|
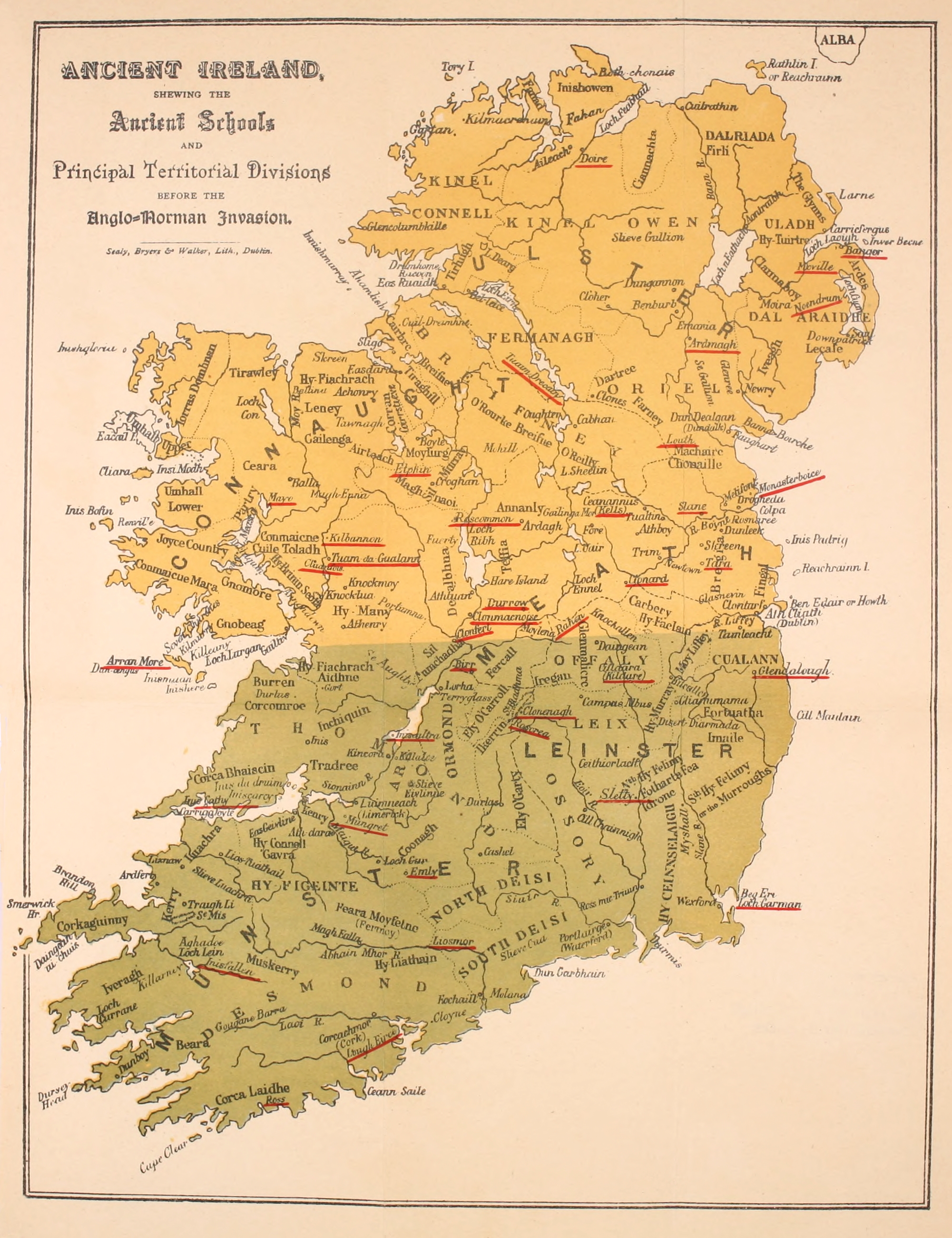
Tuilleadh Feasa Ar Éirinn óigh
Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh ("More knowledge on the entirety of Ireland") is a medieval Gaelic-Irish topographical text, composed by Giolla na Naomh Ó hUidhrín (died 1420). Overview ''Tuilleadh feasa ...'' is both a supplement and a continuation of Seán Mór Ó Dubhagáin's '' Triallam timcheall na Fodla''. Of the two, James Carney wrote: * "These two poems together constitute a compendium of the topography of pre-Norman Ireland, as seen, however, by poets who lived two centuries after the invasion. ''Triallam timcheall na Fodla'' ... is an account of the territories of the northern half of Ireland and Leinster, indicating the ruling family or families of each district. ''Tuilleadh feasa ar Éirinn óigh'' ... treats in similar fashion of the southern half of Ireland, including Leinster, of which we have therefore two independent accounts. The introductory stanzas of Ó hUidhrín's poem, in which he defines the scope of his work and its relation to that of his predecessor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern history, modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanza
In poetry, a stanza (; from Italian language, Italian ''stanza'' , "room") is a group of lines within a poem, usually set off from others by a blank line or Indentation (typesetting), indentation. Stanzas can have regular rhyme scheme, rhyme and Metre (poetry), metrical schemes, but they are not required to have either. There are many different : Stanzaic form, forms of stanzas. Some stanzaic forms are simple, such as four-line quatrains. Other forms are more complex, such as the Spenserian stanza. Fixed verse, Fixed verse poems, such as sestinas, can be defined by the number and form of their stanzas. The stanza has also been known by terms such as ''batch'', ''fit'', and ''stave''. The term ''stanza'' has a similar meaning to ''strophe'', though ''strophe'' sometimes refers to an irregular set of lines, as opposed to regular, rhymed stanzas. Even though the term "stanza" is taken from Italian, in the Italian language the word "strofa" is more commonly used. In music, groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish-language Literature
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as Cork, Donegal, Galway, and Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties Mayo, Meath, and Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second-language speakers. Daily users in Ireland outside the education system number around 73,000 (1.5%), and the total number of persons (aged 3 and over) who claimed they could speak Irish in April 2016 was 1,761,420, representing 39.8% of respondents. For most of recorded Irish hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Manuscripts
This is a list of manuscripts produced in Ireland as well as other manuscripts of Irish interest, including both vellum and paper manuscripts. See also *Cín Dromma Snechtai *Irish Manuscripts Commission Notes Sources *General: ** *Brussels: ** *Dublin ** ** *Cambridge ** ** External links ISOS Irish Script on Screen CELT Corpus of Electronic Texts MsOmit Manuscript Sources to Old and Middle Irish Tales, 2017 Insular Medieval Manuscripts Reproduction Guide CODECS Collaborative Online Database and e-Resources for Celtic Studies by WB Yeats in the Irish Senate in April 1923, concerning the local translation of Irish manuscripts. {{DEFAULTSORT:Irish manuscripts Manuscripts A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in ... Literature lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O Doyne Manuscript
The O Doyne manuscript is a collection of material relating to a dispute among the Gaelic-Irish family of Dunne. Kenneth Nicholls has described its contents as "contemporary copies of documents concerning the lengthy lawsuit between Charles O Doyne (Cathaoir Ó Duinn), a Master in the Irish Court of Chancery who died in 1617, and his elder brother, Thady or Teig (Thadhg) Ó Duinn ... It is precious as a complete record of the landownership pattern in a Gaelic-Irish territory which had remained practically free from outside interference." Charles and Thady were sons of Tadhg Óg Ó Duinn, a landowner and lord of Úi Riagán in Laois from 1558 to 1607. The dispute concerned the succession to Tadhg Óg's lands and chiefries. In the dispute, Nicholls remarks that it was "Charles, the English-educated lawyer and official, who sought to maintain the validity of the customs of tainstry and 'Irish gravelkind' which his brother the chief denounced as 'barbarous.' Charles died without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leabhar Adhamh Ó Cianáin
''Leabhar Adhamh Ó Cianáin'' or ''The Book of Adhamh Ó Cianáin'', now G 2-3 NLI (National Library of Ireland), is a book written in or about the 1340s by Adhamh Ó Cianáin by and for himself, and out of the book of his teacher, Seán Mór Ó Dubhagáin. Kenneth Nicholls has suggested that Adhamh wrote the book's genealogies between 1328 and 1350, which occur in the first half of the manuscript, which also contains the metrical Banshenchas. It is also important as the earliest surviving post-Norman Gaelic genealogy, which Ó Cianáin - as he implies himself - probably derived from Ó Dubhagáin's book. Unusually for a late medieval Irish manuscript, it is illustrated, including human portraits. It is believed to have been part of a movement to revivify Irish culture by antiquarism. Sources * ''The Learned Family of Ó Cianáin/Keenan'', by Nollaig Ó Muraíle Nollaig Ó Muraíle is an Irish scholar. He published an acclaimed edition of Dubhaltach Mac Fhirbhisigh's ''Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crichaireacht Cinedach Nduchasa Muintiri Murchada
Muintir Murchada was the name of an Irish territory which derived its name from the ruling dynasty, who were in turn a branch of the Uí Briúin. The name was derived from Murchadh mac Maenach, King of Uí Briúin Seóla, who died 891. Overview The ruling dynasty was first recorded as a lineage in 1061 and by 1238 the term denoted the territory. It came under the control of the Uí Briúin about the 11th century, its original rulers taking the surname Ó Flaithbheartaigh ( O'Flaherty). They were expelled by the Ua Conchobhair Kings of Connacht to Iar Connacht where they are still to be found. Muintir Murchada appears to have comprised the following parishes: Killursa, Kilkilvery, Killeany, Kilcoona, Cargin, Killower, Cummer. It also is thought to have included parts of Belclare, Donaghpatrick, Corofin, Tuam, Kilbennan and Killererin. Crichaireacht cinedach nduchasa Muintiri Murchada is a tract dating to the reign of its lord, Flaithbertaigh Ua Flaithbertaigh (died 1098), who r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Críchad An Chaoilli
Críchad an Chaoilli ("boundary of the Caoille") is a medieval Irish text. Overview Written in Middle Irish sometime between 1100 and 1300, Críchad an Chaoilli is a topographical text that takes its title from its opening verse: : ''Crichad an caoilli gu cruaidh'' : ''in fuil uaibh nech noimluaidh ?'' : ''tucad do mac Sonaisc sin'' : ''ar an forbhais d'fhoirdhin'' which translates as :''The exact boundary of the Caoille,'' :''is there anyone of you who would describe it?'' :''It was given to the son of Sonasc'' :''for assisting at the siege.'' The rest of the text is written in prose, and describes the land and proprietors of Fermoy, County Cork, an area originally known as the kingdom of Caoille or Fir Maige Féne. It survives in two manuscripts – Book of Lismore, on folio 140a, 2; and in Egerton 92, fo. 13b, preserved in the British Library, London. Authorship Its unknown author is thought to have been a monastic scribe. See also * Crichaireacht cinedach nduchasa M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Shannon
The River Shannon ( ga, Abhainn na Sionainne, ', '), at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , – approximately one fifth of the area of the island of Ireland. The Shannon divides the west of Ireland (principally the province of Connacht) from the east and south (Leinster and most of Munster). (County Clare, being west of the Shannon but part of the province of Munster, is the major exception.) The river represents a major physical barrier between east and west, with fewer than thirty-five crossing points between Limerick city in the south and the village of Dowra in the north. The river takes its name after ''Sionna'', a Celtic goddess. Known as an important waterway since antiquity, the Shannon first appeared in maps by the Graeco-Egyptian geographer Ptolemy ( 100 – 170 AD). The river flows generally southwards from the Shannon Pot in County Cavan before turning west and emptying into the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rí ruirech). Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the ancient kingdoms were shired into Counties of Ireland#2.1 Pre-Norman sub-divisions, counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has seen further sub-division of the historic counties. Munster has no official function for Local government in the Republic of Ireland, local government purposes. For the purposes of the International Organization for Standardization, ISO, the province is listed as one of the provincial sub-divisions of the State (ISO 3166-2:IE) and coded as "IE-M". Geographically, Munster covers a total area of and has a population of 1,364,098, with the most populated city being Cork (city), Cork. Other significant urban centres in the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leath Moga
Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) are legendary ancient divisions of Ireland. Leath Cuinn was the island north of the Esker Riada (east-west drumlin belt from Dublin to Galway Bay). Conn Cétchathach, for whom this division is named, was a retrospective ancestor of the Connachta and Uí Néill dynasties. Ireland's legendary ancient division into Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) resulted from the battle of Maigh Nuadad in 123 A.D. Conn, defeated by Eoghan Mor (also known as Mug Nuadat), was forced to accede to the division of Ireland into two halves: * The North - taking in Connacht, Ulster and Meath - would be Conn's Half * The South - taking in Munster, Osraighe and Leinster - would be Eoghan's Half. To solidify the arrangement, Conn's daughter, Sadhbh was married to Ailill Aulom, son of Eoghan. The Eoganacht dynasty in Munster claimed, as descendants of Oiloill Olum, the historical right as overkings of Leath Moga (i.e. overlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leath Cuinn
Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) are legendary ancient divisions of Ireland. Leath Cuinn was the island north of the Esker Riada (east-west drumlin belt from Dublin to Galway Bay). Conn Cétchathach, for whom this division is named, was a retrospective ancestor of the Connachta and Uí Néill dynasties. Ireland's legendary ancient division into Leath Cuinn (Conn's Half) and Leath Moga (Mugh's half) resulted from the battle of Maigh Nuadad in 123 A.D. Conn, defeated by Eoghan Mor (also known as Mug Nuadat), was forced to accede to the division of Ireland into two halves: * The North - taking in Connacht, Ulster and Meath - would be Conn's Half * The South - taking in Munster, Osraighe and Leinster - would be Eoghan's Half. To solidify the arrangement, Conn's daughter, Sadhbh was married to Ailill Aulom, son of Eoghan. The Eoganacht dynasty in Munster claimed, as descendants of Oiloill Olum, the historical right as overkings of Leath Moga (i.e. overlords ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)