|
Tolerance Rings
Tolerance rings are radially sprung rings that are press fitted between two mating components to act as frictional fasteners. They are flexible shims designed to fix two cylindrical parts together. The wavelike protrusions that run around the circumference of the ring generate a retention force to provide an optimal fit between the two mating components without the need for adhesive or excessive assembly force, simplifying the process for manufacturers. They allow for any misalignment caused by thermal expansion or excessive vibration. Tolerance rings can be used as bearing mounts and as a means of dealing with torque transfer, torque overload protection and axial slip between mating components. They are often used to isolate undesirable vibration in engines and electric motors, for noise-free mechanism operation in passenger vehicles and domestic appliances, where noise reduction has become a major trend in recent years. Modifications to tolerance rings can be made to tune the dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Press Fit
An interference fit, also known as a pressed fit or friction fit is a form of fastening between two ''tight'' fitting mating parts that produces a joint which is held together by friction after the parts are pushed together. Depending on the amount of interference, parts may be joined using a tap from a hammer or ''pressed'' together using a hydraulic ram. Critical components that must not sustain damage during joining may also be cooled significantly below room temperature to shrink one of the components before fitting. This method allows the components to be joined without force and producing a shrink fit interference when the component returns to normal temperature. Interference fits are commonly used with aircraft fasteners to improve the fatigue life of a joint. Introducing interference between parts These fits, though applicable to shaft and hole assembly, are more often used for bearing-housing or bearing-shaft assembly. Tightness of fit The tightness of fit is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
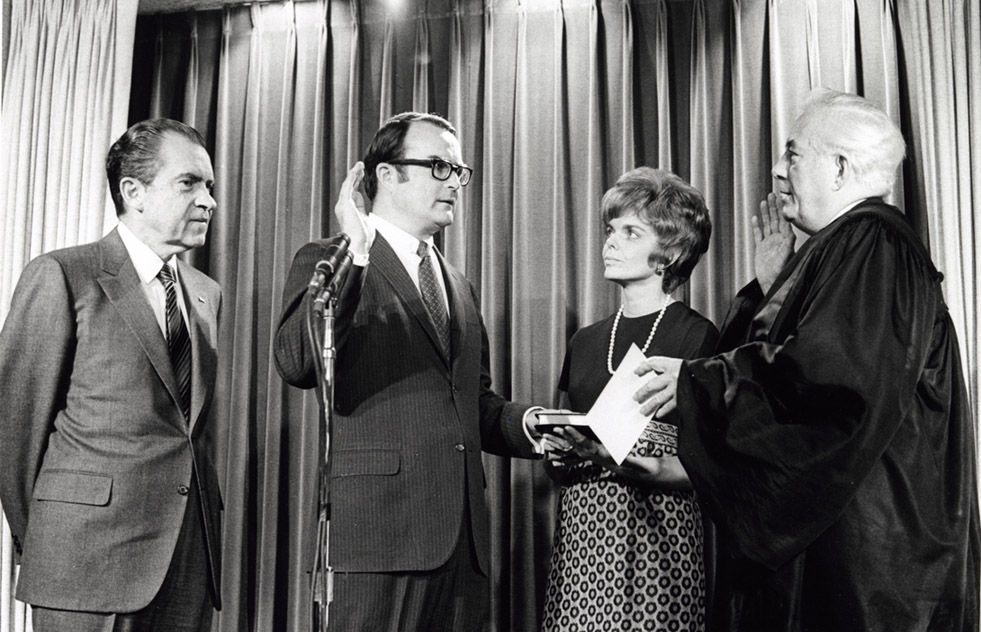
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it began operation on December 2, 1970, after Nixon signed an executive order. The order establishing the EPA was ratified by committee hearings in the House and Senate. The agency is led by its administrator, who is appointed by the president and approved by the Senate. The current administrator is Michael S. Regan. The EPA is not a Cabinet department, but the administrator is normally given cabinet rank. The EPA has its headquarters in Washington, D.C., regional offices for each of the agency's ten regions and 27 laboratories. The agency conducts environmental assessment, research, and education. It has the responsibility of maintaining and enforcing national standards under a variety of environmental laws, in consultation with state, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
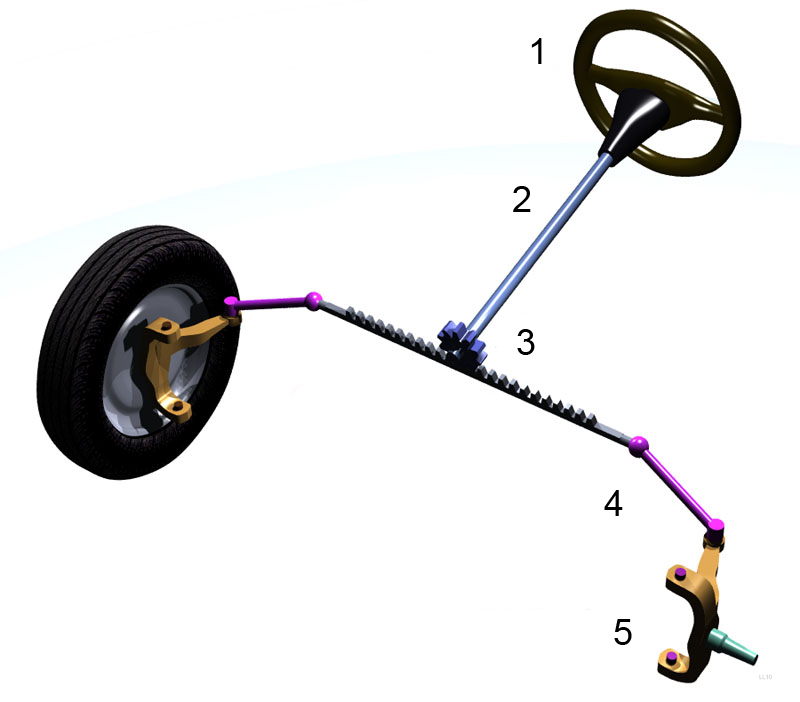
Steering Column
The automotive steering column is a device intended primarily for connecting the steering wheel to the steering mechanism. Secondary functions A steering column may also perform the following secondary functions: *energy dissipation management in the event of a frontal collision; *provide mounting for: the multi-function switch, column lock, column wiring, column shroud(s), transmission gear selector, gauges or other instruments as well as the electro motor and gear units found in EPAS and SbW systems; *offer (height and/or length) adjustment to suit driver preference Steering lock Modern vehicles are fitted with a steering lock which is an anti-theft device. It is fitted to the steering column usually below the steering wheel. The lock is combined with the ignition switch and engaged and disengaged either by a mechanical ignition key or electronically from the vehicles electronic control unit. These locks were introduced on many General Motors products in 1969 drastically re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a ''sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Bridge
A thermal bridge, also called a cold bridge, heat bridge, or thermal bypass, is an area or component of an object which has higher thermal conductivity than the surrounding materials, creating a path of least resistance for heat transfer.Gorse, Christopher A., and David Johnston (2012). "Thermal bridge", in ''Oxford Dictionary of Construction, Surveying, and Civil Engineering''. 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2012 pp. 440-441. Print. Thermal bridges result in an overall reduction in thermal resistance of the object. The term is frequently discussed in the context of a building's thermal envelope where thermal bridges result in heat transfer into or out of conditioned space. Thermal bridges in buildings may impact the amount of energy required to heat and cool a space, cause condensation (moisture) within the building envelope, and result in thermal discomfort. In colder climates (such as the United Kingdom), thermal heat bridges can result in additional heat losses and require addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
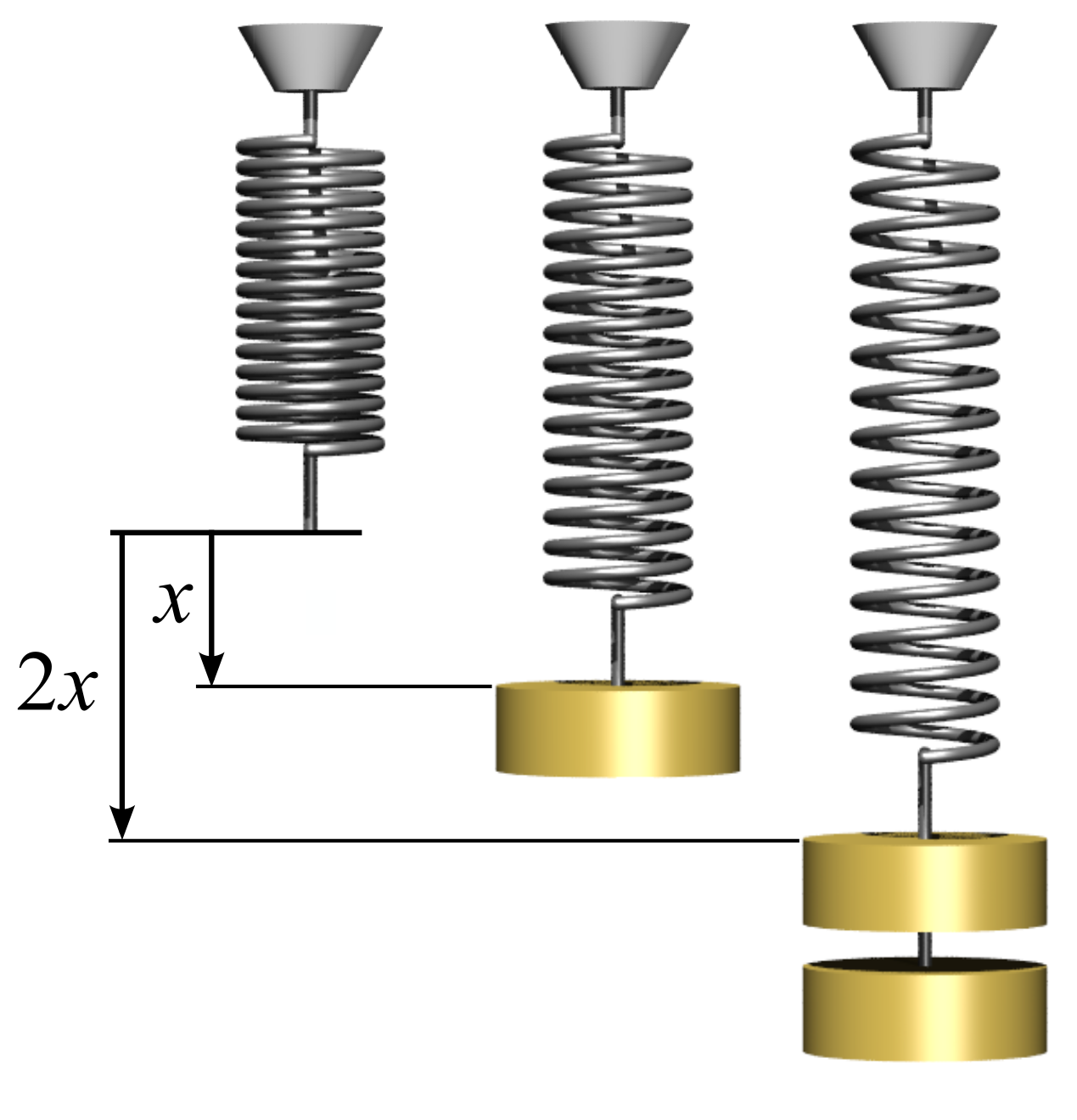
Spring Physics
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elastic body is deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string of a guitar. An elastic body or material for which this equation can be assumed is said to be linear-elastic or Hookean. Hooke's law is onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Press Fitting
An interference fit, also known as a pressed fit or friction fit is a form of fastening between two ''tight'' fitting mating parts that produces a joint which is held together by friction after the parts are pushed together. Depending on the amount of interference, parts may be joined using a tap from a hammer or ''pressed'' together using a hydraulic ram. Critical components that must not sustain damage during joining may also be cooled significantly below room temperature to shrink one of the components before fitting. This method allows the components to be joined without force and producing a shrink fit interference when the component returns to normal temperature. Interference fits are commonly used with aircraft fasteners to improve the fatigue life of a joint. Introducing interference between parts These fits, though applicable to shaft and hole assembly, are more often used for bearing-housing or bearing-shaft assembly. Tightness of fit The tightness of fit is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors or biological rotors. Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core, saving space and weight, and allowing a smaller air gap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shim (spacer)
A shim is a thin and often tapered or wedged piece of material, used to fill small gaps or spaces between objects. Shims are typically used in order to support, adjust for better fit, or provide a level surface. Shims may also be used as spacers to fill gaps between parts subject to wear. Materials Many materials make suitable shim stock (also often styled shimstock), or base material, depending on the context: wood, stone, plastic, metal, or even paper (e.g., when used under a table leg to level the table surface). High quality shim stock can be bought commercially, for example as laminated shims, but shims are often created ad hoc from whatever material is immediately available. Laminated shim stock is stacked foil that can be peeled off one layer at a time to adjust the thickness of the shim. Applications In automobiles, shims are commonly used to adjust the clearance or space between two parts. For example, shims are inserted into or under bucket tappets to cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |