|
Tistrella
''Tistrella'' is a bacterial genus from the family of Rhodospirillaceae. ''Tistrella'' produces didemnin Didemnins are cyclic depsipeptide compounds isolated from a tunicate (ascidian, or sea-squirt) of the genus '' Trididemnum'' (family of Didemnidæ) that were collected in the Caribbean Sea. They were first isolated in 1978 at the University of ...s. References Further reading * * Rhodospirillales Bacteria genera {{Alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tistrella Mobilis
''Tistrella mobilis'' is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, rod-shaped and highly motile bacterium from the genus of ''Tistrella'' which has been isolated from wastewater in Thailand Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo .... ''Tistrella mobilis'' produces didemnins. References External linksType strain of ''Tistrella mobilis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase Rhodospirillales Bacteria described in 2003 {{Alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tistrella Bauzanensis
''Tistrella bauzanensis'' is a Gram-positive, strictly aerobic, rod-shaped and motile bacterium from the genus of ''Tistrella'' which has been isolated from soil from Bozen in Italy Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re .... ''Tistrella bauzanensis'' produces didemnin B. References Rhodospirillales Bacteria described in 2011 {{Alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geminicoccaceae
The ''Geminicoccaceae'' are a family of bacteria from the order Rhodospirillales The Rhodospirillales are an order of Pseudomonadota. Notable Families The ''Acetobacteraceae'' comprise the acetic acid bacteria, which are heterotrophic and produce acetic acid during their respiration.Garrity, George M.; Brenner, Don J.; Kr .... References Rhodospirillales Bacteria families {{Alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as ''Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', ''Vibrio'', ''Yersinia'', ''Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (nonparasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphaproteobacteria
Alphaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (formerly Proteobacteria). The Magnetococcales and Mariprofundales are considered basal or sister to the Alphaproteobacteria. The Alphaproteobacteria are highly diverse and possess few commonalities, but nevertheless share a common ancestor. Like all ''Proteobacteria'', its members are gram-negative and some of its intracellular parasitic members lack peptidoglycan and are consequently gram variable. Characteristics The Alphaproteobacteria are a diverse taxon and comprises several phototrophic genera, several genera metabolising C1-compounds (''e.g.'', ''Methylobacterium'' spp.), symbionts of plants (''e.g.'', ''Rhizobium'' spp.), endosymbionts of arthropods (''Wolbachia'') and intracellular pathogens (''e.g. Rickettsia''). Moreover, the class is sister to the protomitochondrion, the bacterium that was engulfed by the eukaryotic ancestor and gave rise to the mitochondria, which are organelles in eukaryotic ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodospirillales
The Rhodospirillales are an order of Pseudomonadota. Notable Families The ''Acetobacteraceae'' comprise the acetic acid bacteria, which are heterotrophic and produce acetic acid during their respiration.Garrity, George M.; Brenner, Don J.; Krieg, Noel R.; Staley, James T. (eds.) (2005). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume Two: The Proteobacteria, Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria. New York, New York: Springer. . The '' Rhodospirillaceae'' include mainly purple nonsulfur bacteria, which produce energy through photosynthesis. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy of prokaryotes, following the taxonomy requirements and rulings of the International Code of Nomenclature ... (LPSN). The phylogeny is based on whole-genome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodospirillaceae
The Rhodospirillaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota. The majority are purple nonsulfur bacteria, producing energy through photosynthesis; originally all purple nonsulfur bacteria were included here.George M. Garrity, Don J. Brenner, Noel R. Krieg, James T. Staley (Hrsg.): ''Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology''. Vol. 2: ''The Proteobacteria Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteabacteria''. 2. Auflage. Springer, New York 2005, Martin Dworkin, Stanley Falkow, Eugene Rosenberg, Karl-Heinz Schleifer, Erko Stackebrandt: The Prokaryotes, A Handbook of the Biology of Bacteria''. Volume 5: Proteobacteria: Alpha and Beta Subclasses'' They are often found in anaerobic aquatic environments, such as mud and stagnant water, although they are able to survive in air. This family also includes '' Magnetospirillum'', which contains tiny chains of magnetite. These let it sense the Earth's magnetic field, which runs downwards as well as north or south, to return to the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
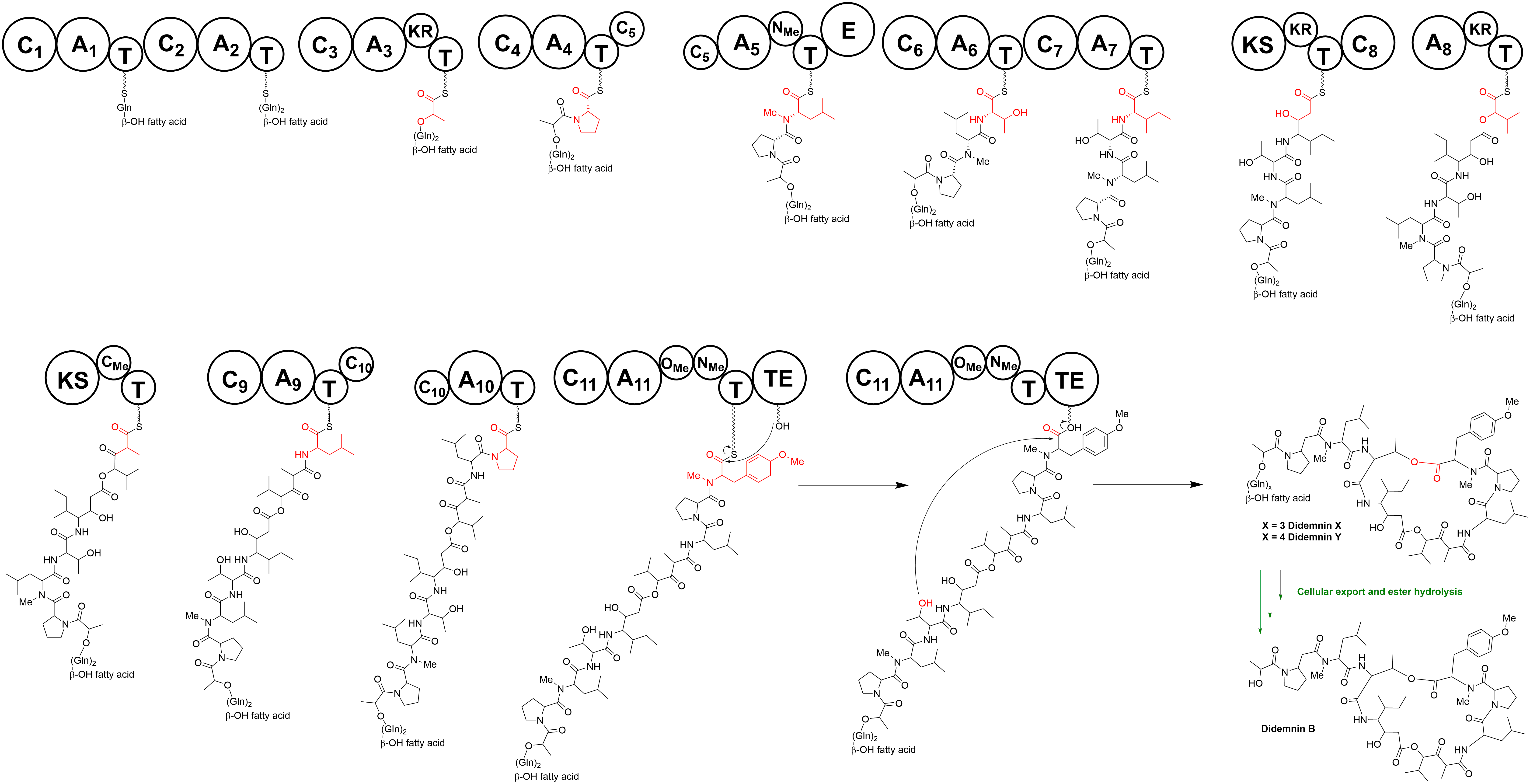
Didemnin
Didemnins are cyclic depsipeptide compounds isolated from a tunicate (ascidian, or sea-squirt) of the genus '' Trididemnum'' (family of Didemnidæ) that were collected in the Caribbean Sea. They were first isolated in 1978 at the University of Illinois. Although more than nine didemnins (didemnins A-E, G, X and Y) have been isolated from the extract of ''Trididemnum solidum'', didemnin B is the one that possesses the most potent biological activities. It is a strong antiviral agent against both DNA and RNA viruses such as herpes simplex virus type 1, a strong immunosuppressant that shows some potential in skin graft and is also very cytotoxic. It shows strong activity against murine leukemia cells. Large amounts of didemnin B were chemically synthesized and it was advanced to clinical trials by the National Cancer Institute. It has completed phase II human clinical trials against adenocarcinoma of the kidney, advanced epithelial ovarian cancer, and metastatic breast cancer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |