|
Thor Peak (California)
Thor Peak is a mountain summit located east of the crest of the Sierra Nevada mountain range in Inyo County, California. It is situated in the John Muir Wilderness on land managed by Inyo National Forest. It is west of the community of Lone Pine, and east of Mount Whitney. Topographic relief is significant as it rises above Whitney Portal in 1.5 mile. Hikers on the Mount Whitney Trail pass below the impressive south face of the peak. Climate According to the Köppen climate classification system, Thor Peak has an alpine climate. Most weather fronts originate in the Pacific Ocean, and travel east toward the Sierra Nevada mountains. As fronts approach, they are forced upward by the peaks, causing them to drop their moisture in the form of rain or snowfall onto the range (orographic lift). Precipitation runoff from this mountain drains east to Owens Valley via Lone Pine Creek. Climbing The first ascent of the summit was made by Norman Clyde, date unknown. Established rock clim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Whitney
Mount Whitney (Paiute: Tumanguya; ''Too-man-i-goo-yah'') is the highest mountain in the contiguous United States and the Sierra Nevada, with an elevation of . It is in East–Central California, on the boundary between California's Inyo and Tulare counties, west-northwest of North America's lowest point, Badwater Basin in Death Valley National Park, at below sea level. The mountain's west slope is in Sequoia National Park and the summit is the southern terminus of the John Muir Trail, which runs from Happy Isles in Yosemite Valley. The eastern slopes are in Inyo National Forest in Inyo County. Geography Mount Whitney's summit is on the Sierra Crest and the Great Basin Divide. It lies near many of the Sierra Nevada's highest peaks. The peak rises dramatically above the Owens Valley, sitting or just over above the town of Lone Pine to the east, in the Owens Valley. It rises more gradually on the west side, lying only about above the John Muir Trail at Guitar Lake. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Northern California
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American 3000 M Summits
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can mean b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Inyo County, California
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountain Peaks Of California
This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaksThis article defines a significant summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence, and a major summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence. All summits in this article have at least 500 meters of topographic prominence. An ultra-prominent summit is a summit with at least of topographic prominence. of the U.S. State of California. The summit of a mountain or hill may be measured in three principal ways: #The topographic elevation of a summit measures the height of the summit above a geodetic sea level.All elevations in this article include an elevation adjustment from the National Geodetic Vertical Datum of 1929 (NGVD 29) to the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD 88). For further information, please see this United States National Geodetic Surveybr>noteIf the elevation or prominence of a summit is calculated as a range of values, the arithmetic mean is shown. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert K
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glen Dawson (mountaineer)
Glen Dawson (June 3, 1912 – March 22, 2016) was an American rock climber, mountaineer, antiquarian bookseller, publisher and environmentalist. Early life His father, Ernest Dawson (1882–1947), was also a climber, antiquarian bookseller, and Sierra Club leader, who served as Sierra Club president from 1934 - 1937. Glen climbed White Mountain Peak in 1927. In 1928, Glen and his father climbed the Matterhorn with two Swiss guides. Climbing career 1929–1930 In 1929, Dawson began serious mountaineering in the Sierra Nevada. With John Nixon and experienced climber Bill Horsfall, he climbed Mount Abbot, Mount Mills, Mount Hooper, Mount Humphreys, and the (later named) Clyde Minaret. On July 6, 1930, during the Sierra Club's annual High Trip, he first teamed up with Jules Eichorn to make the third ascent of Red-and-White Mountain in the Sierra. They continued at a fast pace to climb Mount Abbot, Bear Creek Spire, Mount Dade, Turret Peak, Mount Darwin, The Hermit, Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Ascent
In mountaineering, a first ascent (abbreviated to FA in guide books) is the first successful, documented attainment of the top of a mountain or the first to follow a particular climbing route. First mountain ascents are notable because they entail genuine exploration, with greater risks, challenges and recognition than climbing a route pioneered by others. The person who performs the first ascent is called the first ascensionist. In free climbing, a first ascent (or first free ascent, abbreviated FFA) of a climbing route is the first successful, documented climb of a route without using equipment such as anchors or ropes for aiding progression or resting. History The details of the first ascents of even many prominent mountains are scanty or unknown; sometimes the only evidence of prior summiting is a cairn, artifacts, or inscriptions at the top. Today, first ascents are generally carefully recorded and usually mentioned in guidebooks. The term is also used when referrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
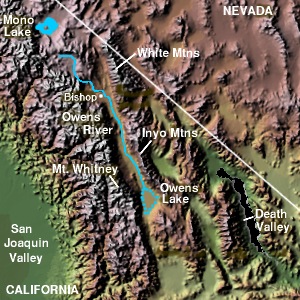
Owens Valley
Owens Valley (Numic Numic is a branch of the Uto-Aztecan language family. It includes seven languages spoken by Native American peoples traditionally living in the Great Basin, Colorado River basin, Snake River basin, and southern Great Plains. The word Numic com ...: ''Payahǖǖnadǖ'', meaning "place of flowing water") is an arid valley of the Owens River in eastern California in the United States. It is located to the east of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada, west of the White Mountains (California), White Mountains and Inyo Mountains, and north of the Mojave Desert. It sits on the west edge of the Great Basin section, Great Basin. The mountain peaks on the West side (including Mount Whitney) reach above in elevation, while the floor of the Owens Valley is about , making the valley the deepest in the United States. The Sierra Nevada casts the valley in a rain shadow, which makes Owens Valley "the Land of Little Rain." The bed of Owens Lake, now a predominantly dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow) is the flow of water occurring on the ground surface when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when the soil is saturated by water to its full capacity, and the rain arrives more quickly than the soil can absorb it. Surface runoff often occurs because impervious areas (such as roofs and pavement) do not allow water to soak into the ground. Furthermore, runoff can occur either through natural or man-made processes. Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent of soil erosion by water. The land area producing runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. Runoff that occurs on the ground surface before reaching a channel can be a nonpoint source of pollution, as it can carry man-made contaminants or natural forms of pollution (such as rotting leaves). Man-made contaminants in runoff i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orographic Lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions, precipitation. Orographic lifting can have a number of effects, including precipitation, rain shadowing, leeward winds, and associated clouds. Precipitation Precipitation induced by orographic lift occurs in many places throughout the world. Examples include: * The Mogollon Rim in central Arizona * The western slope of the Sierra Nevada range in California * The mountains near Baja California North – specifically La Bocana to Laguna Hanson. * The windward slopes of Khasi and Jayantia Hills (see Mawsynram) in the state of Meghalaya in India. * The Western Highlands of Yemen, which receive by far the most rain in Arabia. * The Western Ghats that run along India's western coast. * The Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_11.jpg)