|
Ausonia Mensa
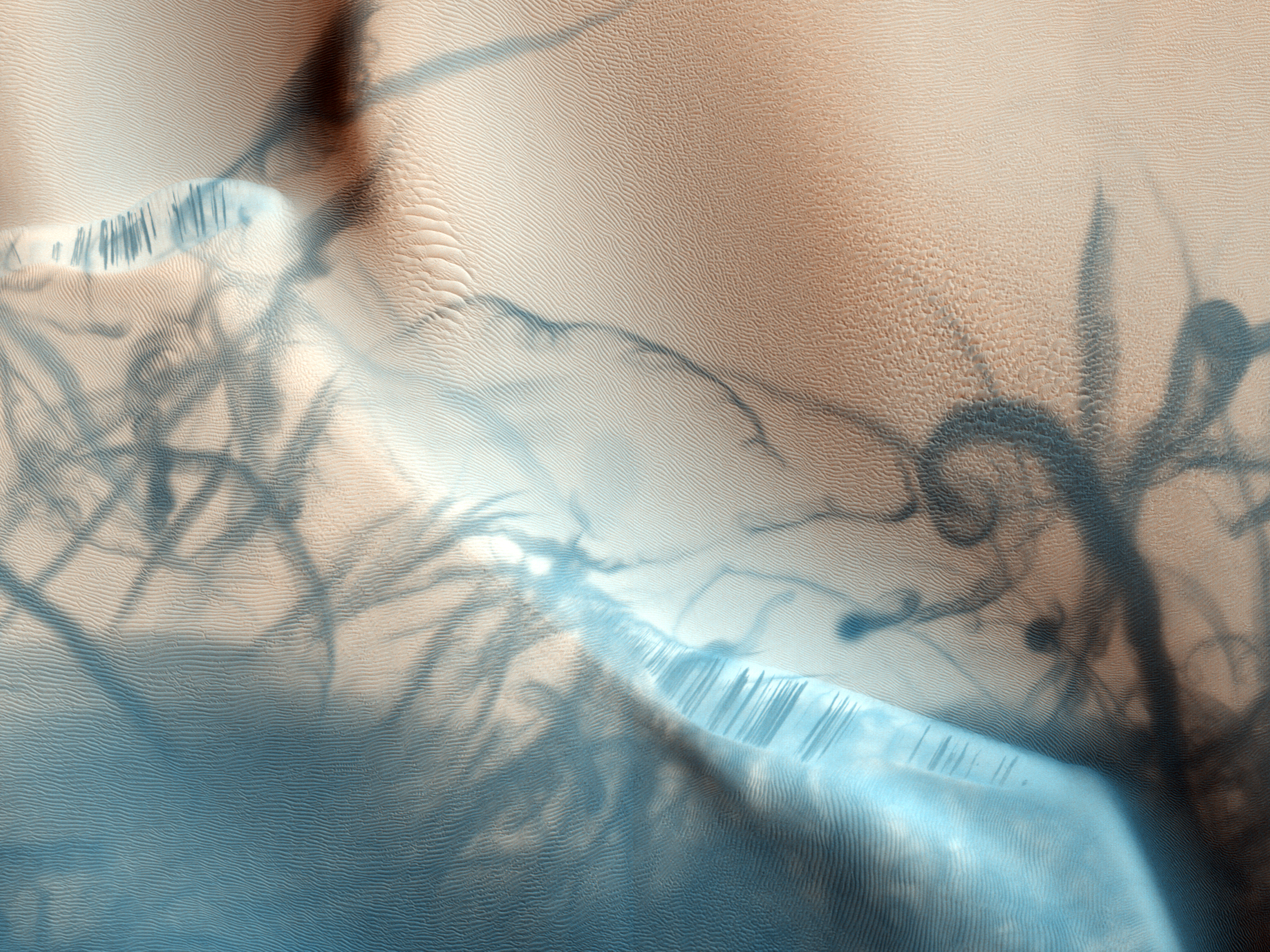
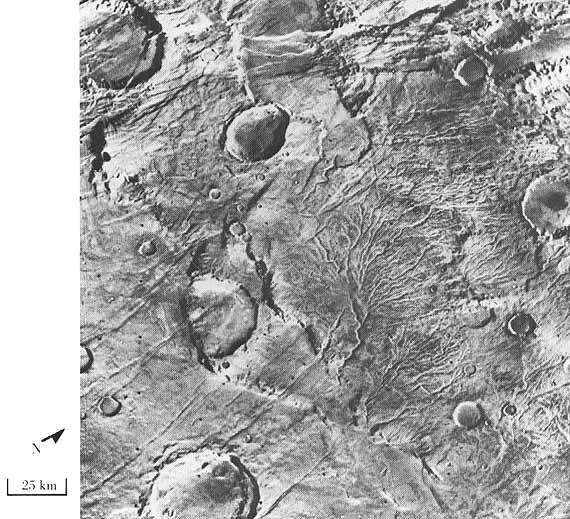
Ausonia Mensa is a mensa in the Hellas quadrangle of Mars, located at 30.3° S and 262.3° W. It is across and was named after an albedo feature name. The term "mensa" is used for a flat-topped prominence with cliff-like edges. Ausonia Mensa has many small channels. Some features look like alluvial fans. These channels add to the mass of evidence that water once flowed on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9 orbiter.Komar, P. 1979. "Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth". ''Icarus'' 37, 156–181. Image:25897ausoniachannel.jpg, Channel in Ausonia Mensa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program See also * HiRISE * HiWish program * MGS * Valley networks (Mars) Valley networks are branching networks of valleys on Mars that superficially resemble terrestrial river drainage basins.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ausonia Mensa
Ausonia Mensa is a mensa in the Hellas quadrangle of Mars, located at 30.3° S and 262.3° W. It is across and was named after an albedo feature name. The term "mensa" is used for a flat-topped prominence with cliff-like edges. Ausonia Mensa has many small channels. Some features look like alluvial fans. These channels add to the mass of evidence that water once flowed on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9 orbiter.Komar, P. 1979. "Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth". ''Icarus'' 37, 156–181. Image:25897ausoniachannel.jpg, Channel in Ausonia Mensa, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program See also * HiRISE * HiWish program * MGS * Valley networks (Mars) Valley networks are branching networks of valleys on Mars that superficially resemble terrestrial river drainage basins.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through the atmosphere to the surface. As part of the larger Mars Exploration Program, Mars Global Surveyor performed atmospheric monitoring for sister orbiters during aerobraking, and helped Mars rovers and lander missions by identifying potential landing sites and relaying surface telemetry. It completed its primary mission in January 2001 and was in its third extended mission phase when, on 2 November 2006, the spacecraft failed to respond to messages and commands. A faint signal was detected three days later which indicated that it had gone into safe mode. Attempts to recontact the spacecraft and resolve the problem failed, and NASA officially ended the mission in January 2007. MGS remains in a stable near-polar circular orbit at about 450 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensa (geology)
In planetary geology, a mensa (pl. mensae ) is a flat-topped prominence with cliff-like edges. The term is derived from the Latin word for table, and has the same root as the Spanish word for table, mesa. Mensa is used in the same manner as mesa is used in the Southwest United States. File:Ganges Mensa.jpg, Ganges Mensa, as seen by HiRISE. Ganges Mensa is found in the Coprates quadrangle of Mars. File:Capri Mensa.JPG, Capri Mensa, as seen by HIRISE. Click on image to see buttes and layers. Capri Mensa is found in the Coprates quadrangle of Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at .... Image:Glacier as seen by ctx.JPG, Mesa in Ismenius Lacus quadrangle, as seen by CTX. Mesa has several glaciers eroding it. References Planetary geology Extraterrestrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
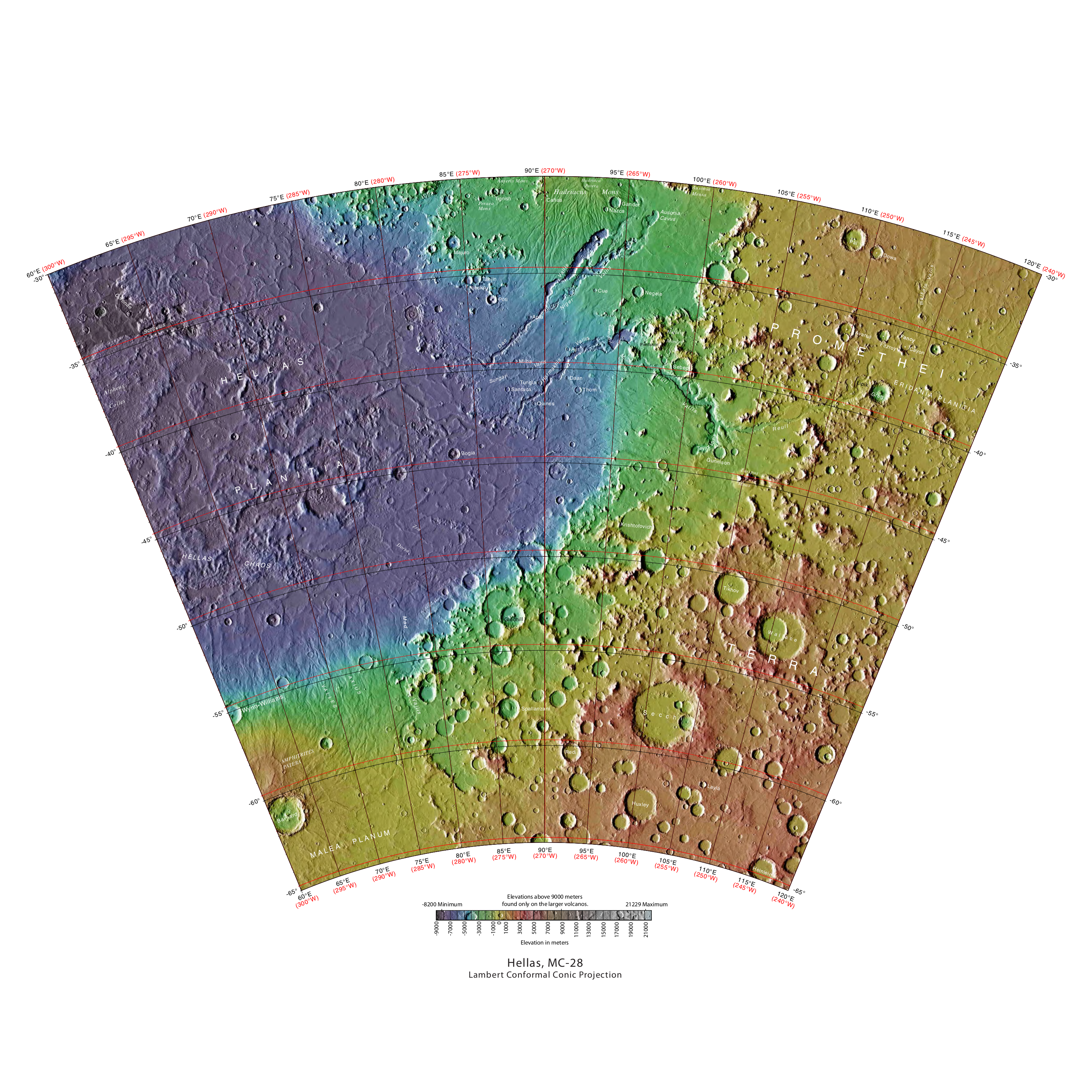
Hellas Quadrangle
The Hellas quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Hellas quadrangle is also referred to as MC-28 (Mars Chart-28). The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 240° to 300° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on the planet Mars. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past. Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs of ice in the ground, especially places with glacier-like flow features. Hellas Basin The Hellas quadrangle contains part of the Hellas Basin, the largest known impact crater on the surface of Mars and the second largest in the solar sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of sunlight, solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation. Surface albedo is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While bi-hemispherical reflectance is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds (as ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial Fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to semiarid climates, but are also found in more humid environments subject to intense rainfall and in areas of modern glaciation. They range in area from less than to almost . Alluvial fans typically form where flow emerges from a confined channel and is free to spread out and infiltrate the surface. This reduces the carrying capacity of the flow and results in deposition of sediments. The flow can take the form of infrequent debris flows or one or more ephemeral or perennial streams. Alluvial fans are common in the geologic record, such as in the Triassic basins of eastern North America and the New Red Sandstone of south Devon. Such fan deposits likely contain the largest accumulations of gravel in the geologic record. Alluvial fans have also been found on Mars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971 from LC-36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, and reached the planet on November 14 of the same year, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit another planet – only narrowly beating the Soviet probes ''Mars 2'' (launched May 19) and ''Mars 3'' (launched May 28), which both arrived at Mars only weeks later. After the occurrence of dust storms on the planet for several months following its arrival, the orbiter managed to send back clear pictures of the surface. Mariner 9 successfully returned 7,329 images over the course of its mission, which concluded in October 1972. Objectives Mariner 9 was designed to continue the atmospheric studies begun by Mariner 6 and 7, and to map over 70% of the Martian surface from the lowest altitude () and at the highest reso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction of the University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. It consists of a 0.5m (19.7 in) aperture reflecting telescope, the largest so far of any deep space mission, which allows it to take pictures of Mars with resolutions of 0.3m/pixel (1ft/pixel), resolving objects below a meter across. HiRISE has imaged Mars exploration rovers on the surface, including the ''Opportunity'' rover and the ongoing ''Curiosity'' mission. History In the late 1980s, of Ball Aerospace & Technologies began planning the kind of high-resolution imaging needed to support sample return and surface exploration of Mars. In early 2001 he teamed up with Alfred McEwen of the University of Arizona to propose such a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiWish Program
HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRISE. The first images were released in April 2010. Over 12,000 suggestions were made by the public; suggestions were made for targets in each of the 30 quadrangles of Mars. Selected images released were used for three talks at the 16th Annual International Mars Society Convention. Below are some of the over 4,224 images that have been released from the HiWish program as of March 2016. Glacial features Some landscapes look just like glaciers moving out of mountain valleys on Earth. Some have a hollowed-out appearance, looking like a glacier after almost all the ice has disappeared. What is left are the moraines—the dirt and debris carried by the glacier. The center is hollowed out because the ice is mostly gone. These supposed alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Networks (Mars)
Valley networks are branching networks of valleys on Mars that superficially resemble terrestrial river drainage basins.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of Mars. Cambridge Planetary Science Series, Cambridge University Press. They are found mainly incised into the terrain of the martian southern highlands, and are typically - though not always - of Noachian age (approximately four billion years old). The individual valleys are typically less than 5 kilometers wide, though they may extend for up to hundreds or even thousands of kilometers across the martian surface. The form, distribution, and implied evolution of the valley networks are of great importance for what they may tell us about the history of liquid water on the martian surface, and hence Mars' climate history. Some authors have argued that the properties of the networks demand that a hydrological cycle must have been active on ancient Mars,Craddock, R.A., and Howard, A.D. (2002), The case for rainfall on a warm, wet earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |