|
Thynias
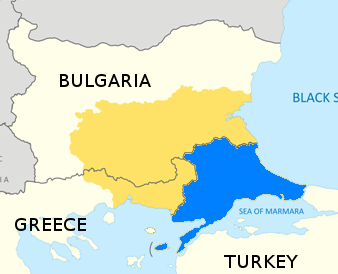
Thynias ( grc, Θυνίας) was a town of ancient Thrace on the coast of the Pontus Euxinus on a promontory of the same name (modern İğneada Burnu), mentioned by numerous ancient authors. It was located north of Salmydessus, which was probably at one time in the territories of the Thyni, although Strabo speaks of the district as belonging to the people of Apollonia. According to Pliny the Elder, the town was placed a little to the south of the promontory. Its site is located near İğneada in European Turkey East Thrace or Eastern Thrace ( tr, Doğu Trakya or simply ''Trakya''; el, Ανατολική Θράκη, ''Anatoliki Thraki''; bg, Източна Тракия, ''Iztochna Trakiya''), also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the pa .... References Populated places in ancient Thrace Former populated places in Turkey History of Kırklareli Province {{Kırklareli-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
İğneada Burnu
İğneada (Greek: Thynias) is a small town within the district of Demirköy in Turkey's Kırklareli Province. It lies on the Black Sea coast and is approximately south of the Mutludere river which forms the border with Bulgaria. Its population was 1,966 in 2010. The land is covered by mainly oak forests, typical flora of the Yıldız (Istranca) Mountains. Forestry, fishing and tourism are the main occupations of the town population. The İğneada Floodplain Forests National Park with its Lake Saka Nature Reserve Area is situated around the town. It harbors one of the few remaining floodplain forests in all of Europe, which is home to many different bird species. The second of Turkey's nuclear power plants is planned to be built in the area. A fourth revision environmental impact assessment Environmental Impact assessment (EIA) is the assessment of the environmental consequences of a plan, policy, program, or actual projects prior to the decision to move forward with the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
İğneada
İğneada (Greek: Thynias) is a small town within the district of Demirköy in Turkey's Kırklareli Province. It lies on the Black Sea coast and is approximately south of the Mutludere river which forms the border with Bulgaria. Its population was 1,966 in 2010. The land is covered by mainly oak forests, typical flora of the Yıldız (Istranca) Mountains. Forestry, fishing and tourism are the main occupations of the town population. The İğneada Floodplain Forests National Park with its Lake Saka Nature Reserve Area is situated around the town. It harbors one of the few remaining floodplain forests in all of Europe, which is home to many different bird species. The second of Turkey's nuclear power plants is planned to be built in the area. A fourth revision environmental impact assessment Environmental Impact assessment (EIA) is the assessment of the environmental consequences of a plan, policy, program, or actual projects prior to the decision to move forward with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Thrace
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area between northern Greece, southern Russia, and north-western Turkey. They shared the same language and culture... There may have been as many as a million Thracians, diveded among up to 40 tribes." Thracians resided mainly in the Balkans (mostly Present (time), modern day Bulgaria, Turkey and Greece) but were also located in Anatolia, Anatolia (Asia Minor) and other locations in Eastern Europe. The exact origin of Thracians is unknown, but it is believed that proto-Thracians descended from a purported mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers, arriving from the rest of Asia and Africa through the Asia Minor (Anatolia). The proto-Thracian culture developed int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontus Euxinus
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea covers (not including the Sea of Azov), has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end of the Balkan Mountains; and the Dobruja Plateau considerably farthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; ) was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period. ''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best source on the campaigns of Alexander the Great. Scholars have generally preferred Arrian to other extant primary sources; though this attitude is beginning to change in light of modern studies into Arrian's method. Arrian's life Arrian was born in Nicomedia (present-day İzmit), the provincial capital of Bithynia. Cassius Dio called him Flavius Arrianus Nicomediensis. In respect of his birth date, sources provide similar dates for his birth; within a few years prior to 90, 89, and 85–90 AD. The line of reasoning for dates belonging to 85–90 AD is from the fact of Arrian being made a consul around 130 AD, and the usual age for this, during this period, being forty-two years of age. (ref. pp. 312, & SYME 1958, ''same page''). Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periplus Ponti Euxini
The ''Periplus of the Euxine Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τοῦ Εὐξείνου Πόντου, ', modern Greek transliteration ', la, Periplus Ponti Euxini) is a periplus or guidebook detailing the destinations visitors encounter when traveling about the shore of the Black Sea. It was written by Arrian of Nicomedia from AD 130–131. Background It is in the form of a letter, from Arrian to the Emperor Hadrian in Rome, who was particularly attached to geographical research and had visited in person a large portion of his extensive dominions. It contains an accurate topographical survey of the coasts of the Euxine (Black Sea), from Trapezus to Byzantium, and was written probably while Arrian held his office of legate of Cappadocia, a short time before war broke out against the Alani; and it was doubtless at the same time that he drew up his instructions for the march of the Roman army against the barbarians, which are found in a short but imperfect fragment annexed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmydessus
Salmydessus or Salmydessos ( grc, Σαλμυδησσός), also Halmydessus or Halmydessos (Ἁλμυδισσός), was a coast-town of ancient Thrace, on the Euxine, about northwest of the entrance of the Bosporus. The eastern offshoots of the Haemus here come very close to the shore, which they divide from the valley of the Hebrus. The people of Salmydessus were thus cut off from communication with the less barbarous portions of Thrace, and became notorious for their savage and inhuman character, which harmonised well with that of their country, the coast of which was extremely dangerous. Aeschylus, who incorrectly places the town in Asia Minor, describes Salmydessus as "the rugged jaw of the sea, hostile to sailors, step-mother of ships;" and Xenophon informs us, that in his time its people carried on the business of wreckers in a very systematic manner, the coast being marked out into portions by means of posts erected along it, and those to whom each portion was assigned havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyni
The Thyni ( el, Θυνοί) were a Thracian tribe that lived in south-eastern Thrace. The Thyni were closely related to the Bithynians, with whom they often exchanged troops and royal marriages, later a section of the Thyni, along with the Bithyni, migrated to the area in Asia Minor that would later be known as and Bithynia, and where they would later be conquered by the Lydia Lydia ( Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish pro ...n and Persian empires. Each respective region (Thynia and Bithynia) got its name, presumably, from the Thracian tribe that was more prominent in the area. Xenophon (Anabasis VII, 2) praises the Thyni: "Teres, with a large army, was said to have had his baggage train taken from him by the natives, who are called Thyni and are supposed to be the most dangerous of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; el, Στράβων ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC 24 AD) was a Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian who lived in Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. Life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus (in present-day Turkey) in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics since at least the reign of Mithridates V. Strabo was related to Dorylaeus on his mother's side. Several other family members, including his paternal grandfather had served Mithridates VI during the Mithridatic Wars. As the war drew to a close, Strabo's grandfather had turned several Pontic fortress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Turkey
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace ( tr, Doğu Trakya or simply ''Trakya''; el, Ανατολική Θράκη, ''Anatoliki Thraki''; bg, Източна Тракия, ''Iztochna Trakiya''), also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically a part of Southeast Europe. It accounts for 3.4% of Turkey's land area but comprises 15% of its total population. The largest city of the region is Istanbul, which straddles the Bosporus between Europe and Asia. East Thrace is of historic importance as it is next to a major sea trade corridor and constitutes what remains of the once-vast Ottoman region of Rumelia. It is currently also of specific geostrategic importance because the sea corridor, which includes two narrow straits, provides access to the Mediterranean Sea from the Black Sea for the navies of five countries: Russia, Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, and Georgia. The region also serves as a future connector of existing Turkish, Bulgarian, and Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Thrace
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |