|
Thalattosaurus
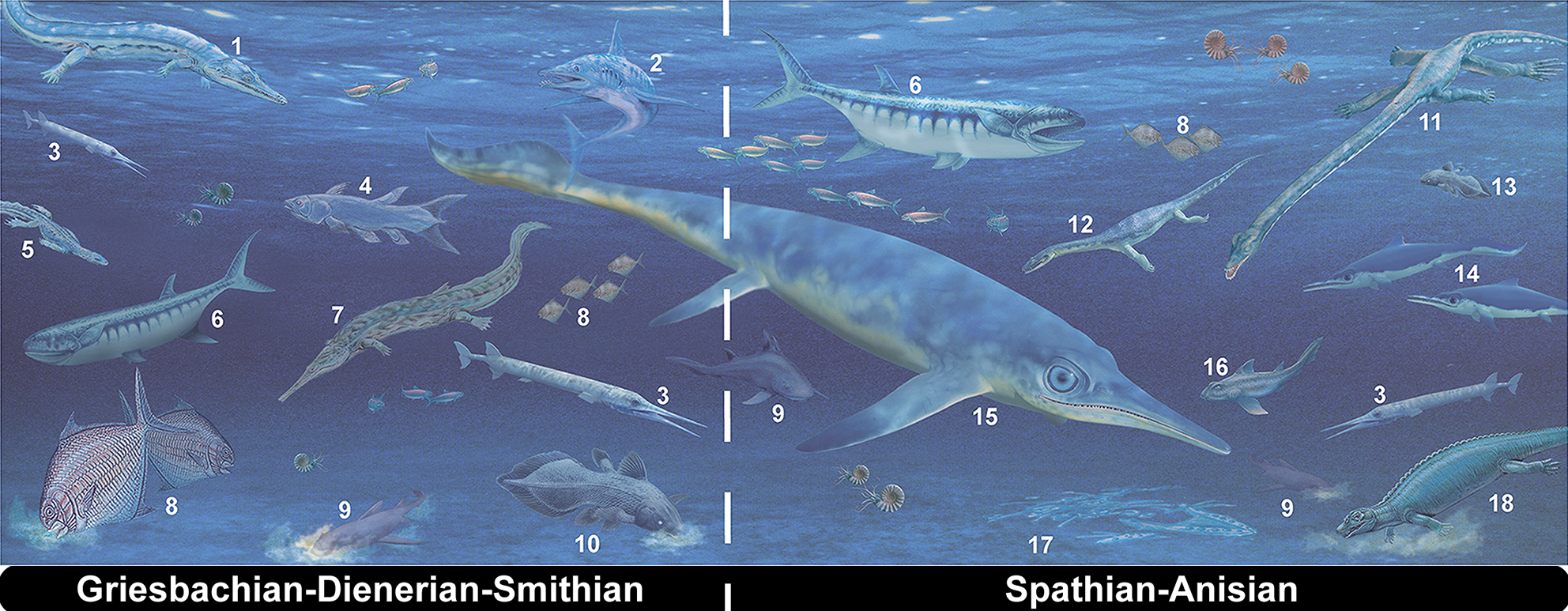
''Thalattosaurus'' (pronounced: , "tha-la-to-SORE-us") meaning "sea lizard," from the Attic Greek ' (), "sea," and ' (), "lizard," is an extinct genus of marine reptile in the family Thalattosauroidea. They were aquatic diapsids that are known exclusively from the Triassic period. It was a long shellfish-eating reptile with paddle-like limbs and a down-turned rostrum occurring in the Lower and Middle Triassic Sulphur Mountain Formation of British Columbia as well as the Upper Triassic Hosselkus Limestone of California. It has gained notoriety as a result of studies on general diapsid phylogeny. Although originally described as four distinct species by Merriam in 1905, one was proven to be ''T. alexandrae'' upon further inspection and another has a missing type specimen. Currently it is believed to include two known species; ''Thalattosaurus alexandrae'' and ''T. borealis''. Discovery and naming In the summer of 1903 Annie Alexander led an expedition with Miss Edna We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosaur
Thalattosauria (Attic Greek, Greek for "sea lizards") is an extinct Order (biology), order of prehistoric marine reptiles that lived in the middle to late Triassic period. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annie Montague Alexander
Annie Montague Alexander (29 December 1867 - 10 September 1950) was an explorer, naturalist, paleontological collector, and philanthropist. She founded the University of California Museum of Paleontology (UCMP) and the Museum of Vertebrate Zoology (MVZ). From its establishment in 1908 until she died in 1950 she financed the museum's collections and supported a series of paleontological expeditions throughout the western United States. Alexander herself took part in many of these expeditions, accumulating a significant collection of fossils and exotic game animals that she would later donate to the museum. Alexander is remembered by the University of California, Berkeley as one of the "builders of Berkeley" and as the benefactress of the museum. Early life Annie Montague Alexander was born December 29, 1867, in Honolulu during the Kingdom of Hawaii. She was the granddaughter of New England missionaries in Maui. Her father Samuel Thomas Alexander and her uncle Henry Perrine Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosauroidea
Thalattosauroidea is a superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. It was named in 1904 by paleontologist John Campbell Merriam to include the genus '' Thalattosaurus'' from California. Thalattosauroids are one of two groups of Thalattosauria, the other being Askeptosauroidea. Thalattosauroids make up the "traditional" thalattosaurs with large downturned snouts, short necks, and long, paddle-like tails. Classification Thalattosauria includes North American genera such as ''Thalattosaurus'' and ''Nectosaurus'' as well as recently described Chinese forms such as ''Xinpusaurus''. A 1999 study of thalattosaurs, which established much of the currently accepted phylogeny of the group, referred to Thalattosauroidea as Thalattosauria, while calling the larger group Thalattosauriformes. More recent phylogenetic studies have come upon the same conclusions, but refer to the group as Thalattosauroidea in order to contrast it with another superfamily of thalattosaurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hosselkus Limestone
The Hosselkus Limestone is an Upper Triassic fossiliferous marine micritic limestone formation that outcrops in Plumas and Shasta Counties, California. It is known for its invertebrate fauna, most notably the many species of shelled cephalopods. Geology The geologic column of the nearby Taylorsville region shows the Hosselkus Limestone as 140 ft thick and of Late Triassic (early Karnian) age. It is well exposed near the Cosmopolitan mine on the divide between the Genesee Valley and Hosselkus Creek. It has been recognized at numerous outcrops between Spanish Ranch and Prattville and northwestward beyond Pit River in the Klamath Mountains, and is considered to be younger than the Swearinger slates and older than the Trail beds. It contains numerous ''Arcestes'' and abundant pentagonal crinoid stems which indicate it is of Late Triassic age. Paleofauna Over 208 described species of invertebrates have been found in the Hosselkus Limestone and nearby Brock Mountain. These speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulphur Mountain Formation
The Sulphur Mountain Formation is a geologic formation of Early to Middle Triassic age. It is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the foothills and Rocky Mountains of western Alberta and northeastern British Columbia. It includes marine fossils from the time shortly after the Permian-Triassic extinction event.Noad, Jon, 2017. Field trip to examine Montney Formation analogs: Exposures of the Sulphur Mountain Formation around Canmore and Kananaskis, western Alberta, Canada. In: J.C.C. Hseih, ed., Geologic field trips of the Canadian Rockies: 2017 meeting of the GSA Rocky Mountain Section, Geological Society of America, Field Guide 48, p. 137-152; doi: 10.1130/2017.0048(05). The Sulphur Mountain Formation was first described as a member of the Spray River Formation by P.S. Warren in 1945, who named it for Sulphur Mountain in Banff National Park. It was later raised to formation status. Its type section is located in the Spray River gorge at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shastasaurus
''Shastasaurus'' ("Mount Shasta lizard") is a very large extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the middle and late Triassic, and is the largest known marine reptile.Hilton, Richard P., ''Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Animals of California'', University of California Press, Berkeley 2003 , at pages 90-91. Specimens have been found in the United States, Canada, and China. Description left, Size of '' Shonisaurus popularis'' (green) and ''S. sikanniensis'' (red), a possible species of ''Shastasaurus'', compared with a human ''Shastasaurus'' lived during the late Triassic period. The type species ''Shastasaurus pacificus'' is known from California. ''S. pacificus'' was a medium-sized ichthyosaur, measuring over in length and weighing . A second possible species of ''Shastasaurus'', ''S. sikanniensis'', is known from the Pardonet Formation British Columbia, dating to the middle Norian age (about 210 million years ago). If ''S.sikanniensis'' belongs to ''Shastasaurus'', it would be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustace L
Eustace, also rendered Eustis, ( ) is the rendition in English of two phonetically similar Greek given names: *Εὔσταχυς (''Eústachys'') meaning "fruitful", "fecund"; literally "abundant in grain"; its Latin equivalents are ''Fæcundus/Fecundus'' *Εὐστάθιος (''Eustáthios'') meaning "steadfast", "stable"; literally "possessing good stability"; its exact Latin equivalents are ''Constans'' and its derivatives, ''Constantius'' and ''Constantinus''. Equivalents in other languages include Ostap (Ukrainian, Russian), Eustachy (Polish), Yevstaphiy (Russian), Eustachio (Italian), Eustache or Eustathe (French), Eustaquio (Spanish), Eustáquio (Portuguese), Eustàquio (Valencian), Ustes (Guyanese) and Eustice (English). The originally Hebrew name Ethan or Eitan can also mean "steadfast" or "stable". The Greek ''Eústachys'' is no longer used; ''Eustáthios/Ευστάθιος'' (usually transliterated ''Efstáthios'') on the other hand is still popular and often us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Million Years Ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds. Usage Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). Together they make a reference system, one to a quantity, the other to a particular place in a year numbering system that is ''time before the present''. Myr is deprecated in geology, but in astronomy ''Myr'' is standard. Where "myr" ''is'' seen in geology it is usually "Myr" (a unit of mega-years). In astronomy it is usually "Myr" (Million years). Debate In geology a debate remains open concerning the use of ''Myr'' (duration) plus ''Ma'' (million years ago) versus using only the term ''Ma''. In either case the term '' Ma'' is used in geology literature conforming to ISO 31-1 (now ISO 80000-3) and NIST 811 recommended practices. Traditional style geology literature is written The "ago" is implied, so that any such year number "X M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnian
The Carnian (less commonly, Karnian) is the lowermost stage of the Upper Triassic Series (or earliest age of the Late Triassic Epoch). It lasted from 237 to 227 million years ago (Ma). The Carnian is preceded by the Ladinian and is followed by the Norian. Its boundaries are not characterized by major extinctions or biotic turnovers, but a climatic event (known as the Carnian pluvial episode characterized by substantial rainfall) occurred during the Carnian and seems to be associated with important extinctions or biotic radiations. Stratigraphic definitions The Carnian was named in 1869 by Mojsisovics. It is unclear if it was named after the Carnic Alps or after the Austrian region of Carinthia (''Kärnten'' in German) or after the Carnia historical region in northwestern Italy. The name, however, was first used referring to a part of the Hallstatt Limestone cropping out in Austria. The base of the Carnian Stage is defined as the place in the stratigraphic record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set (mathematics), set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)