|
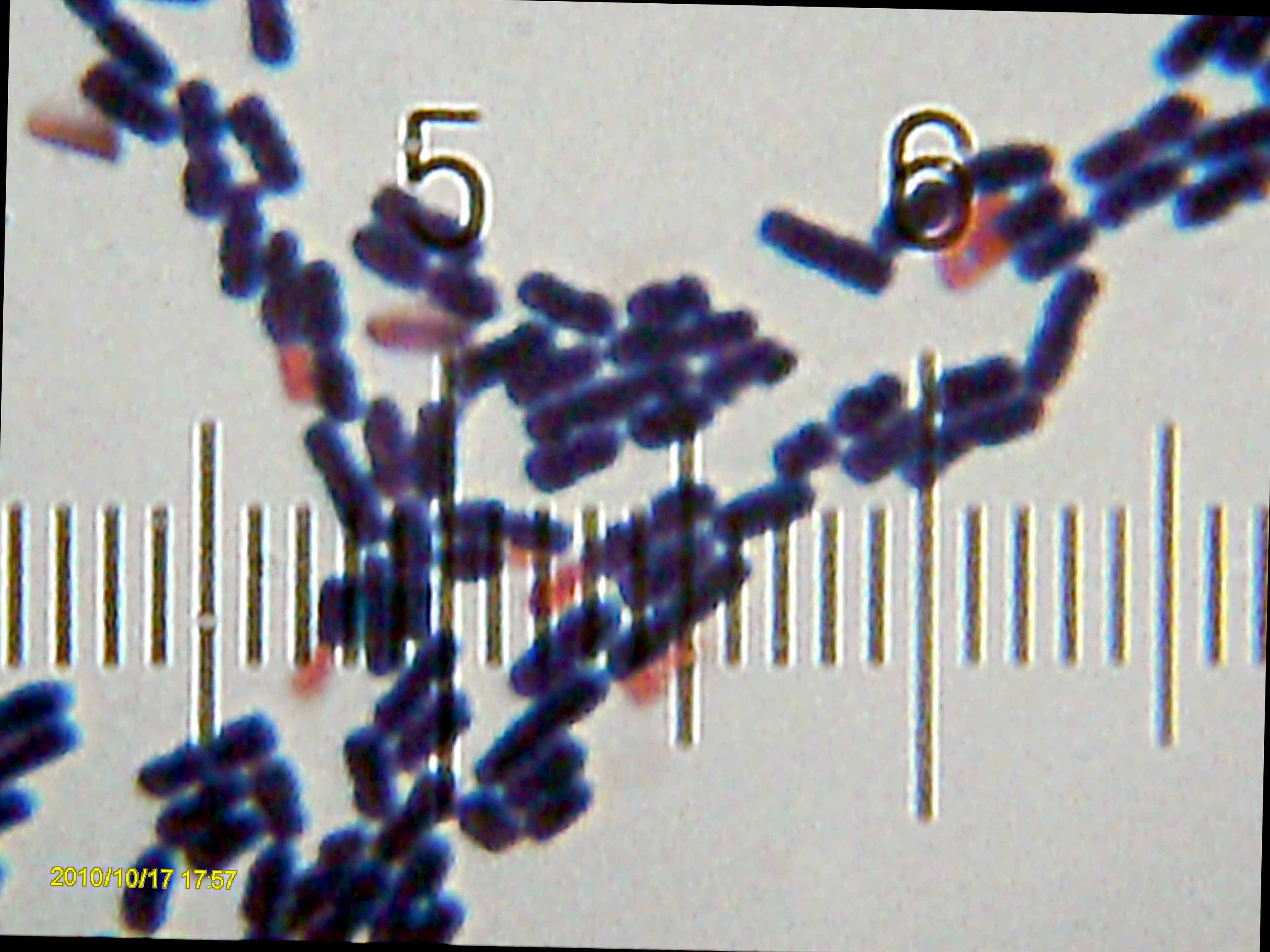
Thioalkalivibrio Denitrificans
''Thioalkalivibrio denitrificancs'' is an obligately alkaliphilic and obligately chemolithoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. It was first isolated from soda lakes in northern Russia. References Further reading *Robb, Frank, et al., eds. Thermophiles: biology and technology at high temperatures. CRC Press, 2007. * * *Shivaji, Sisinthy, et al. "Vertical distribution of bacteria in a lake sediment from Antarctica by culture-independent and culture-dependent approaches."Research in microbiology 162.2 (2011): 191–203. External linksLPSN Chromatiales {{Chromatiales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria) is a major phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. The renaming of phyla in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The phylum Proteobacteria includes a wide variety of pathogenic genera, such as ''Escherichia'', '' Salmonella'', ''Vibrio'', ''Yersinia'', ''Legionella'', and many others.Slonczewski JL, Foster JW, Foster E. Microbiology: An Evolving Science 5th Ed. WW Norton & Company; 2020. Others are free-living (nonparasitic) and include many of the bacteria responsible for nitrogen fixation. Carl Woese established this grouping in 1987, calling it informally the "purple bacteria and their relatives". Because of the great diversity of forms found in this group, it was later informally named Proteobacteria, after Proteus, a Greek god of the sea capable of assuming many different shapes (not after the Proteobacteria genus ''Proteus''). In 2021 the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gammaproteobacteria
Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota (synonym Proteobacteria). It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genera-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. It is composed by all Gram-negative microbes and is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of Proteobacteria. These microorganisms can live in several terrestrial and marine environments, in which they play various important roles, including ''extreme environments'' such as hydrothermal vents. They generally have different shapes - rods, curved rods, cocci, spirilla, and filaments and include free living bacteria, biofilm formers, commensals and symbionts, some also have the distinctive trait of being bioluminescent. Metabolisms found in the different genera are very different; there are both aerobic and anaerobic (obligate or facultative) species, chemolithoautotrophic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectothiorhodospiraceae
The Ectothiorhodospiraceae are a family of purple sulfur bacteria, distinguished by producing sulfur globules outside of their cells.George M. Garrity: ''Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology''. 2. Auflage. Springer, New York, 2005, Volume 2: ''The Proteobacteria, Part B: The Gammaproteobacteria'' The cells are rod-shaped, vibrioid, or spirilla, and they are able to move using flagella A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have f .... In general, they are marine and prefer anaerobic conditions. Ectothiorhodospiraceae are a vibrio bacteria that require salty living conditions to survive and grow: classifying them as slightly halophilic. Like all purple sulfur bacteria, they are capable of photosynthesis. To complete this energy process, Sulfur compounds are used as electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioalkalivibrio
''Thioalkalivibrio'' is a Gram-negative, mostly halophilic bacterial genus of the family Ectothiorhodospiraceae. Occurrence In the last decade, several species of ''Thioalkalivibrio'' have been discovered, but these chemolithoautotrophic, haloalkaliphilic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria had only been found in soda lakes in alkaline and saline habitats. However, Sorokin and colleagues in 2012 isolated and grew out a novel ''Thioalkalivibrio sulfidiphilus, strain HL-EbGr7T,'' from a full-scale wastewater bioreactor after the hydrogen sulfide gas had been removed/ Structure The ''Thioalkalivibrio sulfidiphilus strain HL-EbGr7T'' cells is long, slender, slightly curved, rod-shaped bacteria with a polar flagellum for motility. It has a gram-negative cell wall and the colonies are up to 2 mm in diameter. Genetics ''Thioalkalivibrio sulfidiphilus strain HL-EbGr7T'' is closely related to ''Thioalkalivibrio denitrificans'' within the Gammaproteobacteria based on 16S rRNA gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaliphilic
Alkaliphiles are a class of extremophilic microbes capable of survival in alkaline ( pH roughly 8.5–11) environments, growing optimally around a pH of 10. These bacteria can be further categorized as obligate alkaliphiles (those that require high pH to survive), facultative alkaliphiles (those able to survive in high pH, but also grow under normal conditions) and haloalkaliphiles (those that require high salt content to survive).HORIKOSHI, KOKI. "Alkaliphiles: Some Applications of Their Products for Biotechnology." MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS 63.4 (1999): 735-50. Print. Background information Microbial growth in alkaline conditions presents several complications to normal biochemical activity and reproduction, as high pH is detrimental to normal cellular processes. For example, alkalinity can lead to denaturation of DNA, instability of the plasma membrane and inactivation of cytosolic enzymes, as well as other unfavorable physiological changes.Higashibata, Akira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemolithoautotrophic
A lithoautotroph is an organism which derives energy from reactions of reduced compounds of mineral (inorganic) origin. Two types of lithoautotrophs are distinguished by their energy source; photolithoautotrophs derive their energy from light while chemolithoautotrophs (chemolithotrophs or chemoautotrophs) derive their energy from chemical reactions. Chemolithoautotrophs are exclusively microbes. Photolithoautotrophs include macroflora such as plants; these do not possess the ability to use mineral sources of reduced compounds for energy. Most chemolithoautotrophs belong to the domain Bacteria, while some belong to the domain Archaea. Lithoautotrophic bacteria can only use inorganic molecules as substrates in their energy-releasing reactions. The term "lithotroph" is from Greek ''lithos'' (''λίθος'') meaning "rock" and ''trōphos'' (τροφοσ) meaning "consumer"; literally, it may be read "eaters of rock". The "lithotroph" part of the name refers to the fact that these org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soda Lake
A soda lake or alkaline lake is a lake on the strongly alkaline side of neutrality, typically with a pH value between 9 and 12. They are characterized by high concentrations of carbonate salts, typically sodium carbonate (and related salt complexes), giving rise to their alkalinity. In addition, many soda lakes also contain high concentrations of sodium chloride and other dissolved salts, making them saline or hypersaline lakes as well. High pH and salinity often coincide, because of how soda lakes develop. The resulting hypersaline and highly alkalic soda lakes are considered some of the most extreme aquatic environments on Earth.Grant, W. D. (2006). ''Alkaline environments and biodiversity.'' in ''Extremophiles'', 2006, UNESCO / Eolss Publishers, Oxford, UK In spite of their apparent inhospitability, soda lakes are often highly productive ecosystems, compared to their (pH-neutral) freshwater counterparts. Gross primary production (photosynthesis) rates above (grams of carbon p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |