|
The Geometry Of An Art
''The Geometry of an Art: The History of the Mathematical Theory of Perspective from Alberti to Monge'' is a book in the history of mathematics, on the mathematics of graphical perspective. It was written by Kirsti Andersen, and published in 2007 by Springer-Verlag in their book series Sources and Studies in the History of Mathematics and Physical Sciences. Topics This book covers a wide span of mathematical history, from 1435 to 1800, and a wide field of "around 250 publications by more than 200 authors". After three introductory chapters on the beginnings of perspective with the works of Leon Battista Alberti, Piero della Francesca, Leonardo da Vinci, and others from their time, the remainder of the book is organized geographically rather than chronologically, in order to set the works it discusses into their local context. Thus, Chapter 4 covers the spread of perspective among the artists and artisans of 15th-century Italy, including the works of Luca Pacioli and Daniele Barbaro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Perspective
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
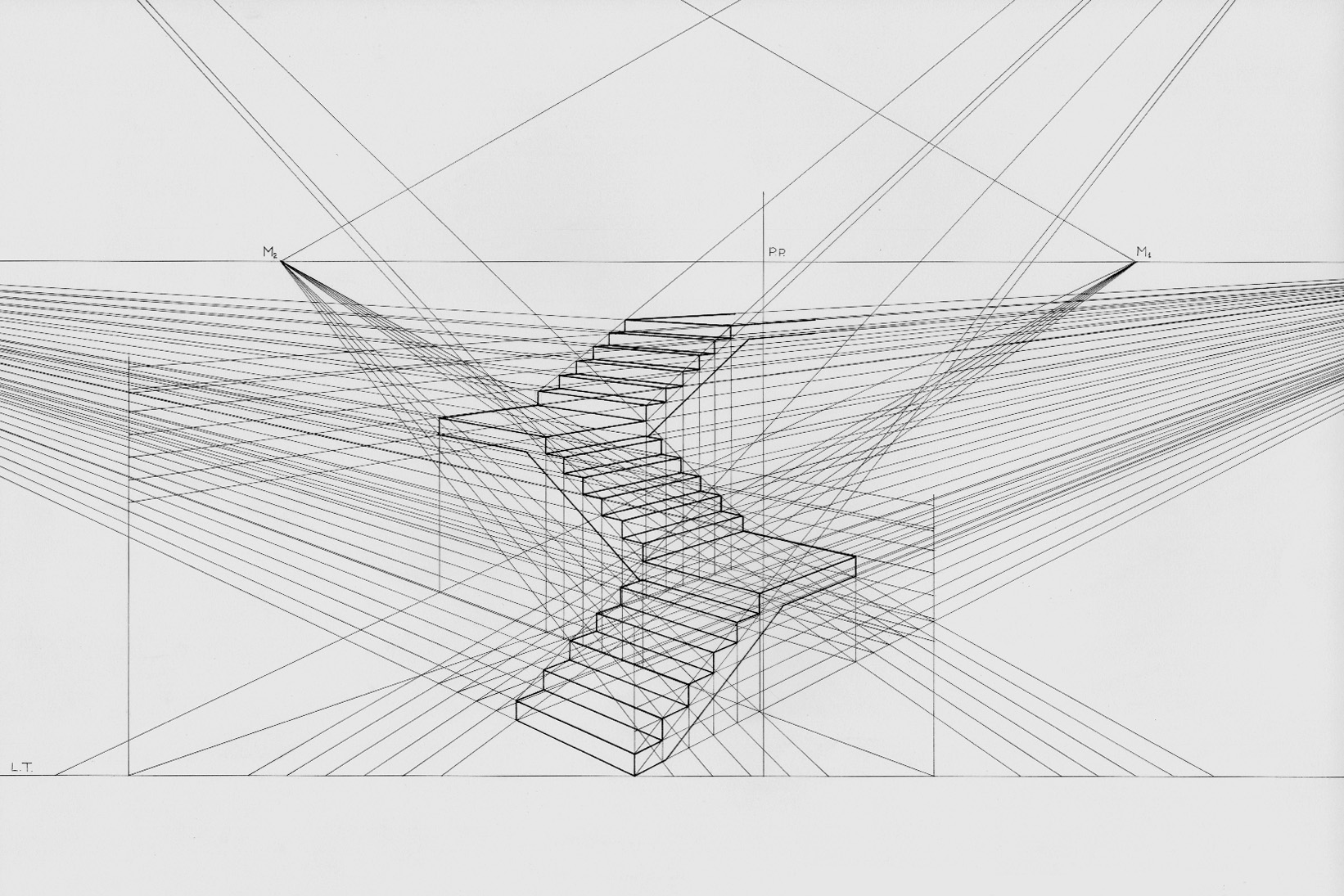
Vanishing Point
A vanishing point is a point on the image plane of a perspective drawing where the two-dimensional perspective projections of mutually parallel lines in three-dimensional space appear to converge. When the set of parallel lines is perpendicular to a picture plane, the construction is known as one-point perspective, and their vanishing point corresponds to the oculus, or "eye point", from which the image should be viewed for correct perspective geometry. Kirsti Andersen (2007) ''Geometry of an Art'', p. xxx, Springer, Traditional linear drawings use objects with one to three sets of parallels, defining one to three vanishing points. Italian humanist polymath and architect Leon Battista Alberti first introduced the concept in his treatise on perspective in art, '' De pictura'', written in 1435. Vector notation The vanishing point may also be referred to as the "direction point", as lines having the same directional vector, say ''D'', will have the same vanishing poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by graphics hardware, computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as Computer-generated imagery, computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of Computer graphics (computer science), computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, sprite (graphics), sprite graphics, Rendering (computer graphics), rendering, ray tracing (graphics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip J
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularized the name include kings of Macedonia and one of the apostles of early Christianity. ''Philip'' has many alternative spellings. One derivation often used as a surname is Phillips. It was also found during ancient Greek times with two Ps as Philippides and Philippos. It has many diminutive (or even hypocoristic) forms including Phil, Philly, Lip, Pip, Pep or Peps. There are also feminine forms such as Philippine and Philippa. Antiquity Kings of Macedon * Philip I of Macedon * Philip II of Macedon, father of Alexander the Great * Philip III of Macedon, half-brother of Alexander the Great * Philip IV of Macedon * Philip V of Macedon New Testament * Philip the Apostle * Philip the Evangelist Others * Philippus of Croton (c. 6th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Descriptive Geometry
Descriptive geometry is the branch of geometry which allows the representation of three-dimensional objects in two dimensions by using a specific set of procedures. The resulting techniques are important for engineering, architecture, design and in art. The theoretical basis for descriptive geometry is provided by planar geometric projections. The earliest known publication on the technique was "Underweysung der Messung mit dem Zirckel und Richtscheyt", published in Linien, Nuremberg: 1525, by Albrecht Dürer. Italian architect Guarino Guarini was also a pioneer of projective and descriptive geometry, as is clear from his ''Placita Philosophica'' (1665), ''Euclides Adauctus'' (1671) and ''Architettura Civile'' (1686—not published until 1737), anticipating the work of Gaspard Monge (1746–1818), who is usually credited with the invention of descriptive geometry. Gaspard Monge is usually considered the "father of descriptive geometry" due to his developments in geometric pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspard Monge
Gaspard Monge, Comte de Péluse (9 May 1746 – 28 July 1818) was a French mathematician, commonly presented as the inventor of descriptive geometry, (the mathematical basis of) technical drawing, and the father of differential geometry. During the French Revolution he served as the Minister of the Marine, and was involved in the reform of the French educational system, helping to found the École Polytechnique. Biography Early life Monge was born at Beaune, Côte-d'Or, the son of a merchant. He was educated at the college of the Oratorians at Beaune. In 1762 he went to the Collège de la Trinité at Lyon, where, one year after he had begun studying, he was made a teacher of physics at the age of just seventeen. After finishing his education in 1764 he returned to Beaune, where he made a large-scale plan of the town, inventing the methods of observation and constructing the necessary instruments; the plan was presented to the town, and is still preserved in their l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Heinrich Lambert
Johann Heinrich Lambert (, ''Jean-Henri Lambert'' in French; 26 or 28 August 1728 – 25 September 1777) was a polymath from the Republic of Mulhouse, generally referred to as either Swiss or French, who made important contributions to the subjects of mathematics, physics (particularly optics), philosophy, astronomy and map projections. Biography Lambert was born in 1728 into a Huguenot family in the city of Mulhouse (now in Alsace, France), at that time a city-state allied to Switzerland. Some sources give 26 August as his birth date and others 28 August. Leaving school at 12, he continued to study in his free time while undertaking a series of jobs. These included assistant to his father (a tailor), a clerk at a nearby iron works, a private tutor, secretary to the editor of ''Basler Zeitung'' and, at the age of 20, private tutor to the sons of Count Salis in Chur. Travelling Europe with his charges (1756–1758) allowed him to meet established mathematicians in the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Geometry
In mathematics, projective geometry is the study of geometric properties that are invariant with respect to projective transformations. This means that, compared to elementary Euclidean geometry, projective geometry has a different setting, projective space, and a selective set of basic geometric concepts. The basic intuitions are that projective space has more points than Euclidean space, for a given dimension, and that geometric transformations are permitted that transform the extra points (called " points at infinity") to Euclidean points, and vice-versa. Properties meaningful for projective geometry are respected by this new idea of transformation, which is more radical in its effects than can be expressed by a transformation matrix and translations (the affine transformations). The first issue for geometers is what kind of geometry is adequate for a novel situation. It is not possible to refer to angles in projective geometry as it is in Euclidean geometry, because an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girard Desargues
Girard Desargues (; 21 February 1591 – September 1661) was a French mathematician and engineer, who is considered one of the founders of projective geometry. Desargues' theorem, the Desargues graph, and the crater Desargues on the Moon are named in his honour. Born in Lyon, Desargues came from a family devoted to service to the French crown. His father was a royal notary, an investigating commissioner of the Seneschal's court in Lyon (1574), the collector of the tithes on ecclesiastical revenues for the city of Lyon (1583) and for the diocese of Lyon. Girard Desargues worked as an architect from 1645. Prior to that, he had worked as a tutor and may have served as an engineer and technical consultant in the entourage of Richelieu. As an architect, Desargues planned several private and public buildings in Paris and Lyon. As an engineer, he designed a system for raising water that he installed near Paris. It was based on the use of the epicycloidal wheel, the principle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean François Niceron
Jean-François Niceron (5 July 1613 – 22 September 1646) was a French mathematician, Minim friar, and painter of anamorphic art, on which he wrote the ground-breaking book ''La Perspective Curieuse'' (Curious Perspectives). Biography Jean-François Niceron was a mathematical prodigy. He studied under Father Marin Mersenne, a famed mathematician and Minim friar, at the College de Nevers. In 1632, at the age of nineteen, he joined the Order of Minims. Niceron was also an artist, with a particular interest in the use of anamorphosis in religious art. He was acquainted with the leading scientists in France and Italy, such as Fermat, Descartes, Cavalieri, and Kircher, and was aware of the latest theoretical developments. Intent on finding a scientific solution to the problems presented by perspective, Niceron worked out the geometric algorithms for producing anamorphic art and in 1638, at the age of 25, published a treatise titled ''La perspective curieuse, ou magie artificie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
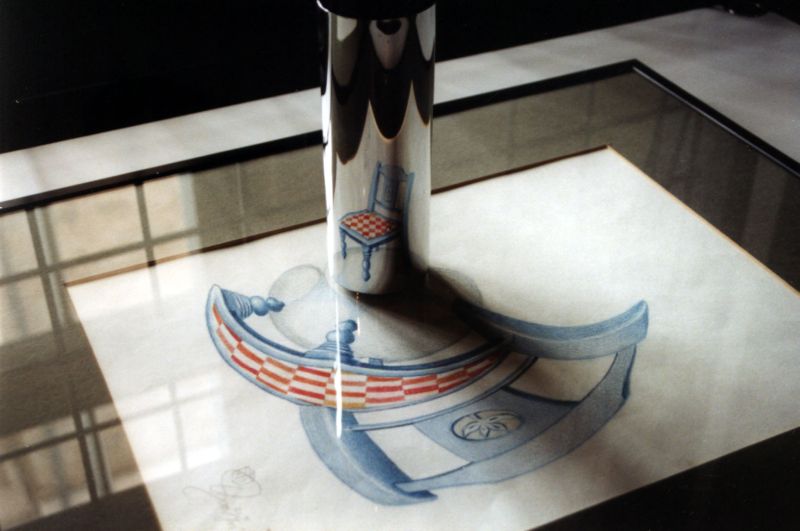
Anamorphosis
Anamorphosis is a distorted projection requiring the viewer to occupy a specific vantage point, use special devices, or both to view a recognizable image. It is used in painting, photography, sculpture and installation, toys, and film special effects. The word is derived from the Greek prefix ''ana-'', meaning "back" or "again", and the word ''morphe'', meaning "shape" or "form". Extreme anamorphosis has been used by artists to disguise caricatures, erotic and scatological scenes, and other furtive images from a casual spectator, while revealing an undistorted image to the knowledgeable viewer. Types of projection There are two main types of anamorphosis: ''perspective'' (oblique) and ''mirror'' (catoptric). More complex anamorphoses can be devised using distorted lenses, mirrors, or other optical transformations. An oblique anamorphism forms an affine transformation of the subject. Early examples of perspectival anamorphosis date to the Renaissance of the fifteenth century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Du Breuil
Jean Dubreuil, also known as Jean Du Breuil (22 July 1602 – 27 April 1670), was a French mathematician, music theorist, writer and essayist. Life Son of the bookseller Claude Du Breuil, he continued his father's profession until he joined the Society of Jesus , image = Ihs-logo.svg , image_size = 175px , caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits , abbreviation = SJ , nickname = Jesuits , formation = , founders .... He lived for a long time in Rome where he studied architecture. He is known for his work about the theory and practice of perspective. Works * * ''La perspective practique'' 1642–1649 * ''L'Art universel des fortifications'' References French mathematicians 1602 births 1670 deaths French essayists French writers {{France-nonfiction-writer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |