|
Tsagantegia
''Tsagantegia'' (; meaning Tsagan Teg) is a genus of medium-sized ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species, ''T. longicranialis''. The specimen consists of a very partial individual, comprising the skull and lacking postcranial remains. Since it only preserves the skull, ''Tsagantegia'' is mainly characterized by its elongated snout and the flattened facial osteoderms, greatly differing from other ankylosaurs. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen, MPC 700/17, is a virtually complete skull that was recovered from the locality Tsagan-Teg (or "White Mountain") of the Bayan Shireh Formation in the southeastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia. It was formally described in 1993 by the Russian paleontologist Tatyana Alekseyevna Tumanova. The generic name, ''Tsagantegia'', is in reference to Tsagan Teg, the locality of its discovery, and the specific name, ''longicranialis'', is derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsagantegia Skeleton Reconstruction
''Tsagantegia'' (; meaning Tsagan Teg) is a genus of medium-sized ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species, ''T. longicranialis''. The specimen consists of a very partial individual, comprising the skull and lacking postcranial remains. Since it only preserves the skull, ''Tsagantegia'' is mainly characterized by its elongated snout and the flattened facial osteoderms, greatly differing from other ankylosaurs. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen, MPC 700/17, is a virtually complete skull that was recovered from the locality Tsagan-Teg (or "White Mountain") of the Bayan Shireh Formation in the southeastern Gobi Desert, Mongolia. It was formally described in 1993 by the Russian paleontologist Tatyana Alekseyevna Tumanova. The generic name, ''Tsagantegia'', is in reference to Tsagan Teg, the locality of its discovery, and the specific name, ''longicranialis'', is derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
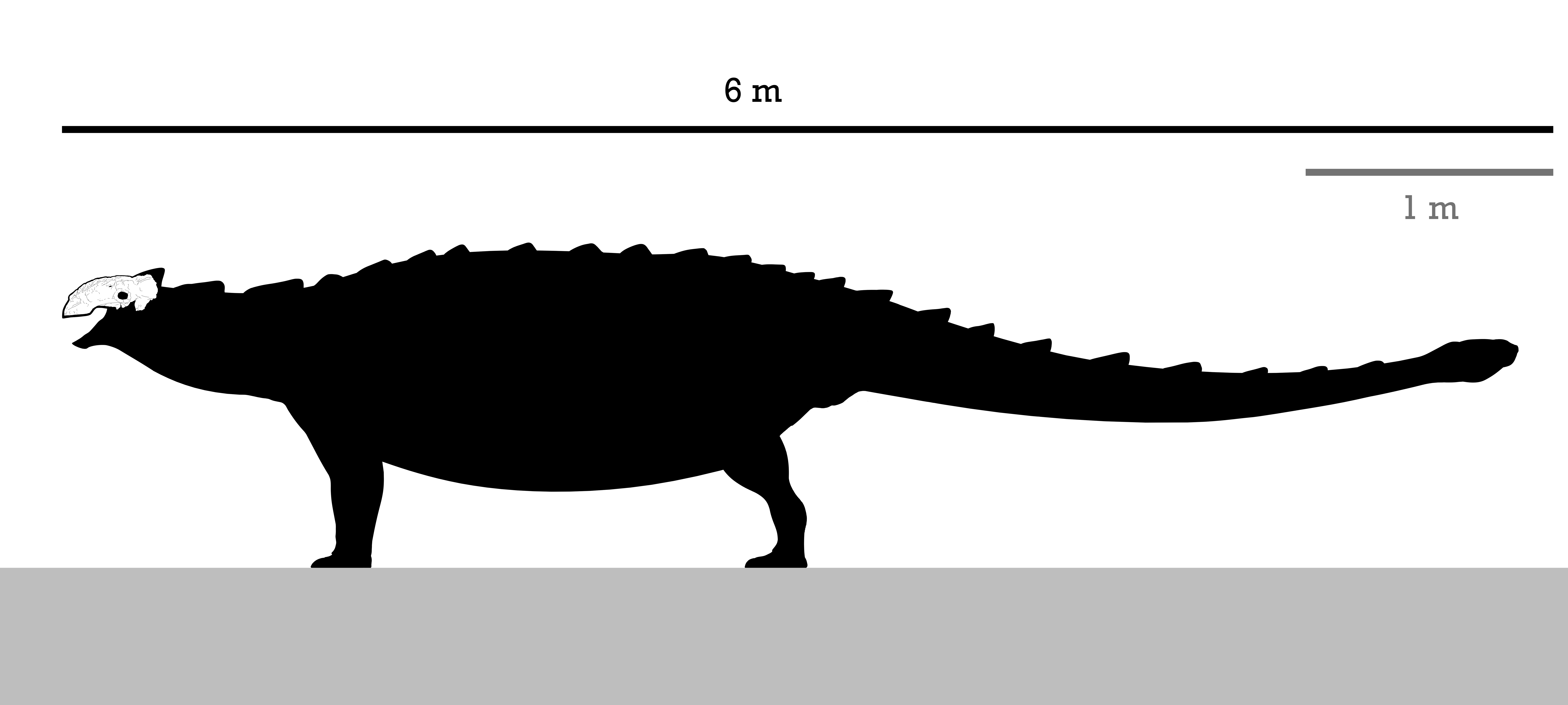
Ankylosaurid
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderms on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club. Ankylosauridae is exclusively known from the northern hemisphere, with specimens found in western North America, Europe, and East Asia. The first discoveries within this family were of the genus ''Ankylosaurus'', by Peter Kaiser and Barnum Brown in Montana in 1906. Brown went on to name Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae in 1908. Anatomy Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saichania
''Saichania'' (Mongolian meaning "beautiful one") is a genus of herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Mongolia and China. The first fossils of ''Saichania'' were found in the early 1970s in Mongolia. In 1977 the type species ''Saichania chulsanensis'' was named. The description of this species has been based on limited fossil material; especially the rear of the animal is not well known. ''Saichania'' was more robustly built than other members of the Ankylosauridae, measuring in length and in body mass. Neck vertebrae, shoulder girdle, ribs and breast bones were fused or firmly connected. Its body was flat and low-slung, standing on four short legs. The forelimbs were very powerful. The head was protected by bulbous armour tiles. It could defend itself against predators like ''Tarbosaurus'' with a tail-club. On the torso keeled osteoderms were present. ''Saichania'' bit off plants in its desert habitat with a horny beak and processed them in its w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayan Shireh Formation
The Bayan Shireh Formation (also known as Baynshiree/Baynshire, Baynshirenskaya Svita or Baysheen Shireh) is a geological formation in Mongolia, that dates to the Cretaceous period. It was first described and established by Vasiliev et al. 1959. Description The Bayan Shireh Formation is primarily composed by varicoloured claystones and sandstones with calcareous concretions and characterized by grey mudstones and yellowish-brown medium grained sandstones. Up to thick, the most complete sections are found in the eastern Gobi Desert, consisting of fine-grained, often cross-stratified gray sandstone interbedded with claystone and concretionary, intraformational conglomerates with relatively thick units of red to brown mudstone in the upper part. The Baynshire and Burkhant localities are mainly composed by mudstone, siltstone, sandstone, and conglomerates, with most of their sedimentation being fluvial. The environments that were present on the Bayan Shireh Formation consisted ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurinae
Ankylosaurinae is a subfamily of ankylosaurid dinosaurs, existing from the Early Cretaceous about 105 million years ago until the end of the Late Cretaceous, about 66 mya. Many genera are included in the clade, such as ''Ankylosaurus'', ''Pinacosaurus'', ''Euoplocephalus'', and ''Saichania''. Features Ankylosaurines are defined as being closer relatives to ''Ankylosaurus'' than to ''Shamosaurus''. Diagnostic features of ankylosaurines include the nuchal shelf that obscures the occiput in dorsal view, and the quadrate condyle which is obscured lightly by the quadratojugal boss. Phylogeny The following cladogram is based on the 50% majority rule phylogenetic analysis In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... of Arbour & Currie (2015): References Ankylosaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1993 In Paleontology ...
Flora Plants Arthropods Insects Archosauromorphs Pseudosuchians Non-avian dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Birds Plesiosaurs References {{portal, Paleontology 1990s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarchia
''Tarchia'' (meaning "brainy one") is a genus of herbivorous ankylosauridae, ankylosaurid dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Discovery and naming In 1970, a Polish-Mongolian expedition discovered an ankylosaurian skull near Khulsan. In 1977, Teresa Maryańska named and described the type species ''Tarchia kielanae''. The generic name is derived from Mongolian language, Mongolian тархи (''tarkhi'', "brain") and Latin ''~ia'', in reference to a brain size presumed larger than that of the related form ''Saichania''. The specific name (zoology), specific name honours Professor Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, the leader of the expedition. The holotype, ZPal MgD-I/111, was discovered in the Upper Cretaceous (possibly Campanian-Maastrichtian) Barun Goyot Formation (previously known as the 'Lower Nemegt Beds') of the Nemegt Basin of Mongolia. It consists of a skull roof, braincase and rear skull elements. Maryańska referred three additional specimens: ZPAL MgDI/43, a large po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinacosaurus
''Pinacosaurus'' (meaning "Plank lizard") is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian, roughly 75 million to 71 million years ago), mainly in Mongolia and China. The first remains of the genus were found in 1923, and the type species ''Pinacosaurus grangeri'' was named in 1933. ''Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus'' named in 1999, is a second possibly valid species differing from the type species in details of the skull armour. Of ''Pinacosaurus grangeri'' many skeletons have been found, more than of any other ankylosaur. These predominantly consist of juveniles that perhaps lived in herds roaming the desert landscape of their habitat. ''Pinacosaurus'' was a medium-sized ankylosaurine, about five metres long and weighed up to two tonnes. Its body was flat and low-slung but not as heavily built as in some other members of the Ankylosaurinae. The head was protected by bone tiles, hence its name. Each nostril was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone. In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians. Anatomy and function In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ... bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestral component of the dermal roof and is typically thin compared to other skull bones. The squamosal bone lies Anatomical terms of location, ventral to the temporal series and otic notch, and is bordered anteriorly by the Postorbital bone, postorbital. Posteriorly, the squamosal articulates with the quadrate bone, quadrate and Pterygoid bone, pterygoid bones. The squamosal is bordered anteroventrally by the jugal and ventrally by the quadratojugal. Function in reptiles In reptiles, the Quadrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food, courtship, and feeding young. The terms ''beak'' and ''rostrum'' are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, anuran tadpoles, monotremes (i.e. echidnas and platypuses, which have a beak-like structure), sirens, pufferfish, billfishes and cephalopods. Although beaks vary significantly in size, shape, color and texture, they share a similar underlying structure. Two bony projections – the upper and lower mandibles – are covered with a thin keratinized layer of epidermis known as the rhamphotheca. In most species, two holes called ''nares'' lead to the respiratory system. Etymology Although the word "beak" was, in the past, generally restricted to the sharpened bills o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia. Discovery and naming In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleton of an unknown ankylosaurian at the Hamrin-Us site in Dornogovi Province. This was the first discovery of an ankylosaur in the Lower Cretaceous of Mongolia.T.A. Tumanova, 1983, "Pervyy ankilozavr iz nizhnego mela Mongolii", In: L.P. Tatarinov, R. Barsbold, E. Vorobyeva, B. Luvsandanzan, B.A. Trofimov, Yu. A. Reshetov, & M.A. Shishkin (eds.), ''Iskopayemyye reptilii mongolii''. Trudy Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya 24: 110-118 In 1983, Tatyana Tumanova named and described the type species ''Shamosaurus scutatus''. The generic name is derived from Mandarin ''sha mo'', "sand desert", the Chinese name for the Gobi. The specific name means "protected by a shield" in Latin, a reference to the body armour. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crichtonpelta
''Crichtonpelta'' is a genus of extinct herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous ( Cenomanian) of China. Discovery and naming In 2007, Lü Junchang, Ji Qiang, Gao Yubo and Li Zhixin named and described a second species of ''Crichtonsaurus'': ''Crichtonsaurus benxiensis''. The specific name refers to the Benxi Geological Museum. The holotype, BXGMV0012, is a skull found near Beipiao in a layer of the Sunjiawan Formation probably dating from the early Cenomanian (~99–95 Ma). Specimen BXGMV0012-1, a skeleton lacking the skull, discovered in the same quarry as the holotype, was referred to the species. Furthermore, a skeleton with skull, displayed by the Sihetun Fossil Museum as a ''Crichtonsaurus bohlini'' specimen, was in 2014 referred to ''Crichtonpelta''. In 2017, a fourth specimen was described, from the same quarry as the holotype, G20090034, consisting of a skull lacking the front snout.YANG Jingtao, YOU Hailu, XIE Li & ZHOU Hongrui, 2017, "A New Spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |