|
Toucouleur People
__NOTOC__ The Tukulor people ( ar, توكولور), also called Toucouleur or Haalpulaar, are a West African ethnic group native to Futa Tooro region of Senegal. There are smaller communities in Mali and Mauritania. The Toucouleur were Islamized in the 11th century; their early and strong Islamic heritage, which is seen as a defining feature, is a "matter of great pride for them".Tukulor Encyclopædia Britannica They have been influential in the spread of Islam to West Africa in the , later founded the vast in the 19th century under |
Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Renndaandi Senegaali); Arabic: جمهورية السنغال ''Jumhuriat As-Sinighal'') is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. Senegal is bordered by Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, Guinea to the southeast and Guinea-Bissau to the southwest. Senegal nearly surrounds the Gambia, a country occupying a narrow sliver of land along the banks of the Gambia River, which separates Senegal's southern region of Casamance from the rest of the country. Senegal also shares a maritime border with Cape Verde. Senegal's economic and political capital is Dakar. Senegal is notably the westernmost country in the mainland of the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. It owes its name to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senegal River
,french: Fleuve Sénégal) , name_etymology = , image = Senegal River Saint Louis.jpg , image_size = , image_caption = Fishermen on the bank of the Senegal River estuary at the outskirts of Saint-Louis, Senegal , map = Senegalrivermap.png , map_size = , map_caption = Map of the Senegal River drainage basin. , pushpin_map = , pushpin_map_size = , pushpin_map_caption= , subdivision_type1 = Country , subdivision_name1 = Senegal, Mauritania, Mali , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name2 = , subdivision_type3 = , subdivision_name3 = , subdivision_type4 = , subdivision_name4 = , subdivision_type5 = , subdivision_name5 = , length = , width_min = , width_avg = , width_max = , depth_min = , depth_avg = , depth_max = , discharge1_location= , discharge1_min = , discharge1_avg = , d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
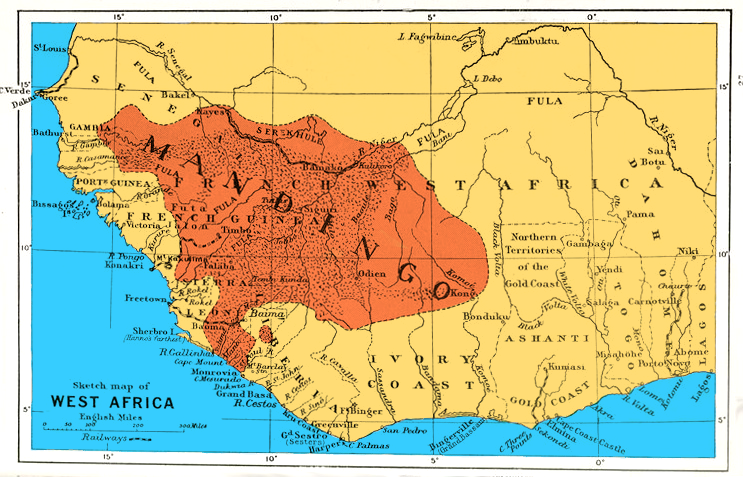
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a '' lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Sene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God's guidance, such as struggle against one's evil inclinations, proselytizing, or efforts toward the moral betterment of the Muslim community (''Ummah''), though it is most frequently associated with war. In classical Islamic law (''sharia''), the term refers to armed struggle against unbelievers, while modernist Islamic scholars generally equate military ''jihad'' with defensive warfare. In Sufi circles, spiritual and moral jihad has been traditionally emphasized under the name of ''greater jihad''. The term has gained additional attention in recent decades through its use by various insurgent Islamic extremist, militant Islamist, and terrorist individuals and organizations whose ideology is based on the Islamic notion of ''jiha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sokoto Caliphate
The Sokoto Caliphate (), also known as the Fulani Empire or the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fulani jihads after defeating the Hausa Kingdoms in the Fulani War. The boundaries of the caliphate are part of present-day Cameroon, Burkina Faso, Niger, and Nigeria. It was dissolved when the British and Germans conquered the area in 1903 and annexed it into the newly established Northern Nigeria Protectorate and Kamerun respectively. The caliphate arose after the Hausa King Yunfa attempted to assassinate Usman dan Fodio in 1802. In order to escape persecution, Usman and his followers migrated towards Gudu in February 1804. Usman's followers pledged allegiance to Usman as the Commander of the Faithful (). By 1808, the Sokoto Caliphate had gained control of several northern Nigerian states. Under the sixth caliph Ahmadu Rufai, the state reached its maximum extent, covering almost the enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joking Relationship
In anthropology, a joking relationship is a relationship between two people that involves a ritualised banter of teasing or mocking. In Niger it is listed on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. Structure Analysed by British social anthropologist Alfred Radcliffe-Brown in 1940, it describes a kind of ritualised banter that takes place, for example between a man and his maternal mother-in-law in some South African indigenous societies. Two main variations are described: an ''asymmetrical'' relationship where one party is required to take no offence at constant teasing or mocking by the other, and a ''symmetrical'' relationship where each party makes fun at the other's expense. The joking relationship is an interaction that mediates and stabilizes social relationships where there is tension, competition, or potential conflict, such as between in-laws and between clans and tribes. Extent While first encountered by Radcliffe-Brown in the 1920s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale University Press publishes approximately 300 new hardcover and 150 new paperback books annually and has a backlist of about 5,000 books in print. Its books have won five National Book Awards, two National Book Critics Circle Awards and eight Pulitzer Prize The Pulitzer Prize () is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine, online journalism, literature, and musical composition within the United States. It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of Joseph Pulitzer, who had made h ...s. The press maintains offices in New Haven, Connecticut and London, England. Yale is the only American university press with a full-scale publishing operation in Europe. It was a co-founder of the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication wherein knowledge, art, ideas and cultural material is received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another. Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (1985), reported statements from present generation which "specifies that the message must be oral statements spoken, sung or called out on musical instruments only"; "There must be transmission by word of mouth over at least a generation". He points out, "Our definition is a working definition for the use of historians. Sociologists, linguists or scholars of the verbal arts propose their own, which in, e.g., sociology, stresses common knowledge. In linguistics, features that distinguish the language from common dialogue (linguists), and in the verbal arts features of form and content that define art (folklorists)."Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: "Methodology and African Prehistory", 1990, ''UNESCO International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takrur
Takrur, Tekrur or Tekrour ( 800 – c. 1285) was an ancient state of West Africa, which flourished roughly parallel to the Ghana Empire. Origin Takrur was the capital of the state which flourished on the lower Senegal River. Takruri was a term, like Bilad-ul-Sudan, that was used to refer to all people of West African ancestry, and is still in use as such in the Middle East, with some corruption, as in ''Takruni'', pl. ''Takarna'' تكروني in Saudi Arabia, and in Ethiopia and Eritrea, in the form Tukrir. The district of ''Bulaq Al-Dakrur'' بولاق الدكرور in Cairo is named after an ascetic from West Africa. The formation of the state may have taken place as an influx of Fulani from the east settled in the Senegal valley. John Donnelly Fage suggests that Takrur was formed through the interaction of Berbers from the Sahara and "Negro agricultural peoples" who were "essentially Serer". Centre of trade Located in the Senegal valley, along the border of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more familiar one. The form or the meaning of an archaic, foreign, or otherwise unfamiliar word is reinterpreted as resembling more familiar words or morphemes. The term ''folk etymology'' is a loan translation from German ''Volksetymologie'', coined by Ernst Förstemann in 1852. Folk etymology is a productive process in historical linguistics, language change, and social interaction. Reanalysis of a word's history or original form can affect its spelling, pronunciation, or meaning. This is frequently seen in relation to loanwords or words that have become archaic or obsolete. Examples of words created or changed through folk etymology include the English dialectal form ''sparrowgrass'', originally from Greek (" asparagus") remade by analogy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |