|
Tropical Storm Arlene (2011)
Tropical Storm Arlene, the first named storm of the 2011 Atlantic hurricane season, brought blustery conditions to much of eastern Mexico in late June to early July 2011. Arlene originated from an Atlantic tropical wave, which crossed the Yucatán Peninsula before emerging over warm waters in the Bay of Campeche. Despite moderate wind shear, the disturbance strengthened and developed a surface circulation, prompting the National Hurricane Center to declare it a tropical storm on June 28. Arlene remained vigorous for most of its existence; the storm peaked in intensity with winds of 65 mph (100 km/h) on June 30, just before making landfall on the coast of Veracruz. Crossing the mountains of eastern Mexico, Arlene weakened to a depression before dissipating early on July 1. The precursor disturbance to Arlene brought significant rainfall to parts of Central America, killing three people and triggering widespread flooding and landslides. Throughout Mexico, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropical cyclogenesis involves the development of a warm-core cyclone, due to significant convection in a favorable atmospheric environment. Tropical cyclogenesis requires six main factors: sufficiently warm sea surface temperatures (at least ), atmospheric instability, high humidity in the lower to middle levels of the troposphere, enough Coriolis force to develop a low-pressure center, a pre-existing low-level focus or disturbance, and low vertical wind shear. Tropical cyclones tend to develop during the summer, but have been noted in nearly every month in most basins. Climate cycles such as ENSO and the Madden–Julian oscillation modulate the timing and frequency of tropical cyclone development. There is a limit on tropical cyclone i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, and to the north by the Gulf of Honduras, a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea. Its capital and largest city is Tegucigalpa. Honduras was home to several important Mesoamerican cultures, most notably the Maya, before the Spanish Colonization in the sixteenth century. The Spanish introduced Catholicism and the now predominant Spanish language, along with numerous customs that have blended with the indigenous culture. Honduras became independent in 1821 and has since been a republic, although it has consistently endured much social strife and political instability, and remains one of the poorest countries in the Western Hemisphere. In 1960, the northern part of what was the Mosquito Coast was transferred from Nicara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Pressure Gradient (atmospheric)
In atmospheric science, the pressure gradient (typically of air but more generally of any fluid) is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure increases the most rapidly around a particular location. The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pascals per metre (Pa/m). Mathematically, it is the gradient of pressure as a function of position. The negative gradient of pressure is known as the force density. In petroleum geology and the petrochemical sciences pertaining to oil wells, and more specifically within hydrostatics, pressure gradients refer to the gradient of vertical pressure in a column of fluid within a wellbore and are generally expressed in pounds per square inch per foot (psi/ft). This column of fluid is subject to the compound pressure gradient of the overlying fluids. The path and geometry of the column is totally irrelevant; only the vertical depth of the column has any relevance to the vertical pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Madre Oriental
The Sierra Madre Oriental () is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica. Setting Spanning the Sierra Madre Oriental runs from the Rio Grande on the border between Coahuila and Texas south through Nuevo León, southwest Tamaulipas, San Luis Potosí, Querétaro, and Hidalgo to northern Puebla, where it joins with the east-west running Eje Volcánico Transversal of central Mexico. The northernmost are the Sierra del Burro and the Sierra del Carmen which reach the border with the United States at the Rio Grande. North of the Rio Grande, the range continues northwestward into Texas and beyond as the Davis and Guadalupe Ranges. Mexico's Gulf Coastal Plain lies to the east of the range, between the mountains and the Gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabo Rojo (Mexico)
Cabo Rojo (Spanish for "Red Cape") (21°47'N 97°35'W) is a barrier of quartzite sand deposited adjacent to the coast of the Mexican state of Veracruz, about south of the city of Tampico, Tamaulipas. It encloses the brackish lagoon called Laguna de Tamiahua. It is located in the municipalities of Ozuluama de Mascareñas and Tamiahua. As one of the few protruding features on this part of the coast, it may be regarded as the boundary between the western coasts of the Bay of Campeche and the Gulf of Mexico proper, and is frequently used by the authorities as a breakpoint for tropical cyclone warnings and watches. Rojo Rojo means "red" in Spanish. Rojo may also refer to: *Rojo (surname) Music * Rojo (band), a Mexican Christian rock band ** ''Rojo'' (Rojo album), 2001 * ''Rojo'' (Red Garland album), 1961 * "Rojo", a song by J Balvin from ''Colores'', 2020 * "R ... Landforms of Veracruz {{Veracruz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvorak Technique
The Dvorak technique (developed between 1969 and 1984 by Vernon Dvorak) is a widely used system to estimate tropical cyclone intensity (which includes tropical depression, tropical storm, and hurricane/typhoon/intense tropical cyclone intensities) based solely on visible and infrared satellite images. Within the Dvorak satellite strength estimate for tropical cyclones, there are several visual patterns that a cyclone may take on which define the upper and lower bounds on its intensity. The primary patterns used are curved band pattern (T1.0-T4.5), shear pattern (T1.5–T3.5), central dense overcast (CDO) pattern (T2.5–T5.0), central cold cover (CCC) pattern, banding eye pattern (T4.0–T4.5), and eye pattern (T4.5–T8.0). Both the central dense overcast and embedded eye pattern use the size of the CDO. The CDO pattern intensities start at T2.5, equivalent to minimal tropical storm intensity (40 mph, 65 km/h). The shape of the central dense overcast is also con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Forecast Model
A tropical cyclone forecast model is a computer program that uses meteorological data to forecast aspects of the future state of tropical cyclones. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or combined statistical-dynamic. Dynamical models utilize powerful supercomputers with sophisticated mathematical modeling software and meteorological data to calculate future weather conditions. Statistical models forecast the evolution of a tropical cyclone in a simpler manner, by extrapolating from historical datasets, and thus can be run quickly on platforms such as personal computers. Statistical-dynamical models use aspects of both types of forecasting. Four primary types of forecasts exist for tropical cyclones: track, intensity, storm surge, and rainfall. Dynamical models were not developed until the 1970s and the 1980s, with earlier efforts focused on the storm surge problem. Track models did not show forecast skill when compared to statistical models until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainband
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands can be stratiform or convective, and are generated by differences in temperature. When noted on weather radar imagery, this precipitation elongation is referred to as banded structure. Rainbands within tropical cyclones are curved in orientation. Rainbands of tropical cyclones contain showers and thunderstorms that, together with the eyewall and the eye, constitute a hurricane or tropical storm. The extent of rainbands around a tropical cyclone can help determine the cyclone's intensity. Rainbands spawned near and ahead of cold fronts can be squall lines which are able to produce tornadoes. Rainbands associated with cold fronts can be warped by mountain barriers perpendicular to the front's orientation due to the formation of a low-level barrier jet. Bands of thunderstorms can form with sea breeze and land breeze boundaries, if enough moisture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
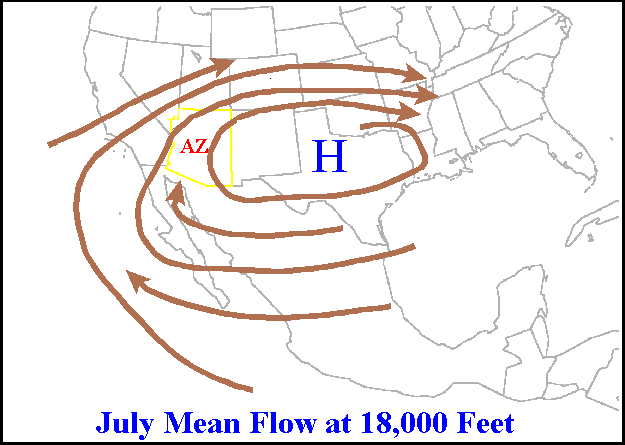
Ridge (meteorology)
A ridge or barometric ridge is a term in meteorology describing an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure compared to the surrounding environment, without being a closed circulation. It is associated with an area of maximum anticyclonic curvature of wind flow. The ridge originates in the center of an anticyclone and sandwiched between two low-pressure areas, and the locus of the maximum curvature is called the ''ridge line''. This phenomenon is the opposite of a trough. Description Ridges can be represented in two ways: * On surface weather maps, the pressure isobars form contours where the maximum pressure is found along the axis of the ridge. * In upper-air maps, geopotential height isohypses form similar contours where the maximum defines the ridge. Related weather Given the direction of the winds around an anticyclonic circulation and the fact that weather systems move from west to east: *ahead of an upper-ridge, the airflow that comes from the polar regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlene 2011 Atlantic NOAA EVL cartoon series.
{{disambiguation ...
Arlene may refer to: * Arleen, a feminine name, also spelled Arlene * "Arlene" (song), the 1985 debut single by American country music artist Marty Stuart * Arlene, a Beanie Baby cat produced by Ty, Inc. * Hurricane Arlene, the name of several tropical storms in the Atlantic Ocean * Arlene, a cat character in the Garfield ''Garfield'' is an American comic strip created by Jim Davis. Originally published locally as ''Jon'' in 1976, then in nationwide syndication from 1978 as ''Garfield'', it chronicles the life of the title character Garfield the cat, his human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)