|
Theileria Electrophori
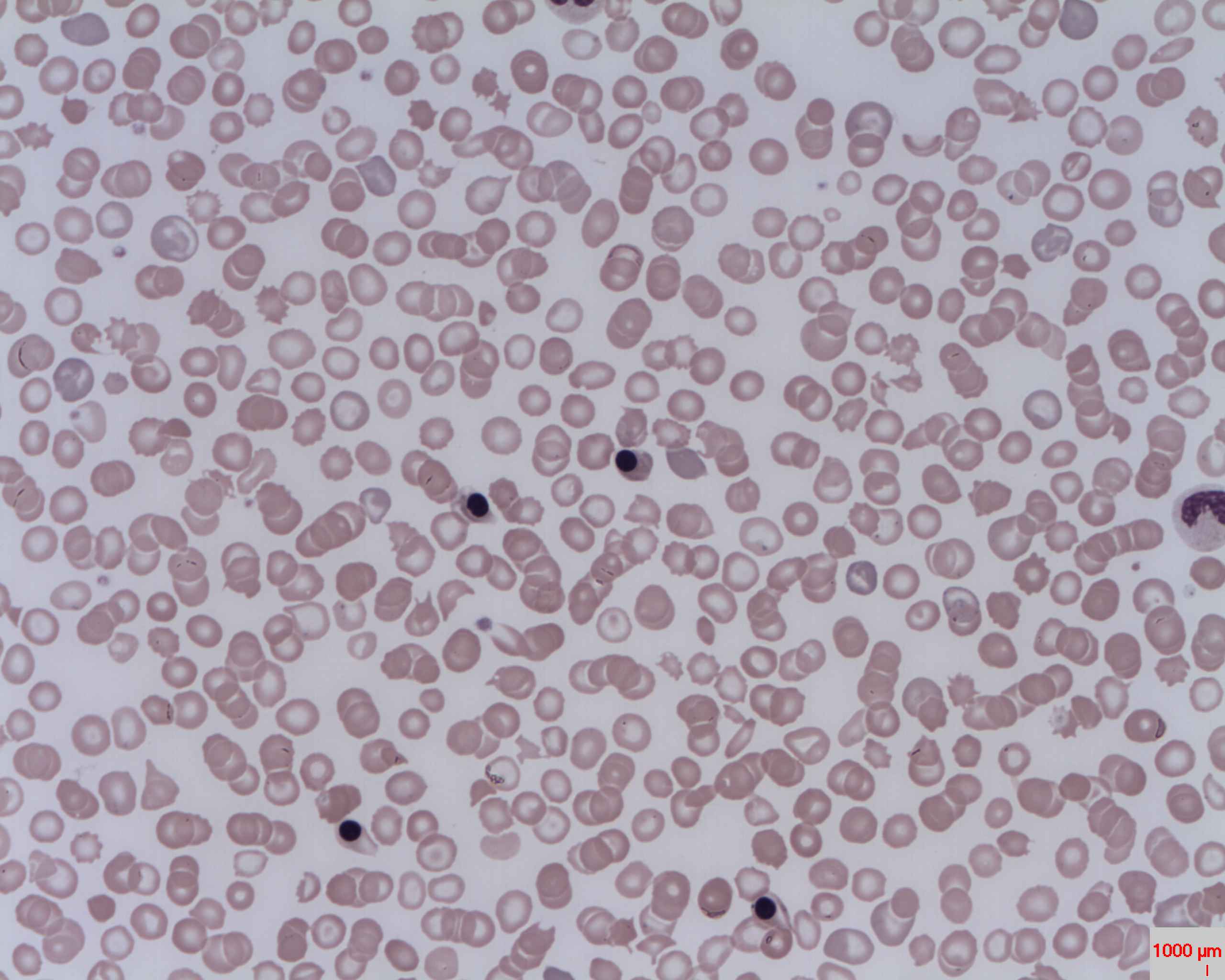
''Theileria'' is a genus of parasites that belongs to the phylum Apicomplexa, and is closely related to ''Plasmodium''. Two ''Theileria'' species, ''T. annulata'' and ''T. parva'', are important cattle parasites. ''T. annulata'' causes tropical theileriosis and ''T. parva'' causes East Coast fever. ''Theileria'' species are transmitted by ticks. The genomes of ''T. orientalis'' Shintoku'', Theileria equi'' WA, ''Theileria annulata'' Ankara and ''Theileria parva'' Muguga have been sequenced and published. ''Theileria equi'' is a known cause of equine piroplasmosis. Vaccines against ''Theileria'' are in development. In May 2010, a vaccine that was reported to protect cattle against East Coast fever had been approved and registered by the governments of Kenya, Malawi, and Tanzania. Description Species in this genus undergo exoerythrocytic merogony in the lymphocytes, histiocytes, erythroblasts, and other cells of the internal organs. This is followed by invasion of the erythrocyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theileria Parva
''Theileria parva'' is a species of parasites, named in honour of Arnold Theiler, that causes East Coast fever (theileriosis) in cattle, a costly disease in Africa. The main vector for ''T. parva'' is the tick ''Rhipicephalus appendiculatus''. Theiler found that East Coast fever was not the same as redwater, but caused by a different protozoan. Life cycle Sporozoites from the tick secrete into the feeding site of the animal. Sporozoites enter lymphoblasts to form a schizont. There is a clonal expansion of schizonts and then multiply by merging to form merozoites. The merozoites go into erythrocytes and invade the cells and are now in the piroplasm stage. When a tick ingests the piroplasms, the parasites undergo syngamy in the gut and can move to hemolymph. The motile kinetes can infect the salivary glands. From this, sporogony occurs to create sporozoites to continue the life cycle. In definitive host In the cattle host ''T. parva'' is an intracellular parasite. Hullinger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythroblast
A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of these red blood cells are nucleated. In mammals, NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells. NRBCs are normally found in the bone marrow of humans of all ages and in the blood of fetuses and newborn infants. After infancy, RBCs normally contain a nucleus only during the very early stages of the cell's life, and the nucleus is ejected as a normal part of cellular differentiation before the cell is released into the bloodstream. Thus, if NRBCs are identified on an adult's complete blood count or peripheral blood smear, it suggests that there is a very high demand for the bone marrow to produce RBCs, and immature RBCs are being released i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran
Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran (18 June 1845 – 18 May 1922) was a French physician who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1907 for his discoveries of parasitic protozoans as causative agents of infectious diseases such as malaria and trypanosomiasis. Following his father, Louis Théodore Laveran, he took up military medicine as his profession. He obtained his medical degree from University of Strasbourg in 1867. At the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War in 1870, he joined the French Army. At the age of 29 he became Chair of Military Diseases and Epidemics at the École de Val-de-Grâce. At the end of his tenure in 1878 he worked in Algeria, where he made his major achievements. He discovered that the protozoan parasite ''Plasmodium'' was responsible for malaria, and that ''Trypanosoma'' caused trypanosomiasis or African sleeping sickness. In 1894 he returned to France to serve in various military health services. In 1896 he joined Pasteur Institute as Chief of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Theileriosis
Tropical theileriosis or Mediterranean theileriosis is a theileriosis of cattle from the Mediterranean and Middle East area, from Morocco to Western parts of India and China. It is a tick-borne disease, caused by ''Theileria annulata''. The vectors are ticks of the genera '' Hyalomma'' and '' Rhipicephalus''. The most prominent symptoms are fever and lymph node enlargement. But there is a wide range of clinical manifestations, especially in enzootic areas. Among them, the Doukkala area of Morocco, where the epidemiology and symptomatology of the disease were minutely studied. AGRIS iFR2002001447 The disease was once considered as "benign" in the literature, in comparison to East Coast fever. With the introduction of European breeds into the region, however, it could become of major economic incidence.With mortalities up to 50 to 80 percent in the 1980sL. Mahin. An efficient treatment with parvaquone, then buparvaquone became available in many countries from the mid-1990s. Ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Theiler
Sir Arnold Theiler KCMG (26 March 1867 – 24 July 1936) Pour le Mérite is considered to be the father of veterinary science in South Africa. He was born in Frick, Canton Aargau, Switzerland. He received his higher education, and later qualified as a veterinarian, in Zurich. In 1891 Theiler travelled to South Africa and at first found employment as a farm worker on Irene Estates near Pretoria, owned by Nellmapius, but later that year started practising as a veterinarian. His success at producing a vaccine to combat an outbreak of smallpox among the miners of the Witwatersrand brought him an appointment as state veterinarian for the Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek, in which capacity he served during the Anglo-Boer War of 1899-1902. During this period his research team developed a vaccine against rinderpest, a malignant and contagious disease of cattle. His tremendous energy, pioneering spirit and professional integrity brought him international recognition. He described in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gertrud Theiler
Gertrud Theiler (11 September 1897 – 2 May 1986) was a South African parasitologist and teacher most noted for her work with nematodes and ticks. Early life Born on 11 September 1897 in Pretoria, South Africa, Theiler graduated from Pretoria Girls' High School and spent a year at Rhodes University College in Grahamstown, South Africa, before transferring to South African College in Cape Town, where she graduated in 1918 with a Bachelor of Science degree. She went to Europe to undertake postgraduate work in helminthology at the University of Neuchâtel, Switzerland, where she took her Doctor of Science degree in 1923. The subject of her doctoral thesis is . She then studied at the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, and the London School of Tropical Medicine, authoring four important scientific papers on research concerning the nematode parasites of South African equines. Teaching and research career She returned to South Africa in 1924 and taught biology for 17 years, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The process, which takes place in the front part of the digestive system and therefore is called foregut fermentation, typically requires the fermented ingesta (known as cud) to be regurgitated and chewed again. The process of rechewing the cud to further break down plant matter and stimulate digestion is called rumination. The word "ruminant" comes from the Latin ''ruminare'', which means "to chew over again". The roughly 200 species of ruminants include both domestic and wild species. Ruminating mammals include cattle, all domesticated and wild bovines, goats, sheep, giraffes, deer, gazelles, and antelopes.Fowler, M.E. (2010).Medicine and Surgery of Camelids, Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 General Biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EuPathDB
The Eukaryotic Pathgen Database, or EuPathDB, is a database of bioinformatic and experimental data related to a variety of eukaryotic pathogens. It was established in 2006 under a National Institutes of Health program to create Bioinformatics Resource Centers to facilitate research on pathogens that may pose biodefense threats. EuPathDB stores data related to its organisms of interest and provides tools for searching through and analyzing the data. It currently consists of 14 component databases, each dedicated to a certain research topic. EuPathDB includes: * Genomics resources covering eukaryotic protozoan parasites * Host responses to parasite infection (HostDB) * Orthologs (OrthoMCL) * Clinical study data (ClinEpiDB) * Microbiome data (MicrobiomeDB) History EuPathDB was established under the NIH Bioinformatics Resource Centers program as ApiDB, a resource meant to cover Apicomplexan parasites. ApiDB originally consisted of component sites CryptoDB (for ''Cryptosporidium''), Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiVet
WikiVet is a wiki of veterinary content based on the MediaWiki platform. The website is a collaborative initiative between various veterinary schools, and its content covers the entire veterinary curriculum. WikiVet is part of the WikiVet Educational Foundation (UK registered charity number 1160546). Full access to WikiVet requires a free registration, which is available to veterinarians, veterinary students and veterinary technicians. Except for content relating specifically to the veterinary curriculum, articles are authored by students or veterinarians, and subsequently peer reviewed by subject specialists. History WikiVet was established in 2007 to provide online access to a comprehensive veterinary undergraduate curriculum. The consortium was initially formed by three UK veterinary schools, London's Royal Veterinary College, the University of Edinburgh's Royal (Dick) School of Veterinary Studies, and the University of Cambridge's Department of Veterinary Medicine, and was su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemaphysalis
''Haemaphysalis'' is a genus of ticks, containing these species: *'' Haemaphysalis aborensis'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis aciculifer'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis aculeata'' Lavarra, 1904 *'' Haemaphysalis adleri'' Feldman-Muhsam, 1951 *'' Haemaphysalis anomala'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis anomaloceraea'' Teng & Cui, 1984 *'' Haemaphysalis anoplos'' Hoogstraal, Uilenberg & Klein, 1967 *'' Haemaphysalis aponommoides'' Warburton, 1913 *'' Haemaphysalis asiatica'' (Supino, 1897) *'' Haemaphysalis atheruri'' Hoogstraal, Trapido & Kohls, 1965 *'' Haemaphysalis bancrofti'' Nuttall & Warburton, 1915 *'' Haemaphysalis bandicota'' Hoogstraal & Kohls, 1965 *'' Haemaphysalis bartelsi'' Schulze, 1938 *'' Haemaphysalis bequaerti'' Hoogstraal, 1956 *'' Haemaphysalis birmaniae'' Supino, 1897 *'' Haemaphysalis bispinosa'' Neumann, 1897 *'' Haemaphysalis bochkovi'' Apanaskevich & Tomlinson, 2019Dmitry Apanaskevich and Jackson A. Tomlinson. 2019. Description of four new species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
