|
Thalattosauroidea
Thalattosauroidea is a superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. It was named in 1904 by paleontologist John Campbell Merriam to include the genus '' Thalattosaurus'' from California. Thalattosauroids are one of two groups of Thalattosauria, the other being Askeptosauroidea. Thalattosauroids make up the "traditional" thalattosaurs with large downturned snouts, short necks, and long, paddle-like tails. Classification Thalattosauria includes North American genera such as ''Thalattosaurus'' and ''Nectosaurus'' as well as recently described Chinese forms such as '' Xinpusaurus''. A 1999 study of thalattosaurs, which established much of the currently accepted phylogeny of the group, referred to Thalattosauroidea as Thalattosauria, while calling the larger group Thalattosauriformes. More recent phylogenetic studies have come upon the same conclusions, but refer to the group as Thalattosauroidea in order to contrast it with another superfamily of thalattosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosaur
Thalattosauria (Greek for "sea lizards") is an extinct order of prehistoric marine reptiles that lived in the middle to late Triassic period. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relationships are unresolved. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosauria
Thalattosauria (Greek for "sea lizards") is an extinct order of prehistoric marine reptiles that lived in the middle to late Triassic period. Thalattosaurs were diverse in size and shape, and are divided into two superfamilies: Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea. Askeptosauroids were endemic to the Tethys Ocean, their fossils have been found in Europe and China, and they were likely semiaquatic fish eaters with straight snouts and decent terrestrial abilities. Thalattosauroids were more specialized for aquatic life and most had unusual downturned snouts and crushing dentition. Thalattosauroids lived along the coasts of both Panthalassa and the Tethys Ocean, and were most diverse in China and western North America. The largest species of thalattosaurs grew to over 4 meters (13 feet) in length, including a long, flattened tail utilized in underwater propulsion. Although thalattosaurs bore a superficial resemblance to lizards, their exact relationships are unresolved. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claraziidae
Thalattosauroidea is a superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. It was named in 1904 by paleontologist John Campbell Merriam to include the genus ''Thalattosaurus'' from California. Thalattosauroids are one of two groups of Thalattosauria, the other being Askeptosauroidea. Thalattosauroids make up the "traditional" thalattosaurs with large downturned snouts, short necks, and long, paddle-like tails. Classification Thalattosauria includes North American genera such as ''Thalattosaurus'' and ''Nectosaurus'' as well as recently described Chinese forms such as ''Xinpusaurus''. A 1999 study of thalattosaurs, which established much of the currently accepted phylogeny of the group, referred to Thalattosauroidea as Thalattosauria, while calling the larger group Thalattosauriformes. More recent phylogenetic studies have come upon the same conclusions, but refer to the group as Thalattosauroidea in order to contrast it with another superfamily of thalattosaurs, As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
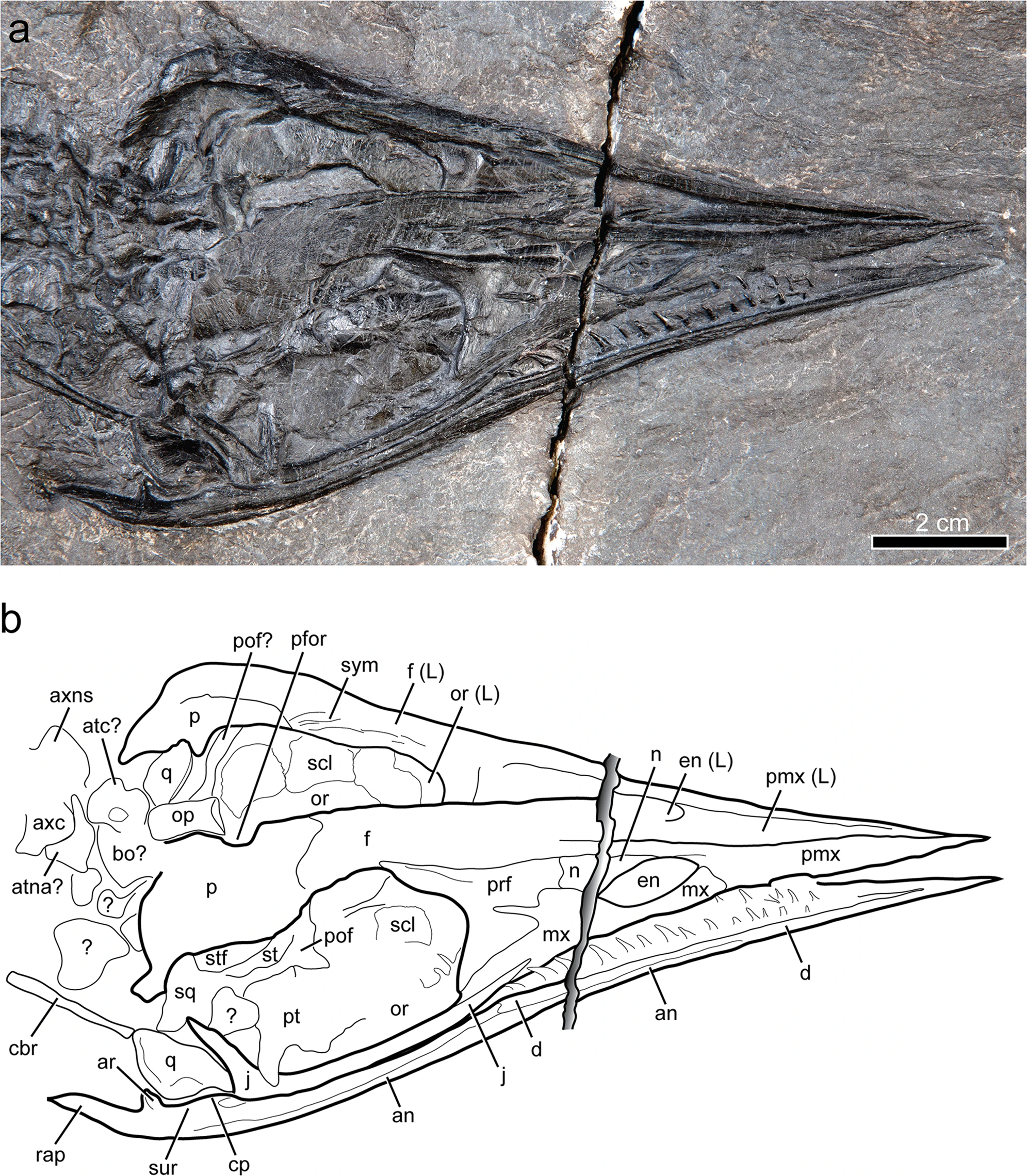
Gunakadeit
''Gunakadeit'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaur. It is known from a single species, ''Gunakadeit joseeae'', which is based on an articulated and mostly complete skeleton from the late Triassic (middle Norian) Hound Island Volcanics of Alaska. ''Gunakadeit'' possessed a variety of features from the two major suborders of thalattosaurs, Askeptosauroidea and Thalattosauroidea, and it is considered the most basal member of the latter group. Despite this, it is also the youngest known thalattosaur genus, with the group going extinct at the end of the Triassic. ''Gunakadeits basal position and relatively recent occurrence implies a 20-million-year ghost lineage connecting it to the rest of Thalattosauria. The skull ends in a sharply pointed and toothless tip like the askeptosauroid ''Endennasaurus'', but unlike ''Endennasaurus'', ''Gunakadeit'' had poorly developed joints and was likely exclusively aquatic in behavior. Discovery The holotype, UAMES 23258, was discovered by rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalattosaurus
''Thalattosaurus'' (pronounced: , "tha-la-to-SORE-us") meaning "sea lizard," from the Attic Greek ' (), "sea," and ' (), "lizard," is an extinct genus of marine reptile in the family Thalattosauroidea. They were aquatic diapsids that are known exclusively from the Triassic period. It was a long shellfish-eating reptile with paddle-like limbs and a down-turned rostrum occurring in the Lower and Middle Triassic Sulphur Mountain Formation of British Columbia as well as the Upper Triassic Hosselkus Limestone of California. It has gained notoriety as a result of studies on general diapsid phylogeny. Although originally described as four distinct species by Merriam in 1905, one was proven to be ''T. alexandrae'' upon further inspection and another has a missing type specimen. Currently it is believed to include two known species; ''Thalattosaurus alexandrae'' and ''T. borealis''. Discovery and naming In the summer of 1903 Annie Alexander led an expedition with Miss Edna Wemple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askeptosauroidea
Askeptosauroidea is a superfamily of thalattosaurs, a Triassic group of marine reptiles. Askeptosauroidea is one of two major subgroups of Thalattosauria, the other being Thalattosauroidea. It includes the family Askeptosauridae and a more basal form called ''Endennasaurus''. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram from Wu ''et al.'' (2009) showing the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... relationships of Askeptosauroidea: References Thalattosaurs Triassic first appearances Triassic extinctions {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concavispina
''Concavispina'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaur reptile from the early Late Triassic (Carnian stage) Xiaowa Formation of Guangling, Guizhou, southern China. It contains a single species, ''Concavispina biseridens''. It is known only from the holotype ZMNH M8804, a nearly complete 364 cm long skeleton. ''Concavispina'' can be differentiated from other thalattosaurs by possessing two rows of blunt teeth on the anterior part of the maxilla (upper jaw bone) and a V-shaped notch on the dorsal margin of each neural spine in the dorsal (back) vertebrae. Both its generic and specific names refer to these autapomorphies (unique characteristics), as ''Concavispina'' means "concave spine" and ''biseridens'' means "two rows of teeth". It is thought to be most closely related to ''Xinpusaurus'', as both taxa share three derived characters: a maxilla that is curved upward at its anterior end, a humerus (upper arm bone) that is wider near the shoulder than near the elbow, and the pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinpusaurus
''Xinpusaurus'' is an extinct genus of thalattosaur from the Late Triassic of Guanling in Guizhou, China. Several species have been named since 2000: the type species ''X. suni'' along with the species ''X. bamaolinensis'' and ''X. kohi''. A 2013 study proposed that all three species are synonymous with each other, in which case ''X. suni'' would be the only valid species, although a 2014 study argued that ''X. kohi'' was also valid. A fourth species, ''X. xingyiensis'', was described in 2016. Description ''Xinpusaurus'' is a thalattosaur, a group of triassic marine reptiles with long, paddle-like tails and short legs with independently movable digits. Specifically, it is a member of the group thalattosauroidea, which are characterized by their downturned premaxillae. ''Xinpusaurus'' had a short neck, a massive quadrate, and one of the few braincases preserved in thalattosaurs. The lower jaws of this genus show two different forms of dentary-surangular sutures, either a v-sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectosaurus
''Nectosaurus'' is a genus of thalattosaur (marine diapsid reptiles) which lived during the Late Triassic in what is now California. The type and only known species, ''Nectosaurus halius'', was found in the Hosselkus Limestone and described by John C. Merriam in 1905, making it one of the first thalattosaurians known (along with '' Thalattosaurus'').Sepkoski, J.J. (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". ''Bulletins of American Paleontology'' 363: 1-560. Discovery ''Nectosaurus'' is known from fragmentary remains. The holotype, UCMP 9124, is an incomplete skeleton including vertebrae, a humerus, coracoid, ulna, radius, and partial skull and mandibles. Many isolated bones from other localities were referred to the genus by Merriam in 1908. In addition, a partial skull from the same locality, UCMP 9120, was referred to the genus as ''Nectosaurus sp.'' in 1905. This specimen is much larger than any specimen of ''Nectosaurus halius'' but is otherwise similar to se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic Reptiles
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the chief terrestrial vertebrates during this time. A specialized subgroup of archosaurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
