|
Thrifty Phenotype
Thrifty phenotype refers to the correlation between low birth weight of neonates and the increased risk of developing metabolic syndromes later in life, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Although early life undernutrition is thought to be the key driving factor to the hypothesis, other environmental factors have been explored for their role in susceptibility, such as physical inactivity. Genes may also play a role in susceptibility of these diseases, as they may make individuals predisposed to factors that lead to increased disease risk. Historical overview The term Thrifty Phenotype was first coined by Charles Nicholas Hales and David Barker in a study published in 1992. In their study, the authors reviewed the literature up to and addressed five central questions regarding role of different factors in type 2 diabetes on which they based their hypothesis. These questions included the following: # The role of beta cell deficiency in type 2 diabetes. # The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Nicholas Hales
Charles Nicholas "Nick" Hales (1935–2005) was an English physician, biochemist, diabetologist, pathologist, and professor of clinical biochemistry Biography After education at King Edward VI High School, Stafford, King Edward VI Grammar School, Stafford, C. Nicholas Hales matriculated in 1953 at Trinity College, Cambridge, graduating BA (Cantab.) in 1956. He studied medicine at University College Hospital Medical School, graduating Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery#United Kingdom, MB BChir in 1959. At University College Hospital he was a house physician under Max Rosenheim. Hales returned to the University of Cambridge for graduate study in biochemistry. He received in 1964 his PhD under the supervision of Philip Randle. From 1964 to 1970 he was lecturer in biochemistry at the University of Cambridge. During the 1960s he was elected a Fellow of Downing College, Cambridge, taught undergraduate classes, and held an appointment at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, where he trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
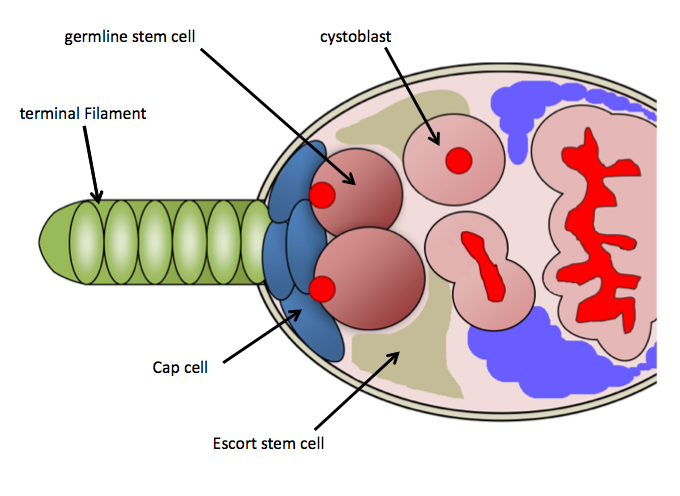
Niche Cell
Stem-cell niche refers to a microenvironment, within the specific anatomic location where stem cells are found, which interacts with stem cells to regulate cell fate. The word 'niche' can be in reference to the ''in vivo'' or ''in vitro'' stem-cell microenvironment. During embryonic development, various niche factors act on embryonic stem cells to alter gene expression, and induce their proliferation or differentiation for the development of the fetus. Within the human body, stem-cell niches maintain adult stem cells in a quiescent state, but after tissue injury, the surrounding micro-environment actively signals to stem cells to promote either self-renewal or differentiation to form new tissues. Several factors are important to regulate stem-cell characteristics within the niche: cell–cell interactions between stem cells, as well as interactions between stem cells and neighbouring differentiated cells, interactions between stem cells and adhesion molecules, extracellular matrix co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Nutrition And Birth Weight
Prenatal nutrition addresses nutrient recommendations before and during pregnancy. Nutrition and weight management before and during pregnancy has a profound effect on the development of infants. This is a rather critical time for healthy development since infants rely heavily on maternal stores and nutrient for optimal growth and health outcome later in life. Prenatal nutrition has a strong influence on birth weight and further development of the infant. There was a study at the National Institution of Health which found that babies born from an obese mother have a higher probability to fail tests of fine motor skills which is the movement of small muscles such as the hands and fingers. A common saying that a woman "is eating for two" while pregnant implies that a mother should consume twice as much during pregnancy, but is misleading. Although maternal consumption will directly affect both herself and the growing fetus, overeating excessively will compromise the baby's health a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrifty Gene Hypothesis
The thrifty gene hypothesis, or Gianfranco's hypothesis is an attempt by geneticist James V. Neel to explain why certain populations and subpopulations in the modern day are prone to diabetes mellitus type 2. He proposed the hypothesis in 1962 to resolve a fundamental problem: diabetes is clearly a very harmful medical condition, yet it is quite common, and it was already evident to Neel that it likely had a strong genetic basis. The problem is to understand how disease with a likely genetic component and with such negative effects may have been favoured by the process of natural selection. Neel suggested the resolution to this problem is that genes which predispose to diabetes (called 'thrifty genes') were historically advantageous, but they became detrimental in the modern world. In his words they were "rendered detrimental by 'progress'". Neel's primary interest was in diabetes, but the idea was soon expanded to encompass obesity as well. Thrifty genes are genes which enable indiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trivers–Willard Hypothesis
In evolutionary biology and evolutionary psychology, the Trivers–Willard hypothesis, formally proposed by Robert Trivers and Dan Willard in 1973, suggests that female mammals adjust the sex ratio of offspring in response to maternal condition, so as to maximize their reproductive success ( fitness). For example, it may predict greater parental investment in males by parents in "good conditions" and greater investment in females by parents in "poor conditions" (relative to parents in good conditions). The reasoning for this prediction is as follows: Assume that parents have information on the sex of their offspring and can influence their survival differentially. While selection pressures exist to maintain a sex ratio of 50, evolution will favor local deviations from this if one sex has a likely greater reproductive payoff than is usual. Trivers and Willard also identified a circumstance in which reproducing individuals might experience deviations from expected offspring reproduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
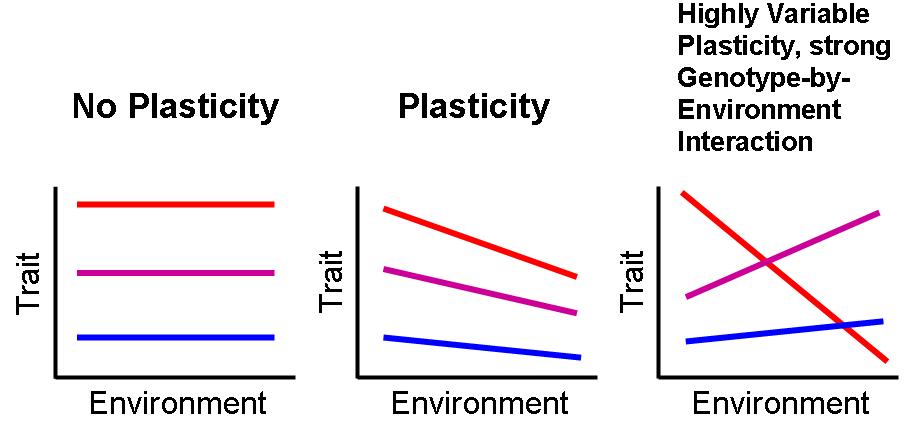
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Physiology
Evolutionary physiology is the study of the biological evolution of physiological structures and processes; that is, the manner in which the functional characteristics of individuals in a population of organisms have responded to natural selection across multiple generations during the history of the population. It is a sub-discipline of both physiology and evolutionary biology. Practitioners in the field come from a variety of backgrounds, including physiology, evolutionary biology, ecology, and genetics. Accordingly, the range of phenotypes studied by evolutionary physiologists is broad, including life history, behavior, whole-organism performance, functional morphology, biomechanics, anatomy, classical physiology, endocrinology, biochemistry, and molecular evolution. The field is closely related to comparative physiology and environmental physiology, and its findings are a major concern of evolutionary medicine. One definition that has been offered is "the study of the physio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Developmental Psychology
Evolutionary developmental psychology (EDP) is a research paradigm that applies the basic principles of evolution by natural selection, to understand the development of human behavior and cognition. It involves the study of both the genetic and environmental mechanisms that underlie the development of social and cognitive competencies, as well as the epigenetic ( gene-environment interactions) processes that adapt these competencies to local conditions. EDP considers both the reliably developing, species-typical features of ontogeny (developmental adaptations), as well as individual differences in behavior, from an evolutionary perspective. While evolutionary views tend to regard most individual differences as the result of either random genetic noise (evolutionary byproducts) and/or idiosyncrasies (for example, peer groups, education, neighborhoods, and chance encounters) rather than products of natural selection, EDP asserts that natural selection can favor the emergence of indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal Physiological Adaptations To Pregnancy
Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy are the adaptations that take place during pregnancy that enable the accommodation of the developing embryo and fetus. These are normal physiological adaptations that cause changes in behavior, the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, metabolism including increases in blood sugar levels, kidney function, posture, and breathing. During pregnancy numerous hormones and proteins are secreted that also have a broad range of effects. Hormonal Pregnant women experience numerous adjustments in their endocrine system that help support the developing fetus. The fetal-placental unit secretes steroid hormones and proteins that alter the function of various maternal endocrine glands. Sometimes, the changes in certain hormone levels and their effects on their target organs can lead to gestational diabetes and gestational hypertension. Fetal-placental unit Levels of progesterone and estrogen rise continually throughout pregnancy, sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive Tract
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical sex organs, organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of sexual differentiation, differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genes, genetic Fitness (biology), fitness of the offspring. Reproductive System 2001 Body Guide powered by Adam Animals In mammals, the major organs of the reproductive system include the external genitalia (penis and vulv ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placental Insufficiency
Placental insufficiency or utero-placental insufficiency is the failure of the placenta to deliver sufficient nutrients to the fetus during pregnancy, and is often a result of insufficient blood flow to the placenta. The term is also sometimes used to designate late decelerations of fetal heart rate as measured by cardiotocography or an NST, even if there is no other evidence of reduced blood flow to the placenta, normal uterine blood flow rate being 600mL/min. Causes The following characteristics of placentas have been said to be associated with placental insufficiency, however all of them occur in normal healthy placentas and full term healthy births, so none of them can be used to accurately diagnose placental insufficiency: * Abnormally thin placenta (less than 1 cm) * Circumvallate placenta (1% of normal placentas) * Amnion cell metaplasia, ( amnion nodosum) (present in 65% of normal placentas) * Increased syncytial knots * Calcifications * Infarcts due to focal or diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |