|
The Baumoff Explosive
"The Baumoff Explosive", also known as "Eloi, Eloi, Lama Sabachthani" is a horror story by William Hope Hodgson, first published in 1919. Plot The story is told using a framework or "story within a story", a method used by Hodgson in many of his stories. It is learned in the framework story that a strange new explosive has been developed. Invented by a man named Baumoff, this substance has the effect of creating a temporary area of darkness, into which light does not readily pass. The main body of the story describes the narrator's meeting with Baumoff, who is described as a scientist who is also profoundly Christians, Christian and obsessed with the crucifixion. Baumoff believes that events following Christ's death (the darkening of the sky, the rending of the temple curtain, and shaking of the ground, as described in the gospels) have a rational, scientific basis. This basis is the ability of the human Psyche (psychology), psyche to affect the luminiferous aether, aether an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horror Story
Horror is a genre of fiction which is intended to frighten, scare, or disgust. Horror is often divided into the sub-genres of psychological horror and supernatural horror, which is in the realm of speculative fiction. Literary historian J. A. Cuddon, in 1984, defined the horror story as "a piece of fiction in prose of variable length... which shocks, or even frightens the reader, or perhaps induces a feeling of repulsion or loathing". Horror intends to create an eerie and frightening atmosphere for the reader. Often the central menace of a work of horror fiction can be interpreted as a metaphor for larger fears of a society. Prevalent elements of the genre include ghosts, demons, vampires, werewolves, ghouls, the Devil, witches, monsters, extraterrestrials, dystopian and post-apocalyptic worlds, serial killers, cannibalism, cults, dark magic, satanism, the macabre, gore and torture. History Before 1000 The horror genre has ancient origins, with roots in folklor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hope Hodgson
William Hope Hodgson (15 November 1877 – 19 April 1918) was an English author. He produced a large body of work, consisting of essays, short fiction, and novels, spanning several overlapping genres including horror, fantastic fiction, and science fiction.Alder, Emily. "Passing the Barrier or Life: Spiritualism, Psychical Research and Boundaries in William Hope Hodgson's "The Night Land"". in Ramone, Jenni and Twitchen, Gemma, eds. ''Boundaries''. Newcastle: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2007. (pp. 120-139). Stableford, Brian, "Hodgson, William Hope", in Pringle, David ed., ''St. James Guide to Horror, Ghost & Gothic Writers''. London: St. James Press, 1998. (pp. 273-275). Hodgson used his experiences at sea to lend authentic detail to his short horror stories, many of which are set on the ocean, including his series of linked tales forming the "Sargasso Sea Stories". His novels, such as '' The House on the Borderland'' (1908) and ''The Night Land'' (1912), feature more cosm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Story Within A Story
A story within a story, also referred to as an embedded narrative, is a literary device in which a character within a story becomes the narrator of a second story (within the first one). Multiple layers of stories within stories are sometimes called nested stories. A play may have a brief play within it, such as Shakespeare's play ''Hamlet''; a film may show the characters watching a short film; or a novel may contain a short story within the novel. A story within a story can be used in all types of narration: novels, short stories, plays, television programs, films, poems, songs, video games, and philosophical essays. The inner stories are told either simply to add entertainment or more usually to act as an example to the other characters. In either case, the inner story often has a symbolic and psychological significance for the characters in the outer story. There is often some parallel between the two stories, and the fiction of the inner story is used to reveal the truth i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or grain dust * pressurized gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or BLEVE * nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high explosives" and materials that deflagrate are said to be "low explosives". Explosives may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χριστός), a translation of the Biblical Hebrew term ''mashiach'' (מָשִׁיחַ) (usually rendered as ''messiah'' in English). While there are diverse interpretations of Christianity which sometimes conflict, they are united in believing that Jesus has a unique significance. The term ''Christian'' used as an adjective is descriptive of anything associated with Christianity or Christian churches, or in a proverbial sense "all that is noble, and good, and Christ-like." It does not have a meaning of 'of Christ' or 'related or pertaining to Christ'. According to a 2011 Pew Research Center survey, there were 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. Today, about 37% of all Christians live in the Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words and deeds of Jesus, culminating in his trial and death and concluding with various reports of his post-resurrection appearances. Modern scholars are cautious of relying on the gospels uncritically, but nevertheless, they provide a good idea of the public career of Jesus, and critical study can attempt to distinguish the original ideas of Jesus from those of the later authors. The four canonical gospels were probably written between AD 66 and 110. All four were anonymous (with the modern names added in the 2nd century), almost certainly none were by eyewitnesses, and all are the end-products of long oral and written transmission. Mark was the first to be written, using a variety of sources. The authors of Matthew and Luke both independently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psyche (psychology)
In psychology, the psyche is the totality of the human mind, conscious and unconscious. Many thinkers, including Carl Jung, also include in this definition the overlap and tension between the personal and the collective elements in man. Psychology is the scientific or objective study of the psyche. The word has a long history of use in psychology and philosophy, dating back to ancient times, and represents one of the fundamental concepts for understanding human nature from a scientific point of view. The English word soul is sometimes used synonymously, especially in older texts. Etymology The basic meaning of the Greek word ψυχή (''psyche'') was "life", although unsupported, some have claimed it is derived from the verb ψύχω (''psycho'', "to blow"). Derived meanings included "spirit", "soul", "ghost", and ultimately "self" in the sense of "conscious personality" or "psyche". Ancient psychology The idea of the psyche is central to the philosophy of Plato. Scholars tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
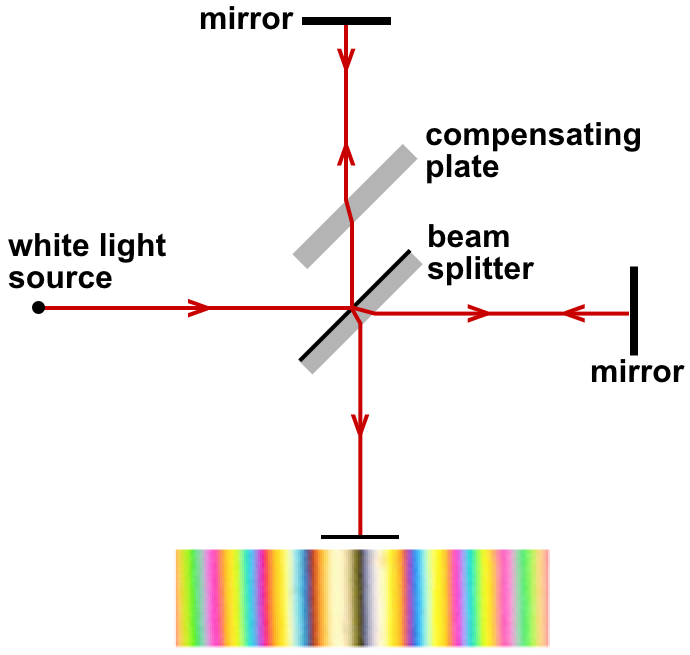
Luminiferous Aether
Luminiferous aether or ether ("luminiferous", meaning "light-bearing") was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 1800s, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. The negative outcome of the Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) suggeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath may occur with exertion or while lying down, and may wake people up during the night. Chest pain, including angina, is not usually caused by heart failure, but may occur if the heart failure was caused by a heart attack. The severity of the heart failure is measured by the severity of symptoms during exercise. Other conditions that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts carried out by the state, but others include non-state organizations. Torture has been carried out since ancient times. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Western countries abolished the official use of torture in the judicial system, but torture continued to be used throughout the world. A variety of methods of torture are used, often in combination; the most common form of physical torture is beatings. Since the twentieth century, many torturers have preferred non-scarring or psychological methods to provide deniability. Torturers are enabled by organizations that facilitate and encourage their behavior. Most victims of torture are poor and marginalized people suspected of crimes, although torture against political prisoners or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1919 Short Stories
Events January * January 1 ** The Czechoslovak Legions occupy much of the self-proclaimed "free city" of Pressburg (now Bratislava), enforcing its incorporation into the new republic of Czechoslovakia. ** HMY ''Iolaire'' sinks off the coast of the Hebrides; 201 people, mostly servicemen returning home to Lewis and Harris, are killed. * January 2– 22 – Russian Civil War: The Red Army's Caspian-Caucasian Front begins the Northern Caucasus Operation against the White Army, but fails to make progress. * January 3 – The Faisal–Weizmann Agreement is signed by Emir Faisal (representing the Arab Kingdom of Hejaz) and Zionist leader Chaim Weizmann, for Arab–Jewish cooperation in the development of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, and an Arab nation in a large part of the Middle East. * January 5 – In Germany: ** Spartacist uprising in Berlin: The Marxist Spartacus League, with the newly formed Communist Party of Germany and the Independent Social Democrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |