|
The White Bird And His Wife
The White Bird and His Wife is an East Asian folktale published as part of the compilation of ''The Bewitched Corpse''. Scholars related it to the cycle of the animal bridegroom: a human woman that marries a supernatural husband in animal form and, after losing him, has to seek him out. Origin The ''Tales of the Bewitched Corpse'' is a compilation of Indo-Tibetan stories that was later brought to Mongolia and translated to Mongolic languages. The collection is known in India as '' Vetala Pañcaviṃśati'', in Tibet as ''Ro-sgrung'', in Mongolia as ''Siditü kegür'', and in Oirat as ''Siddhi kǖr''. Summary The following summary is based on Rachel Harriette Busk's, 's and 's translations of the story. In a distant kingdom called Fair-flower-garden, a man lives with his three daughters grazing their goat herds. One day, the goats vanish, and the elder daughter goes to look for them. She finds a large red door and goes through, then a gate of mother-of-pearl and another of eme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognised by at least one other East Asian state due to severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under Chinese sovereignty. Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau are among the world's largest and most prosperous economies. East Asia borders Siberia and the Russian Far East to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia (a Pacific Ocean island group, classifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Tibet
Kham (; ) is one of the three traditional Tibetan regions, the others being Amdo in the northeast, and Ü-Tsang in central Tibet. The original residents of Kham are called Khampas (), and were governed locally by chieftains and monasteries. Kham presently covers a land area distributed between five regions in China, most of it in Tibet Autonomous Region and Sichuan, with smaller portions located within Qinghai, Gansu and Yunnan provinces. Densely forested with grass plains, its convergence of six valleys and four rivers supported independent Kham polities of Tibetan warrior kingdoms together with Tibetan Buddhist monastic centers.Jann Ronis"An Overview of Kham (Eastern Tibet) Historical Polities" The University of Virginia The early trading route between Central Tibet and China traveled through Kham, and Kham is said to be the inspiration for Shangri-La in James Hilton's novel. Settled as Tibet's eastern frontier in the 7th century, King Songtsen Gampo built temples along its ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick James Gould
Frederick James Gould (19 December 1855 – 6 April 1938) was an English teacher, writer, and pioneer secular humanist. Early life and career He was born in Brighton, the son of William James Gould and his wife Julia, who were evangelical Anglicans. R. W. Morrell, History of the Leicester Secular Society Accessed 4 November 2010 He grew up in London, and at the age of seven was sent to study and sing in the choir at , . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Studies
Mongolian studies is an interdisciplinary field of scholarly inquiry concerning Mongolian language, Mongolian history, and Mongolian culture. Scholars who work in the field of Mongolian studies are often referred to as Mongolists. History Isaac Jacob Schmidt is generally regarded as the "founder" of Mongolian studies as an academic discipline. Schmidt, a native of Amsterdam who emigrated to Russia on account of the French invasion, began his exposure to the Mongolic languages as a missionary of the Moravian Church among the Kalmyks, and translated the Gospel of Matthew into the Kalmyk language. Afterwards he moved to Moscow and then Saint Petersburg, where he produced his most famous work: the first translation of the ''Erdeniin Tobchi'' into a European language. He also compiled a dictionary of Mongolian and a translation of the seven then-known chapters of the '' Epic of King Gesar''. Other major figures in the early history of Mongolian studies in Russia were Józef Kowalewski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Feather Of Finist The Falcon
The Feather of Finist the Falcon or Finist the Falcon (russian: Пёрышко Финиста ясна сокола) is a Russian fairy tale collected by Alexander Afanasyev in ''Narodnye russkie skazki''. It is Aarne–Thompson type 432, the prince as bird. Other tales of this type include The Green Knight, The Blue Bird, and The Greenish Bird. Synopsis A merchant asked his three daughters what they want him to bring them from the fair. The older two ask for dresses or shawls, but the youngest wants either the feather of Finist the Falcon or a red flower. In some variants, he went to the fair twice, able to bring back what her older sisters had asked for, but not hers, but she did not vary her request. In the third or first visit, he found the feather, or else found the flower and must promise that his daughter will marry Finist the Falcon for it. Whether the flower or the feather, the thing brought Finist the Falcon to her at night, and he wooed her. If she was given the fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ralston Shedden-Ralston
William Ralston Shedden-Ralston (1828–1889), known in his early life as William Ralston Shedden, who later adopted the additional surname of Ralston, was a noted British scholar and translator of Russia and Russian. Biography William Ralston Shedden-Ralston (1828-1889) was born on 4 April 1828 in York Terrace, Regent's Park, London, as the third child and only son of William Patrick Ralston Shedden (1794-1880) and Frances Sophia Browne (1804-). His mother was the 3rd daughter of William Browne (1762-1833) of Galway, Calcutta and Sydney. His father, born in New York of Scottish paternity and schooled in Scotland, had made his fortune as a merchant in Calcutta, India, before setting up home in Palmira Square, Brighton. William Ralston Shedden-Ralston spent most of his early years there. Together with three or four other boys he studied under the Rev. John Hogg of Brixham, Devonshire, until he went to Trinity College, Cambridge in 1846, where he studied law and graduated with a BA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ningxia
Ningxia (,; , ; alternately romanized as Ninghsia), officially the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (NHAR), is an autonomous region in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. Formerly a province, Ningxia was incorporated into Gansu in 1954 but was later separated from Gansu in 1958 and reconstituted as an autonomous region for the Hui people, one of the 56 officially recognised nationalities of China. Twenty percent of China's Hui population lives in Ningxia. Ningxia is bounded by Shaanxi to the east, Gansu to the south and west and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north and has an area of around . This sparsely settled, mostly desert region lies partially on the Loess Plateau and in the vast plain of the Yellow River and features the Great Wall of China along its northeastern boundary. Over about 2000 years an extensive system of canals (The total length about 1397 kilometers) has been built from Qin dynasty. Extensive land reclamation and irrigation projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hui People
The Hui people ( zh, c=, p=Huízú, w=Hui2-tsu2, Xiao'erjing: , dng, Хуэйзў, ) are an East Asian ethnoreligious group predominantly composed of Chinese-speaking adherents of Islam. They are distributed throughout China, mainly in the northwestern provinces and in the Zhongyuan region. According to the 2011 census, China is home to approximately 10.5 million Hui people. The 110,000 Dungan people of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan are also considered part of the Hui ethnicity. The Hui have a distinct connection with Islamic culture. For example, they follow Islamic dietary laws and reject the consumption of pork, the most commonly consumed meat in China, and have developed their own variation of Chinese cuisine. They also dress differently than the Han Chinese, some men wear white caps (taqiyah) and some women wear headscarves, as is the case in many Islamic cultures. The Hui people are one of 56 ethnic groups recognized by China. The government defines the Hui pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other iconic cities and towns such as Brașov, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș, Alba Iulia and Sighișoara. It is also the home of some of Romania's List of World Heritage Sites in Romania, UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains and the Rosia Montana Mining Cultural Landsc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
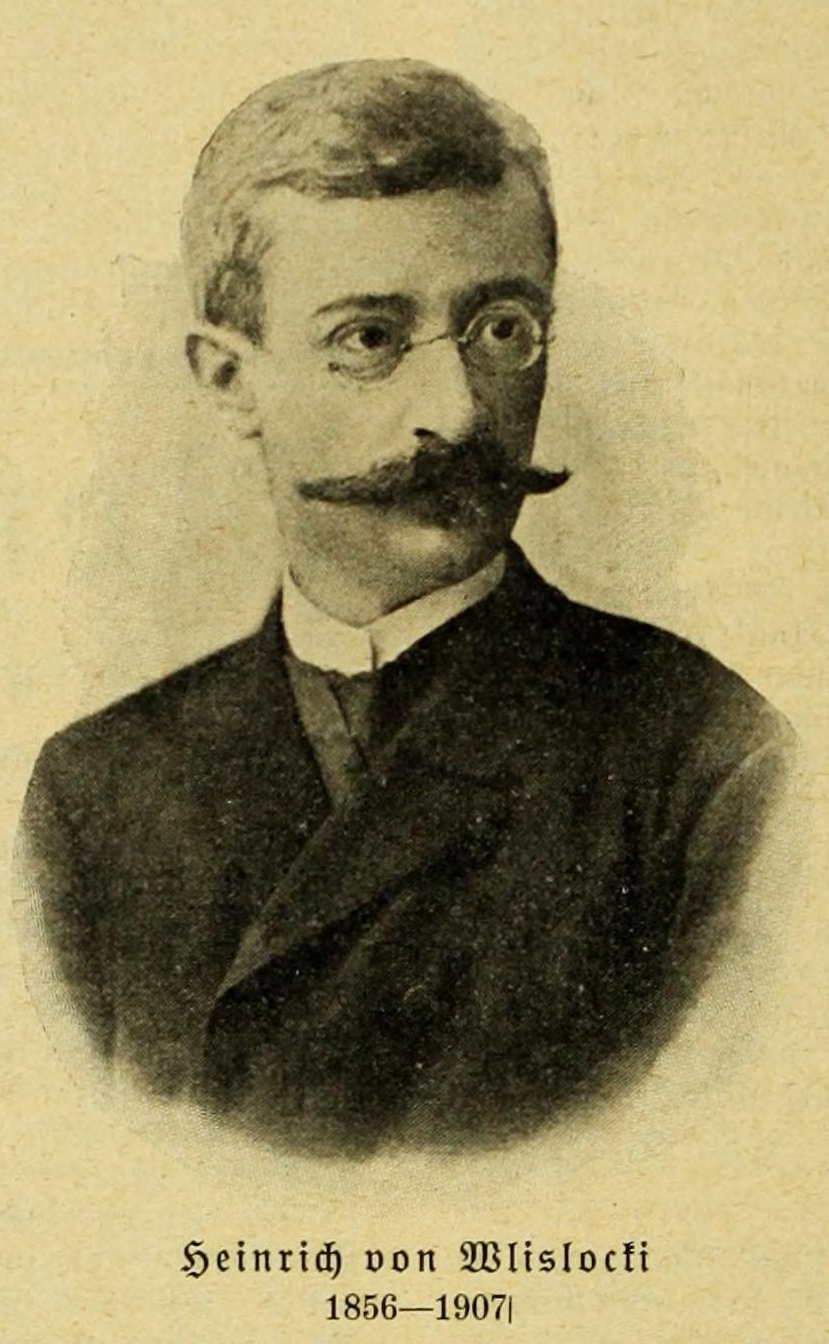
Heinrich Von Wlislocki
Heinrich Adalbert von Wlislocki ( Hungarian: ''Wlislocki Henrik''; born 9 July 1856 in Kronstadt; died 19 February 1907 in Klosdorf bei Kleinkopisch, now in Șona) was a Transylvanian linguist and folklorist. The son of an ethnically Polish Austro-Hungarian Imperial tax collector and a Transylvanian Saxon, he attended the venerable Johannes Honterus Gymnasium (school) in Kronstadt and then the recently founded University of Klausenburg (later Franz Joseph University) from 1875 to 1879. In 1879 he earned his doctorate with a dissertation on Eddic poetry, ''Hapax Legomena im Atlamál'', which was published in ''Acta Comparationis Litterarum Universarum,'' a journal edited by his academic advisors, Hugo Meltzl and Sámuel Brassai. After the death of his father, he worked in humble circumstances as a private tutor. From 1883 to 1890 he lived in Mühlbach (Sebeș). In his specialty, Romani studies, he pursued an extensive literary collection effort and engaged in field studies wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
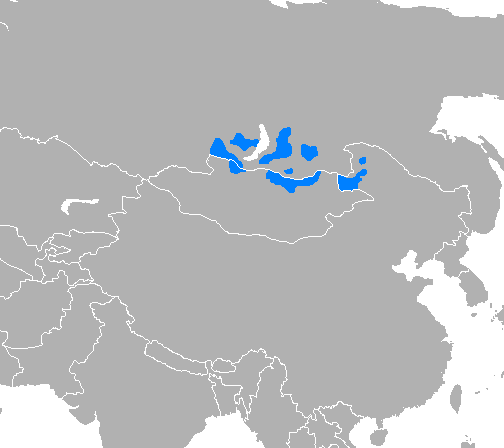
Buryat Language
Buryat, or Buriat (; Buryat Cyrillic: , , ), known in foreign sources as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of Mongolian, and in pre-1956 Soviet sources as Buryat-Mongolian,In China, the Buryat language is classified as the Bargu-Buryat dialect of the Mongolian language. is a variety of the Mongolic languages spoken by the Buryats and Bargas that is classified either as a language or major dialect group of Mongolian. Geographic distribution The majority of Buryat speakers live in Russia along the northern border of Mongolia where it is an official language in the Buryat Republic and was an official language in the former Ust-Orda Buryatia and Aga Buryatia autonomous okrugs. In the Russian census of 2002, 353,113 people out of an ethnic population of 445,175 reported speaking Buryat (72.3%). Some other 15,694 can also speak Buryat, mostly ethnic Russians. Buryats in Russia have a separate literary standard, written in a Cyrillic alphabet. It is based on the Russian alphabet with thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |