|
Topo Volcanic Complex
Volcanic Complex of Topo ( pt, Complexo Vulcânico do Topo) is a complex of scoria cones and volcanic structures, located near the village Topo in the southeastern part of the island of São Jorge, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. History The base of the Topo complex originated in numerous shield volcanoes, erupting from primordial fissural faults that ran along a northwest to southeast and east-southeast to west-northwest alignment. These structures are only observed in the curvature of the higher turf cones, as far as above sea level. These activities initiated around 600,000 years ago. The island of São Jorge had its initial formation from the rising of magma along these fractures through the earth's crust, resulting in effusive volcanism from the area east of Ribeira Seca until Topo (from which it got its name). Owing to age, continuous effusive eruptions occurred simultaneously with the eruption on the island of Faial, along the Volcanic Complex of Ribeirinha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azores
) , motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace") , anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores") , image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg , map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union , map_caption=Location of the Azores within the European Union , subdivision_type=Sovereign state , subdivision_name=Portugal , established_title=Settlement , established_date=1432 , established_title3=Autonomous status , established_date3=30 April 1976 , official_languages=Portuguese , demonym= ( en, Azorean) , capital_type= Capitals , capital = Ponta Delgada (executive) Angra do Heroísmo (judicial) Horta (legislative) , largest_city = Ponta Delgada , government_type=Autonomous Region , leader_title1=Representative of the Republic , leader_name1=Pedro Manuel dos Reis Alves Catarino , leader_title2= President of the Legislative Assembly , leader_name2= Luís Garcia , leader_title3= President of the Regional Government , leader_name3=José Manuel Bolieiro , le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topo (Calheta)
Topo, also known as Nossa Senhora do Rosário, is a ''freguesia'' ("civil parish") on the northeastern corner of the municipality Calheta on the island of São Jorge. It is considered the first settlement on the island of São Jorge to attain the status of municipality; from 1510 to 1867 "Vila do Topo" was the municipal seat of Topo, which included the neighboring parish of Santo Antão. The population in 2011 was 508, in an area of 9.24 km². History Debate still exists on whether Topo was the first settlement on the island; the first colony was founded between 1480 and 1490, when a colony of Flemish people, under the direction of Willem van der Haegen, settled on the eastern coast. This adventurous Fleming, who later adopted the name "Guilherme da Silveira", and whose descendants populate the numerous villages of São Jorge, was later buried in the chapel-annex of the '' Solar dos Tiagos''. Due to its proximity to Terceira, and owing to the difficult overland links to C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Jorge Island
São Jorge () is an island in the central group of the Azores archipelago and part of the autonomous region of Portugal. Separated from its nearest neighbours (Pico and Faial islands) by the Pico-São Jorge Channel, the central group is often referred colloquially as part of the ''Triângulo'' ("Triangle") group or just "The Triangle". São Jorge is a relatively long thin island with tall cliffs, whose 8,381 inhabitants are concentrated on various geological debris fields (''fajãs'') along the north and south coasts; from east to west, the island is long and, north to south, wide: its area is . History It is unclear when the first explorers discovered the island of São Jorge; as part of the politics of human occupation, the Azores were populated after 1430 (probably 1439) through the initiative of Prince Henry the Navigator. 23 April, known as the feast day of Saint George, has been cited by historians as the reason for the island's name, although this is likely conjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serra Do Topo, As Montanhas Sucedem-se A Estrada Sobe A Mais De 900 Metros De Altitude, Calheta, Ilha De São Jorge, Açores
Serra (Latin for "saw") may refer to: People * Serra (footballer) (born 1961), Portuguese footballer * Serra (surname) * Serra (given name) Cities, towns, municipalities Brazil * Serra, Espírito Santo, a city in the Greater Vitória area *Amparo do Serra, in Minas Gerais *Araçoiaba da Serra, in São Paulo *Itapecerica da Serra, in São Paulo *Mirante da Serra, in Rondônia *Natividade da Serra, in São Paulo *Pé de Serra, in Bahia *Redenção da Serra, in São Paulo *Rio Grande da Serra, in São Paulo *Santa Maria da Serra, in São Paulo *São Lourenço da Serra, in São Paulo * Serra Azul, in São Paulo *Serra do Navio, in Amapá *Serra do Navio, in Amapá *Serra Negra, in São Paulo * Serra Talhada, in Pernambuco *Taboão da Serra, in São Paulo Italy *La Serra, San Miniato, in Tuscany *Serra (Rocca Santa Maria), in Abruzzo * Serra d'Aiello, in Calabria * Serra de' Conti, in Marche * Serra Pedace, in Calabria * Serra Riccò, in Liguria * Serra San Bruno, in Calabria * Serr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial planet, rocky planet or natural satellite, moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of volcanism on Venus, Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar mare, lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiite
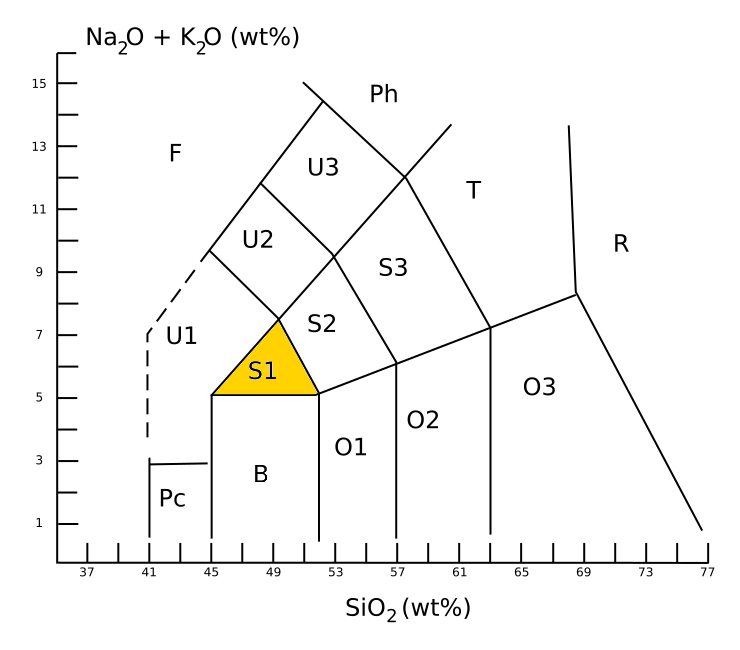
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii. It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Hawaii, which happens to be when the alkaline metals are most present. In gemology, hawaiite is a colloquial term for Hawaii-originated peridot, which is a gem-quality form of the mineral olivine. Description Hawaiite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock produced by rapid cooling of lava moderately poor in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides (potassium oxide plus sodium oxide). It is often impractical to determine the mineral composition of such a fine-grained rock, and so hawaiite is defined chemically. Under the TAS classification, hawaiite is sodic trachybasalt, with a silica content close to 49 wt%, a total alkali metal oxide content close to 6%, and wt% > wt% + 2. This places hawaiite in the S1 field of the TAS dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mugearite
Mugearite () is a type of oligoclase-bearing basalt, comprising olivine, apatite, and opaque oxides. The main feldspar in mugearite is oligoclase. Mugearite is a sodium-rich member of the alkaline magma series. In the TAS classification of volcanic rock, mugearite is classified as sodium-rich basaltic trachyandesite. Examples Western Scotland Mugearite was first identified at Mugeary on the island of Skye, Scotland by Alfred Harker in 1904. Outcrops of mugearite also occur on the island of Isle of Mull, Mull. These examples of mugearite were formed during a period of continental flood basalt volcanic activity that happened in western Scotland during the Paleogene Period (geology), period of the Earth's geological history, when the North Atlantic Ocean opened between Europe and North America. Oceanic islands Mugearite has been erupted by the volcanoes of some High island, oceanic islands at Hotspot (geology), hotspots. Examples are Hawaii (island), Hawaii, Ascension Island, Sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aa (lava Flow)
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. The word ''lava'' comes from Italian and is probably derived from the Latin word ''labes'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroclastic Rock
Pyroclastic rocks (derived from the el, πῦρ, links=no, meaning fire; and , meaning broken) are clastic rocks composed of rock fragments produced and ejected by explosive volcanic eruptions. The individual rock fragments are known as pyroclasts. Pyroclastic rocks are a type of volcaniclastic deposit, which are deposits made predominantly of volcanic particles. 'Phreatic' pyroclastic deposits are a variety of pyroclastic rock that forms from volcanic steam explosions and they are entirely made of accidental clasts. 'Phreatomagmatic' pyroclastic deposits are formed from explosive interaction of magma with groundwater. Unconsolidated accumulations of pyroclasts are described as tephra. Tephra may become lithified to a pyroclastic rock by cementation or chemical reactions as the result of the passage of hot gases (fumarolic alteration) or groundwater (e.g. hydrothermal alteration and diagenesis) and burial, or, if it is emplaced at temperatures so hot that the soft glassy pyrocl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinder Cone
A cinder cone (or scoria cone) is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. Mechanics of eruption Cinder cones range in size from tens to hundreds of meters tall and often have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit. They are composed of loose pyroclastic material (cinder or scoria), which distinguishes them from ''spatter cones'', which are composed of agglomerated volcanic bombs. The pyroclastic material making up a cinder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)