|
Textile Sizing Machine
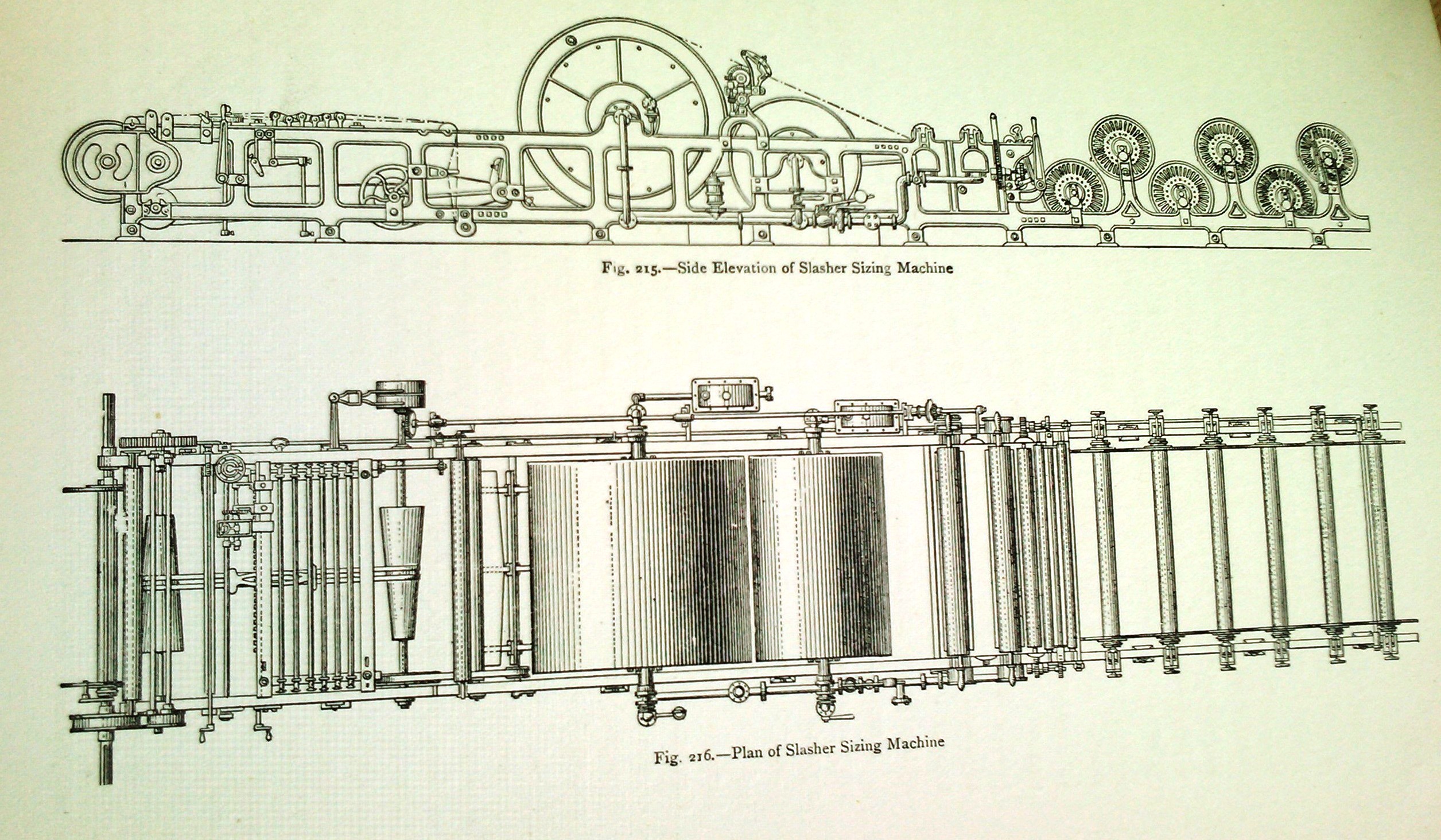
The technique of sizing a warp was mechanised during the nineteenth century when William Radcliffe and his assistant Thomas Johnson invented the sizing machine. The purpose of introducing ''size'', which is either a starchy substance for cotton or gelatinous mixture for woollen fibre, is to reduce the chances of threads fraying and breaking due to the friction of the weaving process. The size stiffens the thread and helps the fibres lie closely together. Many recipes for size can be found in textile manufacturing books. The recipes include flour, sago, china clay, types of soap, fats and some chemicals. Before mechanisation, the sizing process was a time-consuming task. The weaver painted the size onto the warp as it lay on the loom, then fanned it dry before weaving the cloth. The sizing machine improved the process by sizing a warp before putting it into the loom. The warp threads are first wound onto a large beam, which is then placed at one end of the sizing machine. Then th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sizing Machine
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption and wear characteristics of those materials. Sizing is used for oil-based surface preparation for gilding (sometimes called ''mordant'' in this context). It is used by painters and artists to prepare paper and textile surfaces for some art techniques. Sizing is used in photography to increase the sharpness of a print, to change the glossiness of a print, or for other purposes depending on the type of paper and printing technique. Fibers used in composite materials are treated with various sizing agents to promote adhesion with the matrix material. Sizing is used during paper manufacture to reduce the paper's tendency when dry to absorb liquid, with the goal of allowing inks and paints to remain on the surface of the paper and to dry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sago
Sago () is a starch extracted from the pith, or spongy core tissue, of various tropical palm stems, especially those of '' Metroxylon sagu''. It is a major staple food for the lowland peoples of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands, where it is called ''saksak'', ''rabia'' and ''sagu''. The largest supply of sago comes from Southeast Asia, particularly Indonesia and Malaysia. Large quantities of sago are sent to Europe and North America for cooking purposes. It is traditionally cooked and eaten in various forms, such as rolled into balls, mixed with boiling water to form a glue-like paste ( papeda), or as a pancake. Sago is often produced commercially in the form of "pearls" (small rounded starch aggregates, partly gelatinized by heating). Sago pearls can be boiled with water or milk and sugar to make a sweet sago pudding. Sago pearls are similar in appearance to the pearled starches of other origin, e.g. cassava starch (tapioca) and potato starch. They may be used interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burnley
Burnley () is a town and the administrative centre of the wider Borough of Burnley in Lancashire, England, with a 2001 population of 73,021. It is north of Manchester and east of Preston, at the confluence of the River Calder and River Brun. The town is located near the countryside to the south and east, with the towns of Padiham and Brierfield to the west and north respectively. It has a reputation as a regional centre of excellence for the manufacturing and aerospace industries. The town began to develop in the early medieval period as a number of farming hamlets surrounded by manor houses and royal forests, and has held a market for more than 700 years. During the Industrial Revolution it became one of Lancashire's most prominent mill towns; at its peak, it was one of the world's largest producers of cotton cloth and a major centre of engineering. Burnley has retained a strong manufacturing sector, and has strong economic links with the cities of Manchester an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Street Mill
Queen Street Mill is a former weaving mill in Harle Syke, a suburb to the north-east of Burnley, Lancashire, that is a It was built in 1894 for the Queen Street Manufacturing Company. It closed on 12 March 1982 and was mothballed, but was subsequently taken over by Burnley Borough Council and maintained as a museum. In the 1990s ownership passed to Lancashire Museums. Unique in being the world's only surviving operational steam-driven weaving shed, it received an Engineering Heritage Award in November 2010. Previously open to visitors and offering weaving demonstrations, the museum closed in September 2016 (except for pre-booked school parties). In April 2018 Lancashire County Council announced that the museum, along with Helmshore Mills Textile Museum and the Judges Lodgings in Lancaster, would reopen three days a week. Location Queen Street Mill is a former working mill that lies within Harle Syke. It is a suburb of Burnley, an industrial town in the North West of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accrington
Accrington is a town in the Hyndburn borough of Lancashire, England. It lies about east of Blackburn, west of Burnley, east of Preston, north of Manchester and is situated on the culverted River Hyndburn. Commonly abbreviated by locals to "Accy", the town has a population of 35,456 according to the 2011 census. Accrington is a former centre of the cotton and textile machinery industries. The town is famed for manufacturing the hardest and densest building bricks in the world, "The Accrington NORI" (iron), which were used in the construction of the Empire State Building and for the foundations of Blackpool Tower; famous for Accrington Stanley F.C. and the Haworth Art Gallery which holds Europe's largest collection of Tiffany glass. History Origin of the name The name Accrington appears to be Anglo-Saxon in origin. The earliest citing appears in the Parish of Whalley records of 850; where it is written ''Akeringastun''. In later records, the name variously appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same. Etymology and usage The word "loom" derives from the Old English ''geloma'', formed from ''ge-'' (perfective prefix) and ''loma'', a root of unknown origin; the whole word ''geloma'' meant a utensil, tool, or machine of any kind. In 1404 "lome" was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. By 1838 "loom" had gained the additional meaning of a machine for interlacing thread. Weaving Weaving is done by intersecting the longitudinal threads, the warp, i.e. "that which is thrown across", with the transverse threads, the weft, i.e. "that which is woven". The major components of the loom are the warp beam, heddles, harnesses or shafts (as few as two, four is common, sixteen not unheard of), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, and precursors to catalysts. When used for cleaning, soap solubilizes particles and grime, which can then be separated from the article being cleaned. In hand washing, as a surfactant, when lathered with a little water, soap kills microorganisms by disorganizing their membrane lipid bilayer and denaturing their proteins. It also emulsifies oils, enabling them to be carried away by running water. Soap is created by mixing fats and oils with a base. A similar process is used for making detergent which is also created by combining chemical compounds in a mixer. Humans have used soap for millennia. Evidence exists for the production of soap-like materials in ancient Babylon around 280 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Clay
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () octahedra. Rocks that are rich in kaolinite are known as kaolin () or china clay. Kaolin is occasionally referred to by the antiquated term lithomarge, from the Ancient Greek ''litho-'' and Latin ''marga'', meaning 'stone of marl'. Presently the name lithomarge can refer to a compacted, massive form of kaolin. The name ''kaolin'' is derived from Gaoling (), a Chinese village near Jingdezhen in southeastern China's Jiangxi Province. The name entered English in 1727 from the French version of the word: , following François Xavier d'Entrecolles's reports on the making of Jingdezhen porcelain. Kaolinite has a low shrink–swell capacity and a low cation-exchange capacity (1–15 meq/100 g). It is a soft, earthy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flour
Flour is a powder made by grinding raw grains, roots, beans, nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredient of bread, which is a staple food for many cultures. Corn flour has been important in Mesoamerican cuisine since ancient times and remains a staple in the Americas. Rye flour is a constituent of bread in central and northern Europe. Cereal flour consists either of the endosperm, germ, and bran together (whole-grain flour) or of the endosperm alone (refined flour). ''Meal'' is either differentiable from flour as having slightly coarser particle size (degree of comminution) or is synonymous with flour; the word is used both ways. For example, the word '' cornmeal'' often connotes a grittier texture whereas corn flour connotes fine powder, although there is no codified dividing line. The CDC has cautioned not to eat raw flour doughs or batters. Raw flour can contain bacteria lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption and wear characteristics of those materials. Sizing is used for oil-based surface preparation for gilding (sometimes called ''mordant'' in this context). It is used by painters and artists to prepare paper and textile surfaces for some art techniques. Sizing is used in photography to increase the sharpness of a print, to change the glossiness of a print, or for other purposes depending on the type of paper and printing technique. Fibers used in composite materials are treated with various sizing agents to promote adhesion with the matrix material. Sizing is used during paper manufacture to reduce the paper's tendency when dry to absorb liquid, with the goal of allowing inks and paints to remain on the surface of the paper and to dry th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
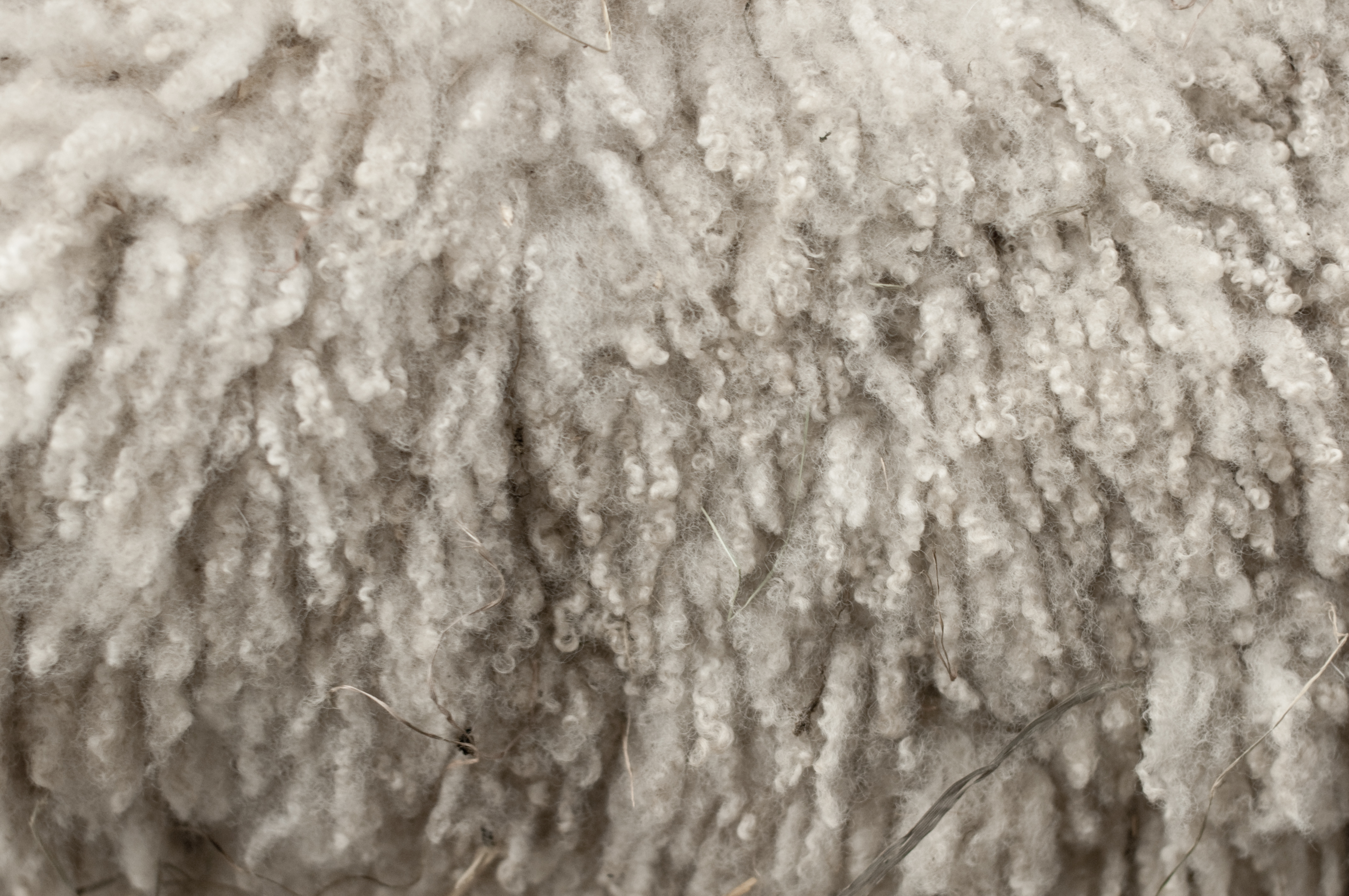
Wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool. As an animal fibre, wool consists of protein together with a small percentage of lipids. This makes it chemically quite distinct from cotton and other plant fibres, which are mainly cellulose. Characteristics Wool is produced by follicles which are small cells located in the skin. These follicles are located in the upper layer of the skin called the epidermis and push down into the second skin layer called the dermis as the wool fibers grow. Follicles can be classed as either primary or secondary follicles. Primary follicles produce three types of fiber: kemp Kemp may refer to: Places * Kemp, Illinois * Kemp, Ohio * Kemp, Oklahoma * Kemp, Texas * Kemp Land and Kemp Coast, Antarctica * Kemp Town, a 19th-century estate in East Sussex, En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_in_New_Guinea.jpg)







