|
Todgarh-Raoli Sanctuary
Todgarh Raoli Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary in Rajasthan, India. Spread over the Ajmer, Pali and Rajsamand districts of the state, it was established in 1983. It occupies about 495 km2 of tropical deciduous forests and grassland. Major wildlife includes leopard, wild boar, chinkara, common langur, sloth bears and Indian wolf. Also, about 143 bird species were recorded here in the 2013 survey. Nearest major town is Ajmer, which is 105 km away. Ajmer Junction Railway Station and Beawar Railway Station are the nearest railheads. Location The sanctuary is located pretty much in the middle of the Aravalli hill ranges, being based on the village of Todgarh, 25 km from Jassa Khera on NH-8 Delhi-Udaipur Highway. Dudhaleshwar Temple An ancient temple dedicated to Shiva, surrounded by tall trees of Karanj, Tamarind, and Banyan, attracts tourists. There is a perennial source of spring water in the temple. There is an ancient shivling and the water stream flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajsamand
Rajsamand is a city, located in Rajsamand district of Rajasthan, western India. The city is named for Rajsamand Lake, an artificial lake created in the 17th century by Rana Raj Singh of Mewar. It is the administrative headquarters of Rajsamand District. Geography Rajsamand is located at . It has an average elevation of 547 metres (1794 ft). Demographics Total population of the Rajsamand district is 987,024 (493,459 male and 493,565 female). This district has a male to female ratio of nearly 1:1. Rajsamand has an average literacy rate of 67%, male literacy is 77%, and female literacy is 57%. In Rajsamand, 15% of the population is under 6 years of age. Economy Although most of the economy of Rajasthan is based on agriculture, this part of the state is rich in mineral resources. The area is one of the prime Indian suppliers of marble, granite and other valuable varieties of stone. The Dariba,Sindesar khurd and Zawar mines are the principal Indian sources of ores for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siriyari
Siriyari is a small town situated in State of Rajasthan, District Pali. It is situated on State Highway 62 connecting Sojat, Sojat Road, Siriyari, Phulad, Jojawar. This village has a police station connected to nearby Police posts in villages. It is famous as death place of Acharya Bhikshu (1726–1803) who was the founder and first spiritual head of the Shwatambar Terapanth sect of Jainism. There is a famous temple on his name, which has been a new landmark. History Siriyari was granted to Khet Singh Solanki, by his father Sawant Singh Solanki of Desuri. Raja Sur Singh of Jodhpur married to Khet Singh's daughter Rani Manorath Kanwar on 18th February 1594. Khet Singh, his son Sanga Singh died fighting for Mewar, in battles against Mughals. Thakur Mahesh Das, son of Rao Kumpa of Marwar, was father of a son, Thakur Aas Karan, who was granted the estate of Digai in 1616. His eldest son, Thakur Amar Singh succeeded in Digai and won Siriyari from the Solanki Rajputs in a bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife Sanctuaries In Rajasthan
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted for sport. Wildlife can be found in all ecosystems. Deserts, plains, grasslands, woodlands, forests, and other areas, including the most developed urban areas, all have distinct forms of wildlife. While the term in popular culture usually refers to animals that are untouched by human factors, most scientists agree that much wildlife is affected by human activities. Some wildlife threaten human safety, health, property, and quality of life. However, many wild animals, even the dangerous ones, have value to human beings. This value might be economic, educational, or emotional in nature. Humans have historically tended to separate civilization from wildlife in a number of ways, including the legal, social, and moral senses. Some animals, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Sanctuaries
An animal sanctuary is a facility where animals are brought to live and to be protected for the rest of their lives. Pattrice Jones, co-founder of VINE Sanctuary defines an animal sanctuary as "a safe-enough place or relationship within the continuing hazards that menace everybody". In addition, sanctuaries are an experimental staging ground for transformative human–animal relations. There are five types of animal sanctuaries reflective of the species-belonging of the residents: 1) companion animal sanctuaries; 2) wildlife sanctuaries; 3) exotic animal sanctuaries; 4) farmed animal sanctuaries; and 5) cetacean sanctuaries. Unlike animal shelters, sanctuaries do not seek to place animals with individuals or groups, instead maintaining each animal until their natural death (either from disease or from other animals in the sanctuary). However, they can offer rehoming services. In some cases, an establishment may have characteristics of both a sanctuary and a shelter; for instance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals And Antiquities Of Rajasthan
Annals ( la, wikt:annales, annāles, from , "year") are a concise history, historical record in which events are arranged chronology, chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record. Scope The nature of the distinction between annals and history is a subject based on divisions established by the ancient Romans. Verrius Flaccus is quoted by Aulus Gellius as stating that the etymology of ''history'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek , , equated with Latin , "to inquire in person") properly restricts it to primary sources such as Thucydides's which have come from the author's own observations, while annals record the events of earlier times arranged according to years. Hayden White, White distinguishes annals from chronicles, which organize their events by topics such as the reigns of kings, and from histories, which aim to present and conclude a narrative implying the moral importance of the events recorded. Generally speaking, annalists recor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
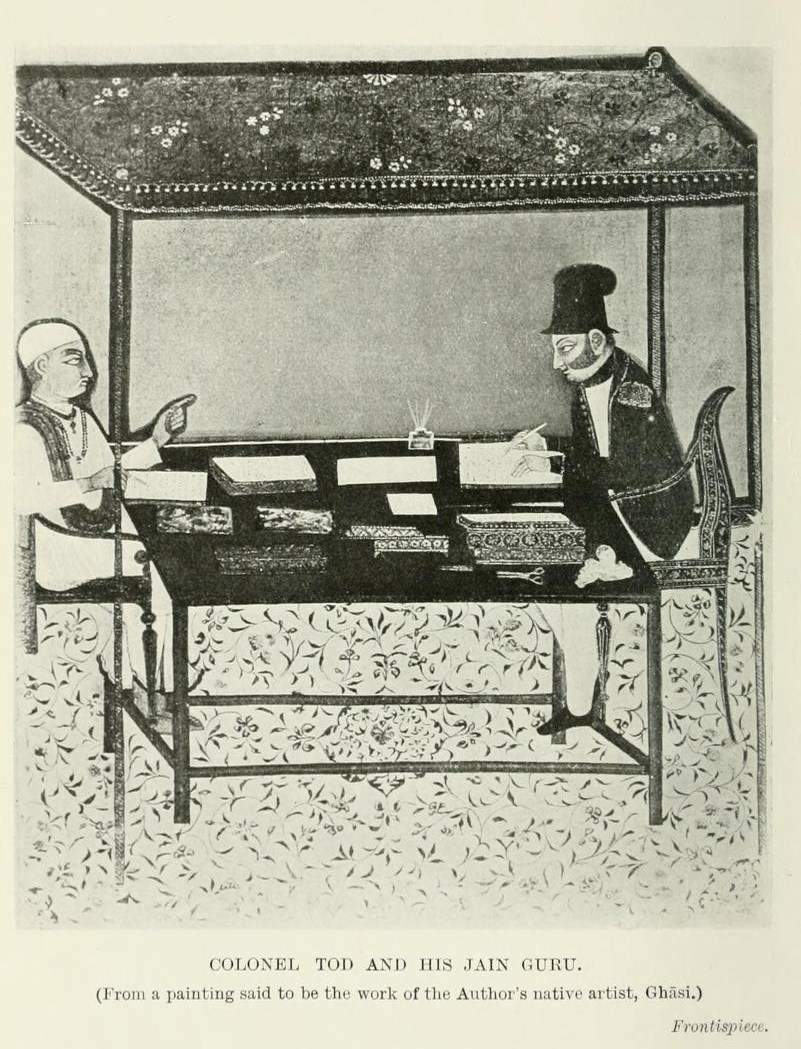
James Tod
Lieutenant-Colonel James Tod (20 March 1782 – 18 November 1835) was an officer of the British East India Company and an Oriental scholar. He combined his official role and his amateur interests to create a series of works about the history and geography of India, and in particular the area then known as Rajputana that corresponds to the present day state of Rajasthan, and which Tod referred to as ''Rajast'han''. Tod was born in London and educated in Scotland. He joined the East India Company as a military officer and travelled to India in 1799 as a cadet in the Bengal Army. He rose quickly in rank, eventually becoming captain of an escort for an envoy in a Sindian royal court. After the Third Anglo-Maratha War, during which Tod was involved in the intelligence department, he was appointed Political Agent for some areas of Rajputana. His task was to help unify the region under the control of the East India Company. During this period Tod conducted most of the resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in India. A strong personality and a successful general, Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent. His power and influence, however, extended over the entire subcontinent because of Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration throughout his empire and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his non-Muslim subjects. Eschewing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Army
The Army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 15th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century. Although its origins, like the Mughals themselves, were in the cavalry-based armies of central Asia, its essential form and structure was established by the empire's third emperor, Akbar. The army had no regimental structure and the soldiers were not directly recruited by the emperor. Instead, individuals, such as nobles or local leaders, would recruit their own troops, referred to as a ''mansab'', and contribute them to the army. Origin The Mughals originated in Central Asia. Like many Central Asian armies, the mughal army of Babur was horse-oriented. The ranks and pay of the officers were based on the horses they retained. Babur's army was small and inherited the Timurid military traditions of central Asia. It would be wrong to assume that Babur introduced a gunpowder warfare system, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
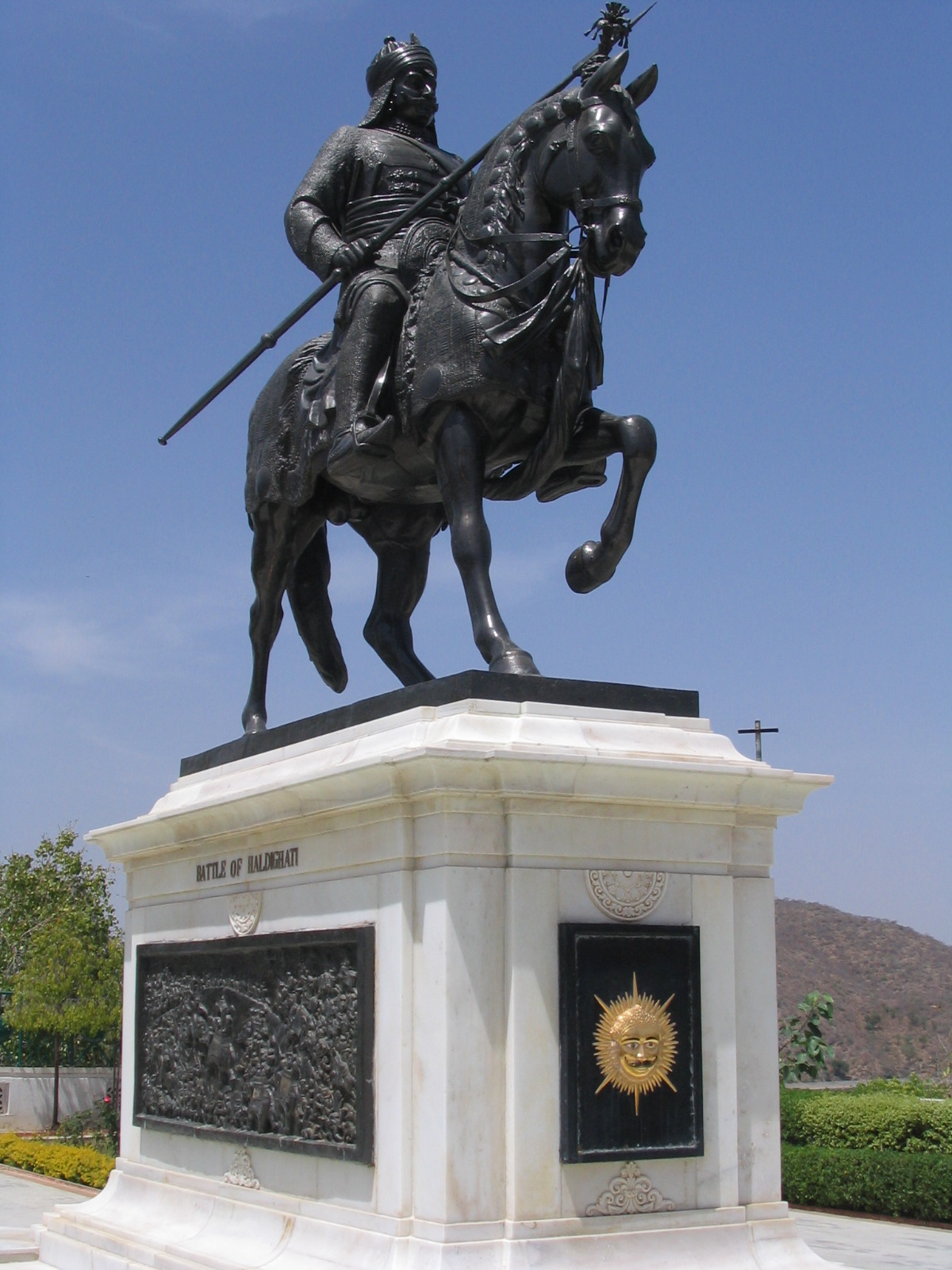
Maharana Pratap
Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap (c. 9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), was a king of Mewar from the Sisodia dynasty. Pratap became a folk hero for his military resistance against the expansionism of the Mughal Empire under Akbar through guerrilla warfare which proved inspirational for later rebels against Mughals including Shivaji. Early life and accession Maharana Pratap was born to Udai Singh II of Mewar and Jaiwanta Bai. His younger brothers were Shakti Singh, Vikram Singh and Jagmal Singh. Pratap also had 2 stepsisters: Chand Kanwar and Man Kanwar. He was married to Ajabde Punwar of Bijolia and he had married 10 other women and was survived by 17 sons and 5 daughters including Amar Singh I. He belonged to the Royal Family of Mewar. After the death of Udai Singh in 1572, Rani Dheer Bai wanted her son Jagmal to succeed him but senior courtiers preferred Pratap, as the eldest son, to be their king. The desire of the nobles prevailed. Udai Singh died in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewair
Dewair or Dawer is a village in Rajsamand district, Rajasthan, India. It has a population of 4480. It is located on National Highway 48 (India) (earlier designated National Highway 8), 40 km from Kumbhalgarh and 22 km from Deogarh. This is the site of the Battle of Dewair (1582) in which Maharana Pratap defeated Mughal forces of Akbar and reclaimed the land that he had lost in the Battle of Haldighati, and the Battle of Dewair (1606) in which Amar Singh I fought Mughal forces of Jahangir. On 10 January 2012, a victory memorial commemorating the victory of Maharana Pratap at Dewair was inaugurated by the President of India, Smt. Pratibha Patil Prathibha DeviSingh Patil (born 19 December 1934) is an Indian politician and lawyer who served as the 12th president of India spanning from 2007 to 2012. She is the first woman to become the president of India. A member of the Indian National .... Victory memorial Dewair Battle.jpg, Victory memorial in Dewair References V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nath
Nath, also called Natha, are a Shaiva sub-tradition within Hinduism in India and Nepal. A medieval movement, it combined ideas from Buddhism, Shaivism and Yoga traditions in India.Natha: Indian religious sect Encyclopedia Britannica (2007) The Naths have been a confederation of devotees who consider , as their first lord or , with varying lists of additional gurus. Of these, the 9th or 10th century |
Samadhi
''Samadhi'' (Pali and sa, समाधि), in Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism and yogic schools, is a state of meditative consciousness. In Buddhism, it is the last of the eight elements of the Noble Eightfold Path. In the Ashtanga Yoga tradition, it is the eighth and final limb identified in the ''Yoga Sutras'' of Patanjali. In the oldest Buddhist suttas, on which several contemporary western Theravada teachers rely, it refers to the development of an investigative and luminous mind which is equanimous and mindful. In the yogic traditions, and the Buddhist commentarial tradition on which the Burmese Vipassana movement and the Thai Forest tradition rely, it is interpreted as a meditative absorption or trance, attained by the practice of '' dhyāna''. Definitions ''Samadhi'' may refer to a broad range of states. A common understanding regards ''samadhi'' as meditative absorption: * Sarbacker: ''samādhi'' is meditative absorption or contemplation. * Diener, Erhard & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)