonian politician * P. Briault (died 1922), French astronomer * Briault (crater), an impact crater in the Mare Tyrrhenum quadrangle of Mars {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barchan
A barchan or barkhan dune (from Kazakh бархан ) is a crescent-shaped dune. The term was introduced in 1881 by Russian naturalist Alexander von Middendorf, based on their occurrence in Turkestan and other inland desert regions. Barchans face the wind, appearing convex and are produced by wind action predominantly from one direction. They are a very common landform in sandy deserts all over the world and are arc-shaped, markedly asymmetrical in cross section, with a gentle slope facing toward the wind sand ridge, comprising well-sorted sand. This type of dune possesses two "horns" that face downwind, with the steeper slope known as the slip face, facing away from the wind, downwind, at the angle of repose of the sand in question, approximately 30–35 degrees for medium-fine dry sand. The upwind side is packed by the wind, and stands at about 15 degrees. Barchans may be high and wide at the base measured perpendicular to the wind. Simple barchan dunes may appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
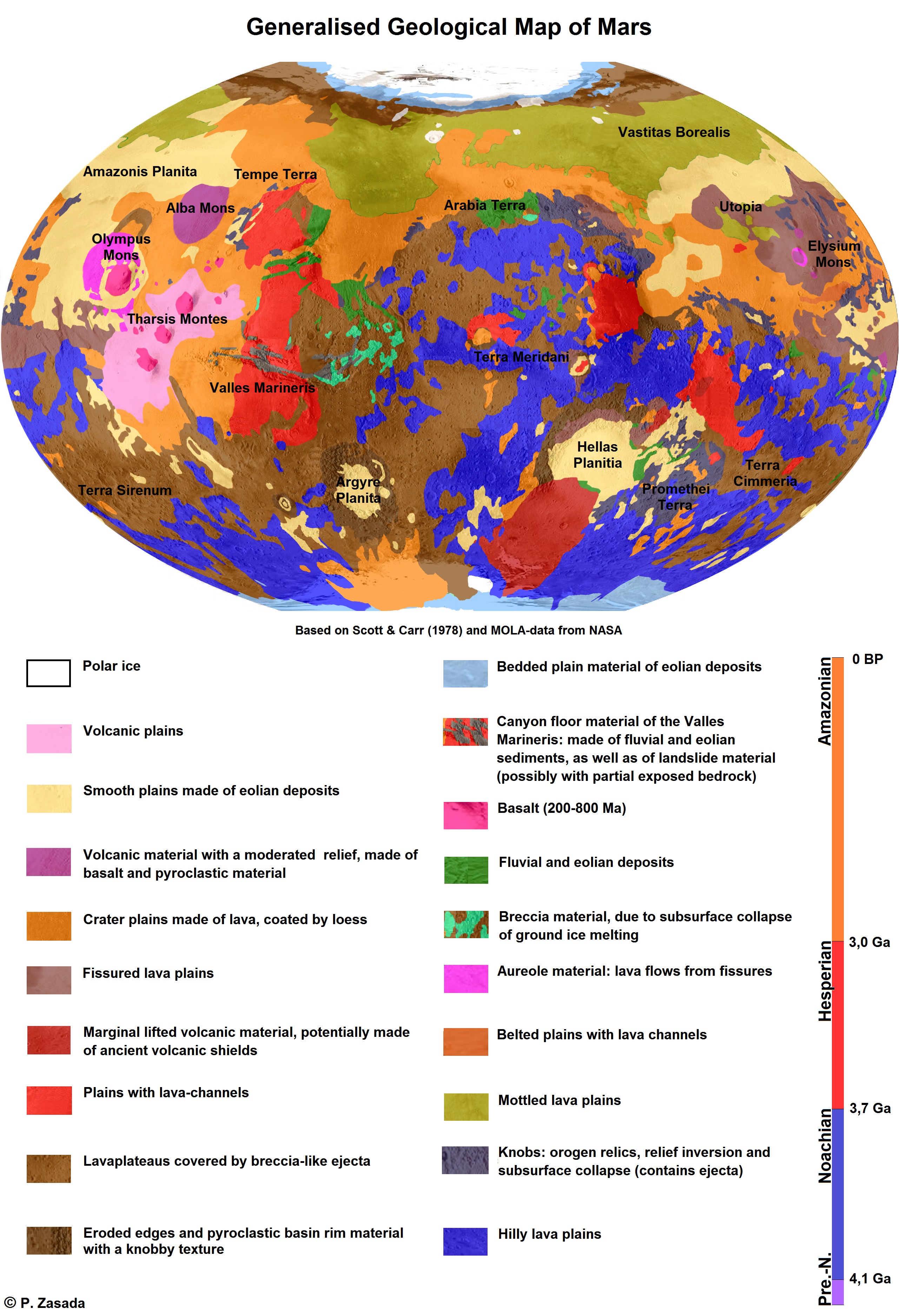
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson, Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Global Martian topography and large-scale features Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columnar Jointing
Columnar jointing is a geological structure where sets of intersecting closely spaced fractures, referred to as Joint (geology), joints, result in the formation of a regular array of polygonal Prism (geometry), prisms, or columns. Columnar jointing occurs in many types of igneous rocks and forms as the rock cools and contracts. Columnar jointing can occur in cooling lava flows and ashflow tuffs (ignimbrites), as well as in some shallow intrusions. Columnar jointing also occurs rarely in sedimentary rocks if they have been heated by nearby hot magma. The columns can vary from 3 meters to a few centimeters in diameter, and can be as much as 30 meters tall. They are typically parallel and straight, but can also be curved and vary in diameter. An array of regular, straight, and larger-diameter columns is called a colonnade; an irregular, less-straight, and smaller-diameter array is termed an entablature. The number of sides of the individual columns can vary from 3 to 8, with 6 sides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Of Mars
The climate of Mars has been a topic of scientific curiosity for centuries, in part because it is the only terrestrial planet whose surface can be directly observed in detail from the Earth with help from a telescope. Although Mars is smaller than the Earth, 11% of Earth's mass, and 50% farther from the Sun than the Earth, its climate has important similarities, such as the presence of polar ice caps, seasonal changes and observable weather patterns. It has attracted sustained study from planetologists and climatologists. While Mars' climate has similarities to Earth's, including periodic ice ages, there are also important differences, such as much lower thermal inertia. Mars' atmosphere has a scale height of approximately , 60% greater than that on Earth. The climate is of considerable relevance to the question of whether life is or ever has been present on the planet. The climate briefly received more interest in the news due to NASA measurements indicating increased sublima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowstone National Park Protection Act and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872. Yellowstone was the first national park in the U.S. and is also widely held to be the first national park in the world. The park is known for its wildlife and its many geothermal features, especially the Old Faithful geyser, one of its most popular. While it represents many types of biomes, the subalpine forest is the most abundant. It is part of the South Central Rockies forests ecoregion. While Native Americans have lived in the Yellowstone region for at least 11,000 years, aside from visits by mountain men during the early-to-mid-19th century, organized exploration did not begin until the late 1860s. Management and control of the park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, and reached Mars on March 10, 2006. In November 2006, after five months of aerobraking, it entered its final science orbit and began its primary science phase. The cost to develop and operate MRO through the end of its prime mission in 2010 was . The spacecraft continues to operate at Mars, far beyond its intended design life. Due to its critical role as a high-speed data-relay for ground missions, NASA intends to continue the mission as long as possible, at least through the late 2020s. Pre-launch After the twin failures of the ''Mars Climate Orbiter'' and the Mars Polar Lander missions in 1999, NASA reorganized and replanned its Mars Exploration Program. In October 2000, NASA announced its reformulated Mars plans, which reduced the numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiWish Program
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016. Glacial features Some landscapes look just like glaciers moving out of mountain valleys on Earth. Some have a hollowed-out appearance, looking like a glacier after almost all the ice has disappeared. What is left are the moraines—the dirt and debris carried by the glacier. The center is hollowed out because the ice is mostly gone. These supposed alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo Feature
An albedo feature is a large area on the surface of a planet (or other Solar System body) which shows a contrast in brightness or darkness (albedo) with adjacent areas. Historically, albedo features were the first (and usually only) features to be seen and named on Mars and Mercury. Early classical maps (such as those of Schiaparelli and Antoniadi) showed only albedo features, and it was not until the arrival of space probes that other surface features such as craters could be seen. On bodies other than Mars and Mercury, an albedo feature is sometimes called a regio. On bodies with a very thick atmosphere like Venus or Titan, permanent albedo features cannot be seen using ordinary optical telescopes because the surface is not visible, and only clouds and other transient atmospheric phenomena are seen. The '' Cassini–Huygens'' probe observed multiple albedo features on Titan after its arrival in Saturn's orbit in 2004. The first albedo feature ever seen on another plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ausonia Mensa
Ausonia Mensa is a mensa in the Hellas quadrangle of Mars, located at 30.3° S and 262.3° W. It is across and was named after an albedo feature name. The term "mensa" is used for a flat-topped prominence with cliff-like edges. Ausonia Mensa has many small channels. Some features look like alluvial fans. These channels add to the mass of evidence that water once flowed on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9 orbiter.Komar, P. 1979. "Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth". ''Icarus'' 37, 156–181. Image:25897ausoniachannel.jpg, Channel in Ausonia Mensa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program See also * HiRISE * HiWish program * MGS * Valley networks (Mars) Valley networks are branching networks of valleys on Mars that superficially resemble terrestrial river drainage basins.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iapygia Quadrangle
The Iapygia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Iapygia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-21 (Mars Chart-21). The Iapygia quadrangle covers the area from 270° to 315° west longitude and from 0° to 30° south latitude on Mars. Parts of the regions Tyrrhena Terra and Terra Sabaea are found in this quadrangle. The largest crater in this quadrangle is Huygens. Some interesting features in this quadrangle are dikes.Head, J. et al. 2006. The Huygens-Hellas giant dike system on Mars: Implications for Late Noachian-Early Hesperian volcanic resurfacing and climatic evolution. Geology. 34:4: 285-288. the many layers found in Terby crater, and the presence of carbonates on the rim of Huygens crater. Dikes Near Huygens, especially just to the east of it, are a number of narrow ridges which appear to be the remnants of dikes, like the ones around Shiprock, New Mexico. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |