|
Three Books Of Occult Philosophy
''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' (''De Occulta Philosophia libri III'') is Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa's study of occult philosophy, acknowledged as a significant contribution to the Renaissance philosophical discussion concerning the powers of magic, and its relationship with religion. The first book was printed in 1531 in Paris, Cologne, and Antwerp, while the full three volumes first appeared in Cologne in 1533. The three books deal with elemental, celestial and intellectual magic. The books outline the four elements, astrology, Kabbalah, numerology, angels, names of God, the virtues and relationships with each other as well as methods of utilizing these relationships and laws in medicine, scrying, alchemy, ceremonial magic, origins of what are from the Hebrew, Greek and Chaldean context. These arguments were common amongst other hermetic philosophers at the time and before. In fact, Agrippa's interpretation of magic is similar to the authors Marsilio Ficino, Pico della ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phys M 6 Tb 1
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through Spacetime, space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental science, scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved throughout history as the main liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. Hebrew is the only Canaanite language still spoken today, and serves as the only truly successful example of a dead language that has been revived. It is also one of only two Northwest Semitic languages still in use, with the other being Aramaic. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' Lashon Hakodesh'' (, ) since an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library Of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The library is housed in three buildings on Capitol Hill in Washington, D.C.; it also maintains a conservation center in Culpeper, Virginia. The library's functions are overseen by the Librarian of Congress, and its buildings are maintained by the Architect of the Capitol. The Library of Congress is one of the largest libraries in the world. Its "collections are universal, not limited by subject, format, or national boundary, and include research materials from all parts of the world and in more than 470 languages." Congress moved to Washington, D.C., in 1800 after holding sessions for eleven years in the temporary national capitals in New York City and Philadelphia. In both cities, members of the U.S. Congress had access to the sizable collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
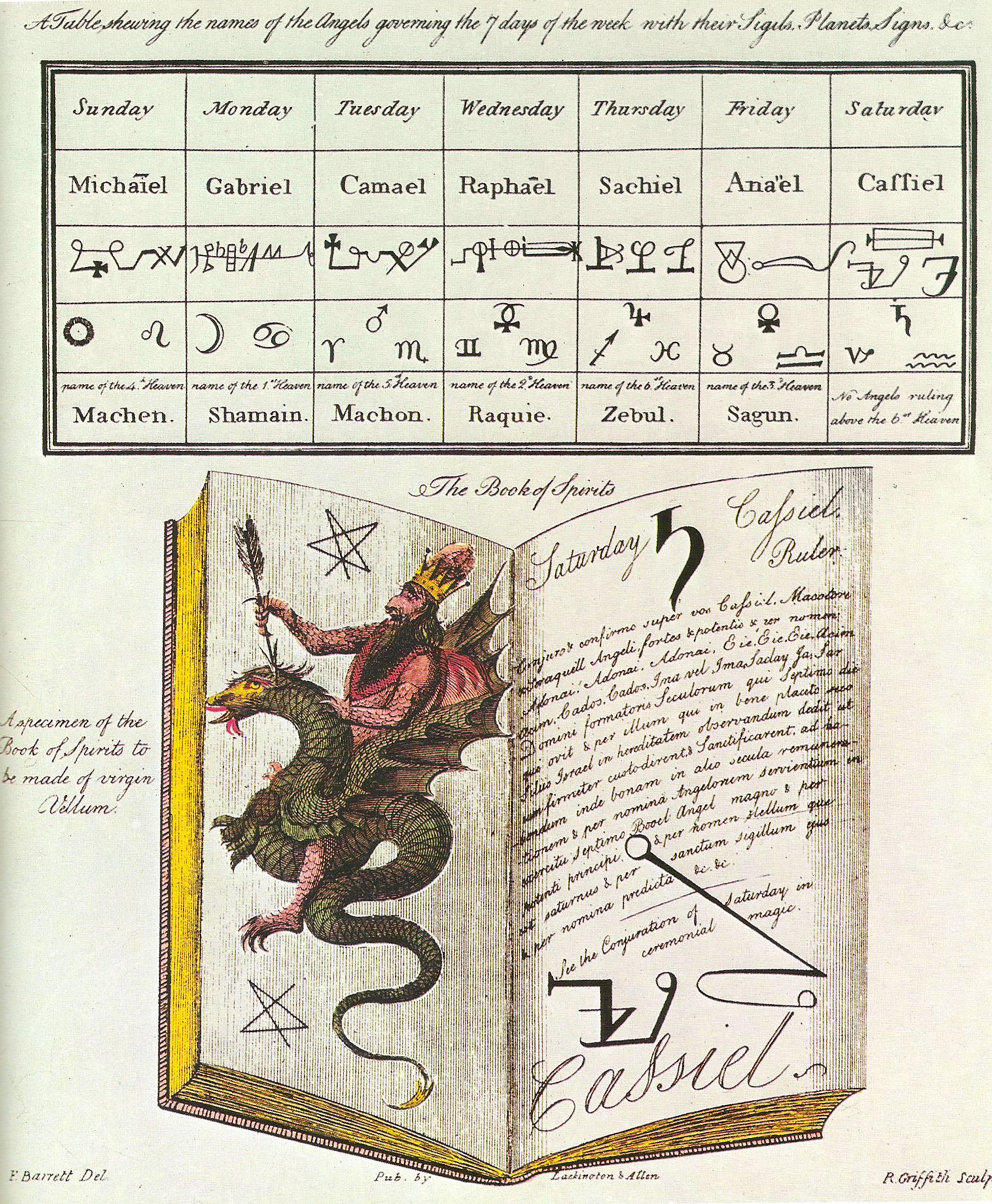
The Magus (Barrett Book)
''The Magus, or Celestial Intelligencer'' is a handbook of the occult and ceremonial magic compiled by occultist Francis Barrett published in 1801. Contents and Sources Much of the material was actually collected by Barrett from older occult handbooks, as he hints in the preface: We have collected out of the works of the most famous magicians, such as Zoroaster, Hermes, Apollonius, Simon of the Temple, Trithemius, Agrippa, Porta (the Neapolitan), Dee, Paracelsus, Roger Bacon, and a great many others... In fact, most of the material comes from Agrippa's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' and Pietro d'Abano's ''Heptameron''. Previous demonologists such as Binsfeld (1589) had drawn up lists that comprised a hierarchy of devils, and attributed them with the power to instigate people to commit the seven deadly sins. Lucifer was associated with Pride, Satan with Anger and so forth. In ''The Magus'' Barrett altered the "roster of devils" and Satan now became a prince of deluders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermetic Qabalah
Hermetic Qabalah () is a Western esoteric tradition involving mysticism and the occult. It is the underlying philosophy and framework for magical societies such as the Golden Dawn, Thelemic orders, mystical-religious societies such as the Builders of the Adytum and the Fellowship of the Rosy Cross, and is a precursor to the Neopagan, Wiccan and New Age movements. The Hermetic Qabalah is the basis for Qliphothic Qabala as studied by left-hand path orders, such as the Typhonian Order. Hermetic Qabalah arose alongside and united with the Christian Cabalistic involvement in the European Renaissance, becoming variously Esoteric Christian, non-Christian, or anti-Christian across its different schools in the modern era. It draws on a great many influences, most notably: Jewish Kabbalah, Western astrology, Alchemy, Pagan religions, especially Egyptian and Greco-Roman (it is from the latter that the term "Hermetic" is derived), neoplatonism, gnosticism, the Enochian system of ange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimoire
A grimoire ( ) (also known as a "book of spells" or a "spellbook") is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms and divination, and how to summon or invoke supernatural entities such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons.Davies (2009:1) In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers, although in many cultures, other sacred texts that are not grimoires (such as the Bible) have been believed to have supernatural properties intrinsically. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all ''books on magic'' could be thought of as grimoires, not all ''magical books'' should be thought of as grimoires. While the term ''grimoire'' is originally European—and many Europeans throughout hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Demons
There have been various attempts at the classification of demons within the contexts of classical mythology, demonology, occultism, and Renaissance magic. These classifications may be for purposes of traditional medicine, exorcisms, ceremonial magic, witch-hunts, lessons in morality, folklore, religious ritual, or combinations thereof. Classifications might be according to astrological connections, elemental forms, noble titles, or parallels to the angelic hierarchy; or by association with particular sins, diseases, and other calamities; or by what angel or saint opposes them. Many of the authors identified as Christian, though Christians authors are not the only ones who have written on the subject. Classification by domain The Testament of Solomon The ''Testament of Solomon'' is a pseudepigraphical work, purportedly written by King Solomon, in which the author mostly describes particular demons whom he enslaved to help build the temple, the questions he put to them abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim (; ; 14 September 1486 – 18 February 1535) was a German polymath, physician, legal scholar, soldier, theologian, and occult writer. Agrippa's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' published in 1533 drew heavily upon Kabbalah, Hermeticism, and neo-Platonism. His book was widely influential among occultists of the early modern period, and was condemned as heretical by the inquisitor of Cologne. Life Agrippa was born in Nettersheim, near Cologne on 14 September 1486 to a family of middle nobility.Valente, Michaela "Agrippa, Heinrich Cornelius". In: ''Dictionary of Gnosis and Western Esotericism'' (Wouter J. Hanegraaff, ed.), pp. 4–8. Brill, 2006. . Many members of his family had been in the service of the House of Habsburg. Agrippa studied at the University of Cologne from 1499 to 1502, (age 13–16) when he received the degree of ''magister artium''. The University of Cologne was one of the centers of Thomism, and the faculty of ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Reuchlin
Johann Reuchlin (; sometimes called Johannes; 29 January 1455 – 30 June 1522) was a German Catholic humanist and a scholar of Greek and Hebrew, whose work also took him to modern-day Austria, Switzerland, and Italy and France. Most of Reuchlin's career centered on advancing German knowledge of Greek and Hebrew. Early life Johann Reuchlin was born at Pforzheim in the Black Forest in 1455, where his father was an official of the Dominican monastery. According to the fashion of the time, his name was graecized by his Italian friends into Capnion (Καπνίων), a nickname which Reuchlin used as a sort of transparent mask when he introduced himself as an interlocutor in the ''De Verbo Mirifico''. He remained fond of his home town; he constantly calls himself Phorcensis, and in the ''De Verbo'' he ascribes to Pforzheim his inclination towards literature. Here he began his Latin studies in the monastery school, and, though in 1470 he was for a short time at Freiburg, that univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Pico Della Mirandola
Giovanni Pico della Mirandola (24 February 1463 – 17 November 1494) was an Italian Renaissance nobleman and philosopher. He is famed for the events of 1486, when, at the age of 23, he proposed to defend 900 theses on religion, philosophy, natural philosophy, and magic against all comers, for which he wrote the ''Oration on the Dignity of Man'', which has been called the "Manifesto of the Renaissance", and a key text of Renaissance humanism and of what has been called the "Hermetic Reformation". He was the founder of the tradition of Christian Kabbalah, a key tenet of early modern Western esotericism. The ''900 Theses'' was the first printed book to be universally banned by the Church.Hanegraaff p. 54 Pico is sometimes seen as a proto-Protestant, because his 900 theses anticipated many Protestant views. Biography Family Giovanni was born at Mirandola, near Modena, the youngest son of Gianfrancesco I Pico, Lord of Mirandola and Count of Concordia, by his wife Giulia, daugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsilio Ficino
Marsilio Ficino (; Latin name: ; 19 October 1433 – 1 October 1499) was an Italian scholar and Catholic priest who was one of the most influential humanist philosophers of the early Italian Renaissance. He was an astrologer, a reviver of Neoplatonism in touch with the major academics of his day, and the first translator of Plato's complete extant works into Latin. His Florentine Academy, an attempt to revive Plato's Academy, influenced the direction and tenor of the Italian Renaissance and the development of European philosophy. Early life Ficino was born at Figline Valdarno. His father, Diotifeci d'Agnolo, was a physician under the patronage of Cosimo de' Medici, who took the young man into his household and became the lifelong patron of Marsilio, who was made tutor to his grandson, Lorenzo de' Medici. Giovanni Pico della Mirandola, the Italian humanist philosopher and scholar was another of his students. Career and thought Platonic Academy During the sessions at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


_-_BEIC_6329210.jpg)
