|
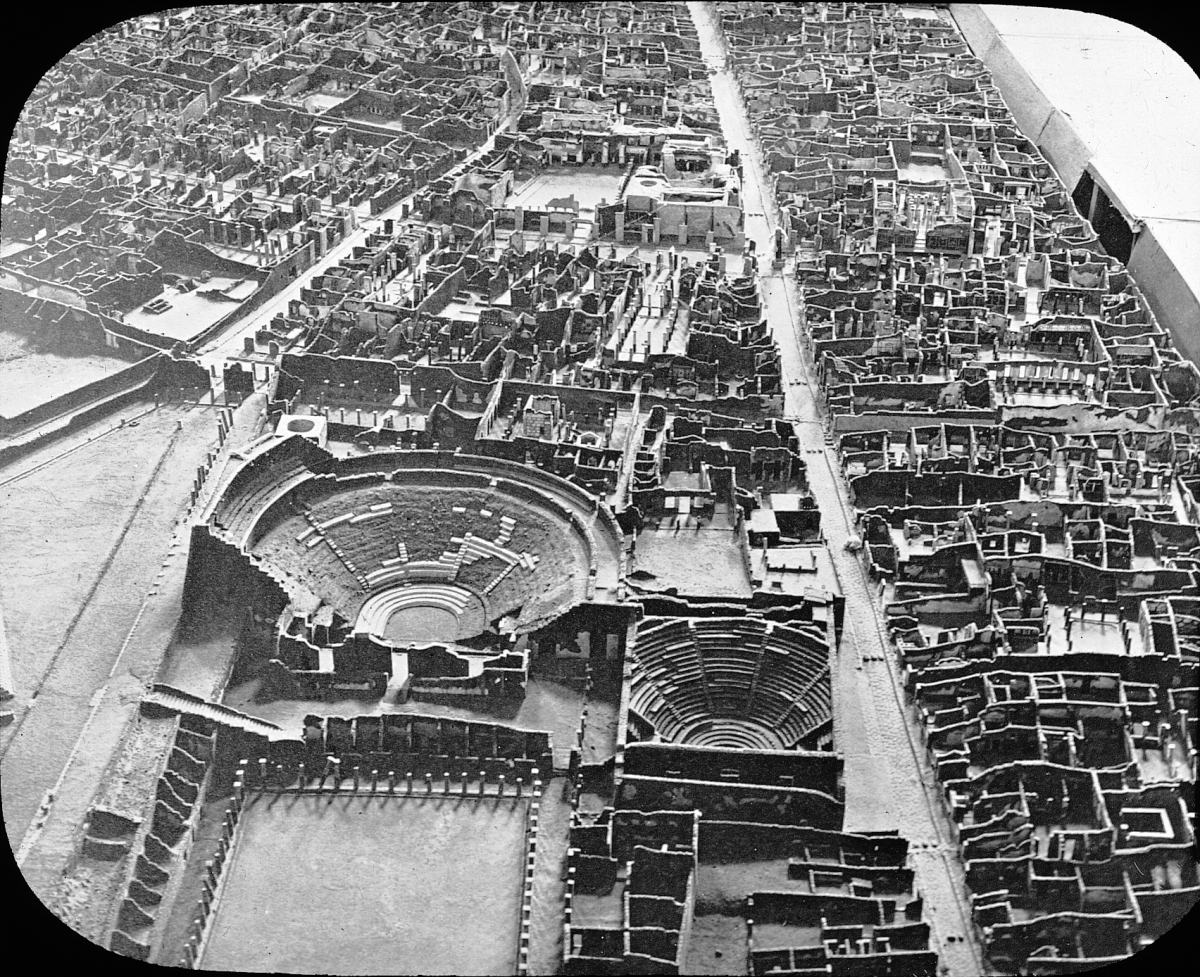
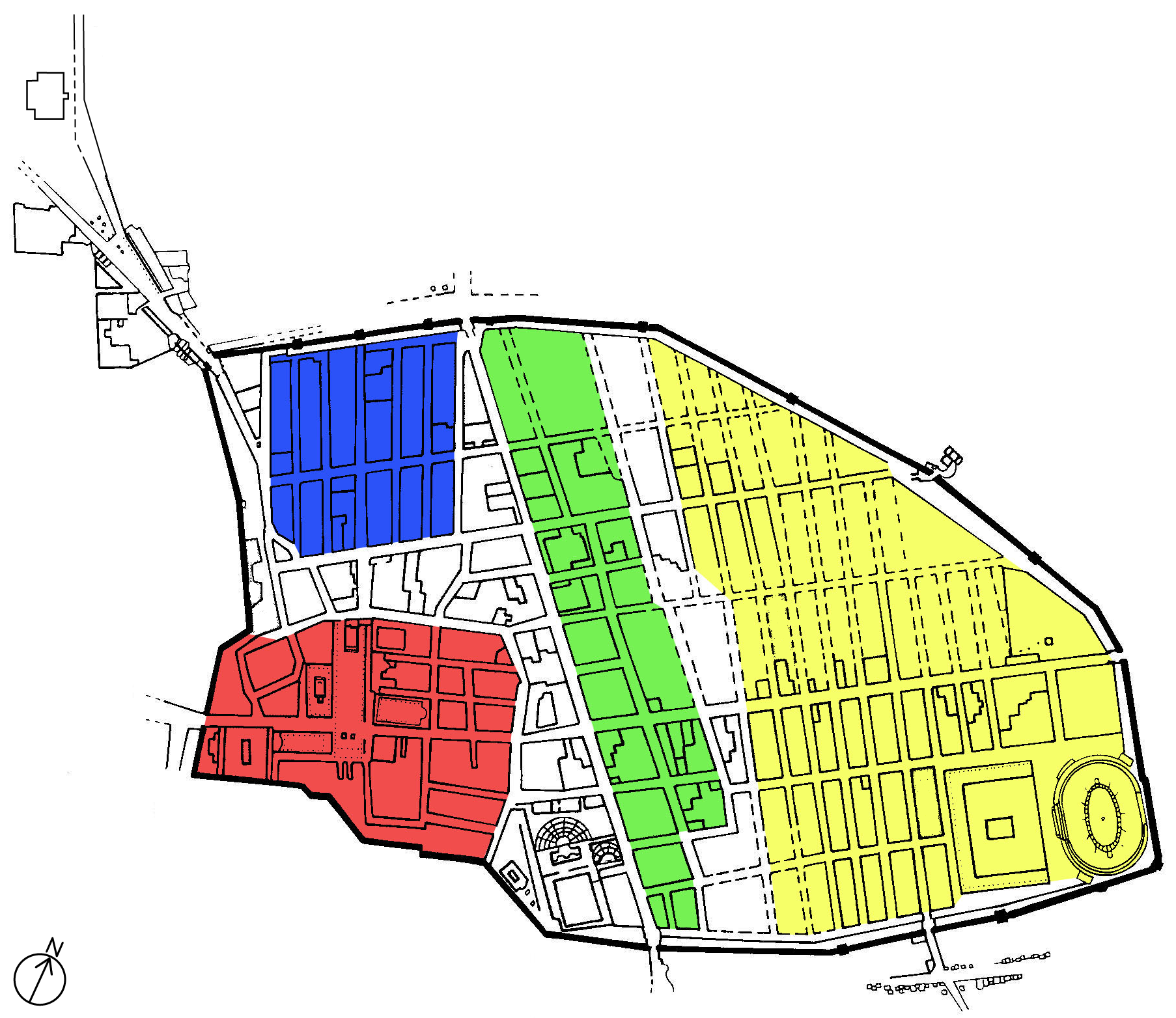
Theatre Area Of Pompeii
The theatre area of Pompeii is located in the southwest region of the city. There are three main buildings that make up this area: the Large Theatre, the Odeon (small theatre), and the Quadriporticum. These served as an entertainment and meeting centre of the city. Pompeii had two stone theatres of its own nearly two decades before the first permanent stone theatre was erected in Rome in the 50s BC. The Large Theatre The Large Theatre was built into a natural hill in the second century BC and was one of the first permanent stone theatres in the Roman empire. It sat roughly 5,000 spectators. In the Greek style, the tiered seating extends from the ''orchestra'' carved out of the hillside. Around 2 BC, the theatre was renovated and presented to the city of Pompeii as a gift by two relatives, M. Holconius Rufus and M. Holconius Celer, according to an inscription in the theatre. Both of these men were wealthy politicians, and acting as benefactors for the renovation would have helped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S03 06 01 024 Image 3121
S, or s, is the nineteenth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''. History Origin Northwest Semitic abjad, Northwest Semitic Shin (letter), šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative (as in 'ip'). It originated most likely as a pictogram of a tooth () and represented the phoneme via the acrophonic principle. Ancient Greek did not have a phoneme, so the derived Greek letter Sigma (letter), sigma () came to represent the voiceless alveolar sibilant . While the letter shape Σ continues Phoenician ''šîn'', its name ''sigma'' is taken from the letter ''samekh'', while the shape and position of ''samekh'' but name of ''šîn'' is continued in the ''Ξ, xi''. Within Greek, the name of ''sigma'' was influenced by its association with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odeon (building)
Odeon or Odeum (, , lit. "singing place") is the name for several ancient Ancient Greece, Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman buildings built for musical activities such as singing, musical shows, and poetry competitions. Odeons were smaller than List of ancient Greek theatres, Greek and Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatres. Etymology The ancient Greek word comes from the verb (, "I sing") which is also the root of (, "ode") and of (, "singer"). Description In a general way, the construction of an odeon was similar to that of an ancient Greek theatre (structure), ancient Greek theatre and Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatre, but it was only a quarter of the size and was provided with a roof for acoustics, acoustic purposes, a characteristic difference. The prototype odeon was the Odeon of Pericles (Odeon of Athens), a mainly wooden building by the southern slope of the Acropolis of Athens. It was described by Plutarch as "many-seated and many-columned" and may have been sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek theatre was a theatrical culture that flourished in ancient Greece from 700 BC. The city-state of Athens, which became a significant cultural, political, and religious place during this period, was its centre, where the theatre was institutionalised as part of a festival called the Dionysia, which honoured the god Dionysus. Tragedy (late 500 BC), comedy (490 BC), and the satyr play were the three dramatic genres to emerge there. Athens exported the festival to its numerous colonies. Modern Western theatre comes, in large measure, from the theatre of ancient Greece, from which it borrows technical terminology, classification into genres, and many of its themes, stock characters, and plot elements. Etymology The word grc, τραγῳδία, tragoidia, label=none, from which the word "tragedy" is derived, is a compound of two Greek words: grc, τράγος, tragos, label=none or "goat" and grc, ᾠδή, ode, label=none meaning "song", from grc, ἀείδειν, ae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Theatre (structure)
Roman theatres derive from and are part of the overall evolution of earlier Greek theatres. Indeed, much of the architectural influence the Romans came from the Greeks, and theatre structural design was no different from other buildings. However, Roman theatres have specific differences, such as generally being built upon their own foundations instead of earthen works or a hillside and being completely enclosed on all sides. Buildings Roman theatres were built in all areas of the Empire, from Spain to the Middle East. Because of the Romans' ability to influence local architecture, we see numerous theatres around the world with uniquely Roman attributes. Similarities exist between the theatres and amphitheaters of ancient Rome. They were constructed out of the same material, Roman concrete, and provided a place for the public to go and see numerous events. However, they are two entirely different structures, with specific layouts that lend to the different events they held. Amp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Of Ancient Rome
The architectural form of theatre in Rome has been linked to later, more well-known examples from the 1st century BC to the 3rd Century AD. The theatre of ancient Rome referred to as a period of time in which theatrical practice and performance took place in Rome has been linked back even further to the 4th century BC, following the state’s transition from monarchy to republic. Theatre during this era is generally separated into genres of tragedy and comedy, which are represented by a particular style of architecture and stage play, and conveyed to an audience purely as a form of entertainment and control. When it came to the audience, Romans favored entertainment and performance over tragedy and drama, displaying a more modern form of theatre that is still used in contemporary times. 'Spectacle' became an essential part of an everyday Romans expectations when it came to theatre. Some works by Plautus, Terence, and Seneca the Younger that survive to this day, highlight the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitheatre Of Pompeii
The Amphitheatre of Pompeii is one of the oldest surviving Roman amphitheatres. It is located in the ancient Roman city of Pompeii, and was buried by the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD, that also buried the city of Pompeii and the neighbouring town of Herculaneum. Six bodies were found during the excavations. Design and construction Built around 70 BC, the amphitheatre is one of the earliest Roman amphitheatres built of stone; previously, they had been built out of wood. Contemporarily, it was known as a ''spectacula'' rather than an ''amphitheatrum'', since the latter term was not yet in use at the time. It was built with the private funds of Gaius Quinctius Valgus and Marcus Porcius (a relative of Julius Caesar's rival). The space was constructed shortly after Pompeii's induction as a Roman colony, and an inscription on the amphitheatre honoring the donors, Gaius Quinctius Valgus and Marcus Porcius, cites one of their motives, being, "to demonstrate the honour of the colony," ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Architectura
(''On architecture'', published as ''Ten Books on Architecture'') is a treatise on architecture written by the Roman architect and military engineer Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It contains a variety of information on Greek and Roman buildings, as well as prescriptions for the planning and design of military camps, cities, and structures both large (aqueducts, buildings, baths, harbours) and small (machines, measuring devices, instruments). Since Vitruvius published before the development of cross vaulting, domes, concrete, and other innovations associated with Imperial Roman architecture, his ten books give no information on these hallmarks of Roman building design and technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled ''De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attributes: , , and ("strength", "utility", and "beauty"). These principles were later widely adopted in Roman architecture. His discussion of perfect proportion in architecture and the human body led to the famous Renaissance drawing of the ''Vitruvian Man'' by Leonardo da Vinci. Little is known about Vitruvius' life, but by his own descriptionDe Arch. Book 1, preface. section 2. he served as an artilleryman, the third class of arms in the Roman military offices. He probably served as a senior officer of artillery in charge of ''doctores ballistarum'' (artillery experts) and ''libratores'' who actually operated the machines. As an army engineer he specialized in the construction of ''ballista'' and '' scorpio'' artillery war machines for sieges. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opus Sectile
''Opus sectile'' is a form of pietra dura popularized in the ancient and medieval Roman world where materials were cut and inlaid into walls and floors to make a picture or pattern. Common materials were marble, mother of pearl, and glass. The materials were cut in thin pieces, polished, then trimmed further according to a chosen pattern. Unlike tessellated mosaic techniques, where the placement of very small uniformly sized pieces forms a picture, ''opus sectile'' pieces are much larger and can be shaped to define large parts of the design. Origin and evolution Early examples Early examples have been found from Egypt and Asia Minor. The Herodian Temple in Jerusalem was built during the second half of the 1st century BCE and the first half of the 1st century CE. Recent work by the Temple Mount Sifting Project has recovered enough pieces of polished stone triangles and squares from the Herodian Temple Mount to reconstruct geometric patterns of ''opus sectile'' flooring. Eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompei 17 35 25 282000
Pompei (; nap, Pumpeje, ) or Pompeii (, as in the name of the ancient city) is a city and commune in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy, home of the ancient Roman ruins of Pompeii that are part of the UNESCO World Heritage Sites. History Modern Pompei was founded in 1891 after the building of the Shrine of Our Lady of Pompei by the lawyer Bartolo Longo. Geography The town of Pompei is located at the eastern borders of its province, and its urban area is contiguous with Scafati, in the Province of Salerno. It borders also with Torre Annunziata, Castellammare di Stabia, Boscoreale, Santa Maria la Carità and Sant'Antonio Abate. Main attractions The ancient city of Pompeii Modern Pompei is mainly famous for the ruins of the ancient city of Pompeii, located in the zone of Pompei Scavi. The vast archaeological area is under Unesco patronage and attracts tourists from all around the world. The Shrine of Our Lady of Pompei The Shrine of Our Lady of Pompei, dedicated to Our L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii Odeion Plan
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offered a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost in the excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found could be used as moulds to make plaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, the excavated city offered a unique snapshot of Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, although much of the detailed evidence of the everyday life of its inhabitants was lost in the excavations. It was a wealthy town, with a population of ca. 11,000 in AD 79, enjoying many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and works of art which were the main attractions for the early excavators. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the ash. Over time, they decayed, leaving voids that archaeologists found could be used as moulds to make plaste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |