|
TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng
TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng (HÃḂn táṠḟ: éæ£Ḃ; 9 July 1686 â 20 December 1729) was the lord who ruled Tonkin from 1709 to 1729 (his title as ruler was ''An ÄÃṀ VÆḞÆḂng''). TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng was born to TráṠnh BÃnh, a grandson of the former lord TráṠnh CÄn. He belonged to the line of TráṠnh lords who had ruled parts of Vietnam since 1545. Like his great-grandfather and predecessor, TráṠnh CÄn, his reign was mostly devoted to administrative reforms. __TOC__ Biography TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng ruled ViáṠt Nam during a time of external peace but growing internal strife. He enacted many governmental reforms in both financial matters and judicial rules. His main concern was the growing problem of landless peasants. Unlike the NguyáṠ n lords who were constantly expanding their territory south, the TráṠnh lords had little room for expansion. Hence, the land supply was essentially fixed but the population kept growing. TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng tried various legislative means to solve the problem. He tried to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TráṠnh Lords
The TráṠnh lords ( vi, ChÃẃa TráṠnh; CháṠŸ NÃṀm: äẁṠé; 1545â1787), formal title TráṠnh Viceroy (; ), also known as TráṠnh clan (éæḞ, ''TráṠnh tháṠ'') or the House of TráṠnh, were a noble feudal clan who de facto ruled Northern Vietnam as known as Tonkin by foreigners during the Later LÃẂ dynasty, ÄáẃḂi ViáṠt. The TráṠnh clan and their rivals, the NguyáṠ n clan, were both referred by their subjects as "ChÃẃa" (lord) and controlled ÄáẃḂi ViáṠt while the Later LÃẂ emperors were reduced to only a titular position. The TráṠnh lords traced their descent from TráṠnh Kháẃ£, a friend and advisor to the 15th-century Vietnamese Emperor LÃẂ LáṠ£i. The TráṠnh clan produced 12 lords who dominated the royal court of Later LÃẂ dynasty and ruled northern Vietnam for more than 2 centuries. Origin of TráṠnh clan Rise of TráṠnh family After the death of emperor LÃẂ Hiáẃṡn TÃṀng in 1504, the LÃẂ dynasty began to decline. In 1527, the courtier MáẃḂc ÄÄng Dung gained the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1729 Deaths
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: * 17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines * ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine * ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels * ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by KenzaburÅ Åe * ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film * ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *''Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock * ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *''Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film * ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film * ''17 Again'' (film), a 2009 film whose working title was ''17'' * ''Seventeen'' (2019 film), a Spanish drama film Television * ''Seventeen'' (TV drama), a 1994 UK dramatic short starring Chris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Monarchs Of Vietnam
This article lists the monarchs of Vietnam. Under the emperor at home, king abroad system used by later dynasties, Vietnamese monarchs would use the title of ''emperor'' (çåẁ, Hoà ng Äáẃṡ; or other equivalents) domestically, and the more common term ''king'' (ç, vÆḞÆḂng), ''sovereign'' (ŵẂỳ, vua), or ''his Majesty'' (éäẁ, BáṠ háẃḂ). Overview Some Vietnamese monarchs declared themselves kings (''vÆḞÆḂng'') or emperors (''hoà ng Äáẃṡ''). Imperial titles were used for both domestic and foreign affairs, except for diplomatic missions to China where Vietnamese monarchs were regarded as kingship or prince. Many of the Later LÃẂ monarchs were figurehead rulers, with the real powers resting on feudal lords and princes who were technically their servants. Most Vietnamese monarchs are known through their posthumous names or temple names, while the NguyáṠ n dynasty, the last reigning house is known through their era names. Titles Vietnamese titles Vietnamese monarchs used and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LÃẂ Dynasty
The LÃẂ dynasty, also known as Later LÃẂ dynasty ( vi, Háẃu LÃẂ triáṠu, cháṠŸ HÃḂn: åẅéṠæ or vi, nhà Háẃu LÃẂ, link=no, cháṠŸ NÃṀm: èṗåẅéṠ), was the longest-ruling Vietnamese dynasty, ruling ÄáẃḂi ViáṠt from 1428 to 1789. The LÃẂ dynasty is divided into two historical periods â the Early period ( Vietnamese: LÃẂ sÆḂ triáṠu, cháṠŸ HÃḂn: éṠåæ, or Vietnamese: nhà LÃẂ sÆḂ, cháṠŸ NÃṀm: èṗéṠå; 1428â1527) before usurpation by the MáẃḂc dynasty (1527â1683), in which emperors ruled in their own right, and the restored period or Revival LÃẂ ( Vietnamese: LÃẂ Trung hÆḞng triáṠu, cháṠŸ HÃḂn: éṠäẁèæ, or Vietnamese: nhà LÃẂ trung hÆḞng, cháṠŸ NÃṀm: èṗéṠäẁè; 1533â1789), in which figurehead emperors reigned under the auspices of the powerful TráṠnh family. The Restored LÃẂ period is marked by two lengthy civil wars: the LÃẂâMáẃḂc War (1533â1592) in which two dynasties battled for legitimacy in northern Vietnam and the TráṠnhâNguyáṠ n War ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LÃẂ DáṠċ TÃṀng
LÃẂ DáṠċ TÃṀng (cháṠŸ HÃḂn: éṠè£å®, 1679 â 27 February 1731), born LÃẂ Duy ÄÆḞáṠng (éṠç¶çḊ) was an emperor of Vietnam, the 22nd emperor of Vietnamese Later LÃẂ dynasty. He reigned as emperor from 1705â1729 (24 years), the first ten years of which his father LÃẂ Hy TÃṀng was alive and elevated in semi-retirement to Retired Emperor ( vi, ThÃḂi thÆḞáṠ£ng hoà ng, links=no). He was succeeded by LÃẂ Duy PhÆḞáṠng, also known as the second emperor to carry the name HÃṀn ÄáṠ©c CÃṀng.Hoà n tÃḂng thi hà i vua LÃẂ DáṠċ TÃṀng: káṠṖ yáẃṡu HáṠi ÄáṠng háṠ LÃẂ ViáṠt Nam â 2010 Process ceremony of digging and re-burying corpse of the King LÃẂ Du TÃṀng in Thanh HÃġa Province, Vietnam. Issue He had five sons. They are LÃẂ Duy PhÆḞáṠng, LÃẂ Duy Máẃt, LÃẂ Duy QuÃẄ, LÃẂ Thuáẃ§n TÃṀng and LÃẂ à TÃṀng LÃẂ à TÃṀng (éṠæṡå® 29 March 1719 â 10 August 1759) was the third-last emperor of the Vietnamese LÃẂ dynasty, reigning only nominally under the power of TráṠnh Giang of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagodas
A pagoda is an Asian tiered tower with multiple eaves common to Nepal, India, China, Japan, Korea, Myanmar, Vietnam, and other parts of Asia. Most pagodas were built to have a religious function, most often Buddhist but sometimes Taoist, and were often located in or near viharas. The pagoda traces its origins to the stupa of ancient India. Chinese pagodas () are a traditional part of Chinese architecture. In addition to religious use, since ancient times Chinese pagodas have been praised for the spectacular views they offer, and many classical poems attest to the joy of scaling pagodas. Chinese sources credit the Nepalese architect Araniko with introducing the pagoda to China. The oldest and tallest pagodas were built of wood, but most that survived were built of brick or stone. Some pagodas are solid with no interior. Hollow pagodas have no higher floors or rooms, but the interior often contains an altar or a smaller pagoda, as well as a series of staircases for the vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
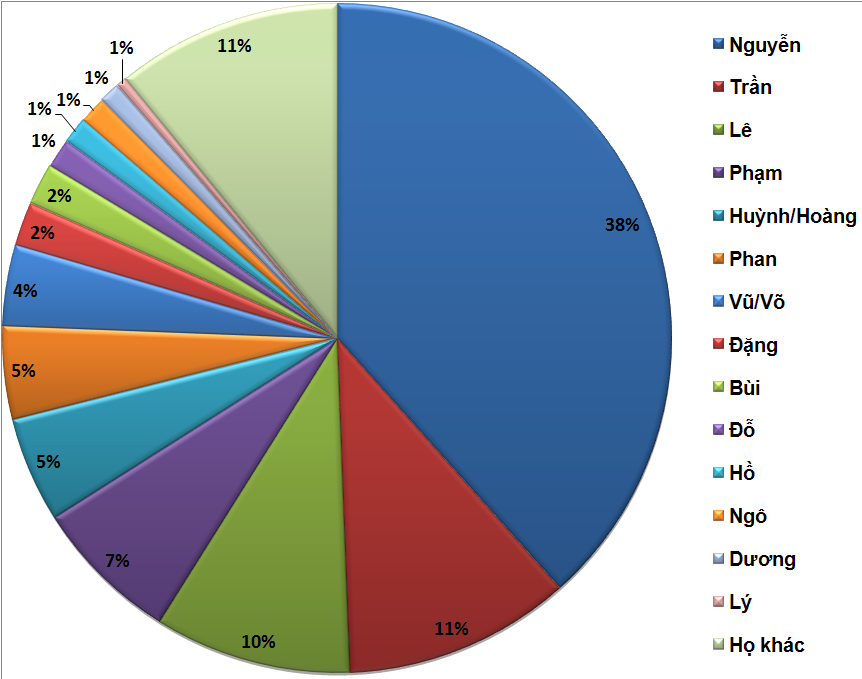
NguyáṠ
n Lords
NguyáṠ n () is the most common Vietnamese surname. Outside of Vietnam, the surname is commonly rendered without diacritics as Nguyen. NguyÃẂn (å ïỳis a different word and surname. By some estimates 39 percent of Vietnamese people bear this surname.LÃẂ Trung Hoa, ''HáṠ và tÃẂn ngÆḞáṠi ViáṠt Nam'', NXB Khoa háṠc - Xã háṠi, 2005 Origin and usage "NguyáṠ n" is the spelling of the Sino-Vietnamese pronunciation of the Han character é® (, ). The same Han character is often romanized as ''RuÇn'' in Mandarin, ''Yuen'' in Cantonese, ''Gnieuh'' or ''NyoeÂṗ'' in Wu Chinese, or ''Nguang'' in Hokchew. . Hanja reading (Korean) is ì (''Wan'') or ì (''Won'') and in Hiragana is a Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with ''katakana'' as well as ''kanji''. It is a phonetic lettering system. The word ''hiragana'' literally means "flowing" or "simple" kana ("simple" originally as contrast ..., it is ãã (''Gen''), old reading as ããã (Ngen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TrÆḞÆḂng TháṠ Trong
TrÆḞÆḂng TháṠ Trong ( vi-hantu, åỳṁæḞŵĊŸ, ? - ?) was a consort of lord TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng. __TOC__ Biography Consort TrÆḞÆḂng TháṠ Trong had the courtesy name NgáṠc Trong (çŵĊŸ), was born at LÃẂ village, NhÆḞ QuáṠġnh commune, VÄn LÃḃm district, Háẃ£i ÄÃṀng town (now HÆḞng YÃẂn province). She was the third daughter of military official TrÆḞÆḂng ÄÃṀn Háẃu and his wife NguyáṠ n TháṠ (posthumous name Lady TháṠċc Tiáẃṡt). Essentially LÃẂ village's TrÆḞÆḂng clan was the distaff-side relations of TráṠnh lords, so lady TrÆḞÆḂng TháṠ Trong has entered TráṠnh's palace to become the consort ''NáṠi-tháṠ cung-táẃ§n'' (å §äẅå®®åỲẂ) of lord TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng (1686â1729) when she grew up. She always spent free and boring times composing verses. See also * TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng (HÃḂn táṠḟ: éæ£Ḃ; 9 July 1686 â 20 December 1729) was the lord who ruled Tonkin from 1709 to 1729 (his title as ruler was ''An ÄÃṀ VÆḞÆḂng''). TráṠnh CÆḞÆḂng was born to TráṠnh BÃnh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled ''Tongkin'', ''Tonquin'' or ''Tongking'', is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain ''Äà ng Ngoà i'' under TráṠnh lords' control, including both the Northern and Thanh- NgháṠ regions, north of the Gianh River. From 1884 to early 1945, this term was used for the French protectorate of Tonkin, composed of only the Northern region. Names "Tonkin" is a Western rendition of æḟäẃỲ ''ÄÃṀng Kinh'', meaning 'Eastern Capital'. This was the name of the capital of the LÃẂ dynasty (present-day Hanoi). Locally, Tonkin is nowadays known as ''miáṠn BáẃŸc'', or ''BáẃŸc BáṠ'' (åéẀ), meaning ' Northern Region'. The name was used from 1883 to 1945 for the French protectorate of Tonkin (Vietnamese: ''BáẃŸc KáṠġ'' ååṠ), a constituent territory of French Indochina. Geography It is south of Yunnan (VÃḃn Nam) and Guangxi (Quáẃ£ng TÃḃy) Provinces of China; east of northern Laos and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TráṠnh Lords
The TráṠnh lords ( vi, ChÃẃa TráṠnh; CháṠŸ NÃṀm: äẁṠé; 1545â1787), formal title TráṠnh Viceroy (; ), also known as TráṠnh clan (éæḞ, ''TráṠnh tháṠ'') or the House of TráṠnh, were a noble feudal clan who de facto ruled Northern Vietnam as known as Tonkin by foreigners during the Later LÃẂ dynasty, ÄáẃḂi ViáṠt. The TráṠnh clan and their rivals, the NguyáṠ n clan, were both referred by their subjects as "ChÃẃa" (lord) and controlled ÄáẃḂi ViáṠt while the Later LÃẂ emperors were reduced to only a titular position. The TráṠnh lords traced their descent from TráṠnh Kháẃ£, a friend and advisor to the 15th-century Vietnamese Emperor LÃẂ LáṠ£i. The TráṠnh clan produced 12 lords who dominated the royal court of Later LÃẂ dynasty and ruled northern Vietnam for more than 2 centuries. Origin of TráṠnh clan Rise of TráṠnh family After the death of emperor LÃẂ Hiáẃṡn TÃṀng in 1504, the LÃẂ dynasty began to decline. In 1527, the courtier MáẃḂc ÄÄng Dung gained the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
