|
Sizing Machine
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption and wear characteristics of those materials. Sizing is used for oil-based surface preparation for gilding (sometimes called ''mordant'' in this context). It is used by painters and artists to prepare paper and textile surfaces for some art techniques. Sizing is used in photography to increase the sharpness of a print, to change the glossiness of a print, or for other purposes depending on the type of paper and printing technique. Fibers used in composite materials are treated with various sizing agents to promote adhesion with the matrix material. Sizing is used during paper manufacture to reduce the paper's tendency when dry to absorb liquid, with the goal of allowing inks and paints to remain on the surface of the paper and to dry the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filler (materials)
Filler materials are particles added to binders (resin, thermoplastics, cement) to make a composite material. Filler materials improve specific properties or make the product cheaper. Coarse filler materials such as construction aggregate and rebar are used in the building industry to make plaster, mortar and concrete. Powdered fillers are mixed in with elastomers and plastics. Worldwide, more than 53 million tons of fillers (with a net worth of ca. US$18 billion) are used every year in the production of paper, plastics, rubber, paints, coatings, adhesives, and sealants. Fillers are produced by more than 700 companies, rank among the world's major raw materials and are contained in a variety of goods for daily consumer needs. The top filler materials used are ground calcium carbonate (GCC), precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC), kaolin, talc, and carbon black. Filler materials can affect the tensile strength, toughness, heat resistance, color, clarity, etc. This can be util ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Writing Paper
Printing and writing papers are paper grades used for newspapers, magazines, catalogs, books, notebooks, commercial printing, business forms, stationeries, copying and digital printing. About 1/3 of the total pulp and paper marked (in 2000) is printing and writing papers. The pulp or fibers used in printing and writing papers are extracted from wood using a chemical or mechanical process. Paper standards The most common paper size in office use is US letter in the US, and A4 where the ISO paper series are in use. A4 ("metric") paper is easier to obtain in the US than US letter can be had elsewhere.. The ISO 216:2007 is the current international standard for paper sizes, including writing papers and some types of printing papers. This standard describes the paper sizes under what the ISO calls the A, B, and C series formats. Not all countries follow ISO 216. North America, for instance, uses certain terms to describe paper sizes, such as Letter, Legal, Junior Legal, and Ledger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linseed Oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colorless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by solvent extraction. Owing to its polymer-forming properties, linseed oil is often blended with combinations of other oils, resins or solvents as an impregnator, drying oil finish or varnish in wood finishing, as a pigment binder in oil paints, as a plasticizer and hardener in putty, and in the manufacture of linoleum. Linseed oil use has declined over the past several decades with increased availability of synthetic alkyd resins—which function similarly but resist yellowing. Structure and composition : 450px, Representative triglyceride found in a linseed oil, a triester ( , and Linseed oil is a triglyceride, like other fats. Linseed oil is distinctive for its unusually large amount of α-linolenic acid, which oxidises in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbit-skin Glue
Rabbit-skin glue is a type of animal glue used as a sizing and an adhesive, it is essentially refined rabbit collagen. The glue has been used for centuries for stretching and priming canvases for oil painting. It has also been an ingredient in traditional gesso. History In traditional oil painting as practiced by the Renaissance painter, skin glue was used to seal the canvas. This is necessary because the linseed oil that forms the base of most oil paint contains linolenic acid that will destroy the canvas fibers over time. Renaissance artists also knew that pure size (hide glue) became brittle once dry, and would mix it with oil and chalk to make a "half-ground" for canvases. Pure hide glue was usually applied only to rigid supports like panels. Though this does help to seal the canvas or panel, artists still applied a layer of "oil ground", which was often lead based paint, in order to provide a binding layer for the final oil paint to adhere to. Production Rabbit skin glue is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic films, papers, and cosmetics. Substances containing gelatin or functioning in a similar way are called gelatinous substances. Gelatin is an irreversibly hydrolyzed form of collagen, wherein the hydrolysis reduces protein fibrils into smaller peptides; depending on the physical and chemical methods of denaturation, the molecular weight of the peptides falls within a broad range. Gelatin is present in gelatin desserts, most gummy candy and marshmallows, ice creams, dips, and yogurts. Gelatin for cooking comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosin
Rosin (), also known as colophony or Greek pitch (), is a resinous material obtained from pine trees and other plants, mostly conifers. The primary components of rosin are diterpenoids, i.e., C20 carboxylic acids. Rosin consists mainly of resin acids, especially abietic acid. Rosin often appears as a semi-transparent, brittle substance that ranges in color from yellow to black and melts at stove-top temperatures. In addition to industrial applications such as in varnishes, adhesives, and sealing wax, rosin is used with string instruments on the bow hair to enhance its ability to grip and sound the strings, and it provides grip in various sports and activities. Rosin also serves as an ingredient in medicinal and pharmaceutical formulations and can cause contact dermatitis or occupational asthma in sensitive individuals. It is an FDA approved food additive. The name "colophony" originates from , Latin for "resin from Colophon" (), an ancient Ionic city. Properties R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinic Anhydride
Succinic anhydride, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2CO)2O. This colorless solid is the acid anhydride of succinic acid. Preparation In the laboratory, this material can be prepared by dehydration of succinic acid. Such dehydration can occur with the help of acetyl chloride or phosphoryl chloride, or thermally. Industrially, succinic anhydride is prepared by catalytic hydrogenation of maleic anhydride. Reactions Succinic anhydride hydrolyzes readily to give succinic acid: :(CH2CO)2O + H2O → (CH2CO2H)2 With alcohols (ROH), a similar reaction occurs, delivering the monoester: :(CH2CO)2O + ROH → RO2CCH2CH2CO2H Succinic anhydride is used in acylations under Friedel-Crafts conditions, as illustrated by the industrial route to the drug Fenbufen. Related compounds Maleic anhydride undergoes the Alder-ene reaction with alkenes to give alkenylsuccinic anhydrides. Such compounds are sizing agents in the paper industry. In this role, the anhydride is propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
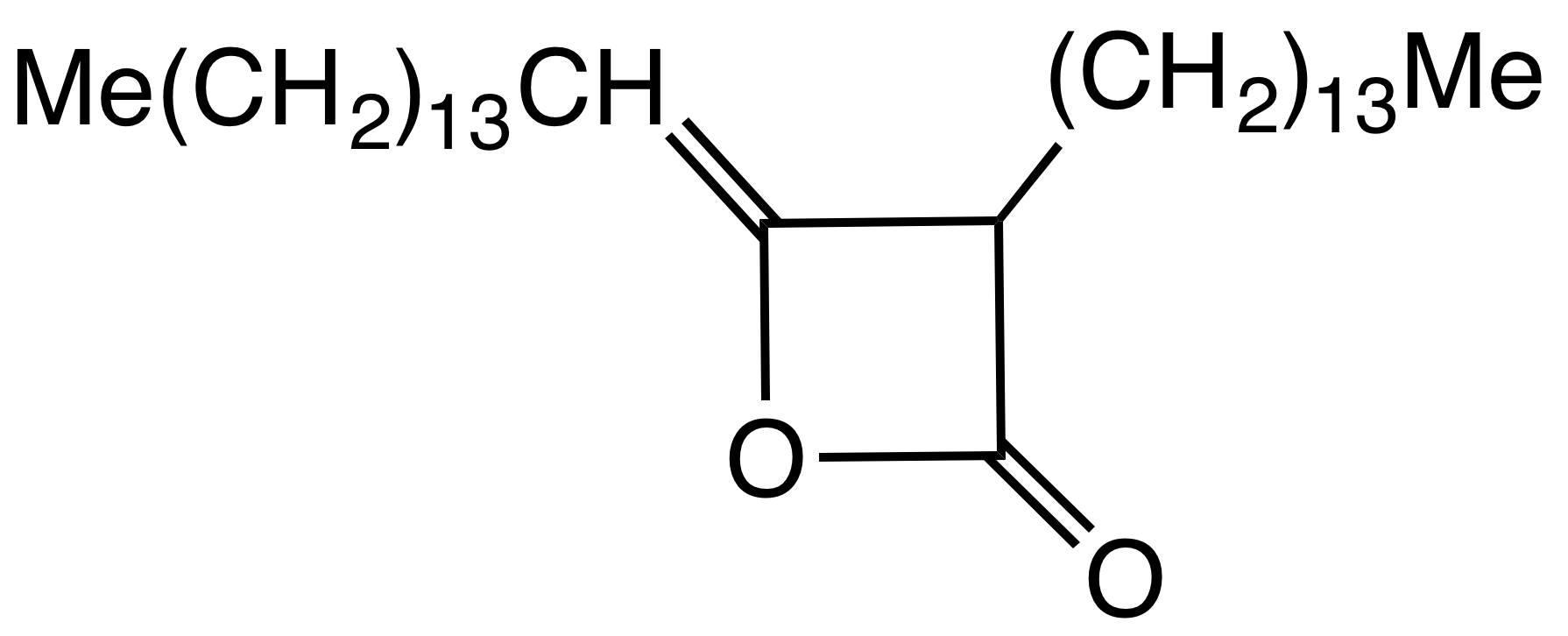
Alkyl Ketene Dimer
Alkyl ketene dimers (AKDs) are a family of organic compounds based on the 4-membered ring system of 2-oxetanone, oxetan-2-one, which is also the central structural element of propiolactone and diketene. Attached to the oxetane ring of technically relevant alkyl ketene dimers there is a C12 – C16 alkyl group in the 3-position and a C13 – C17 alkylidene group in the 4-position. The main application of alkylated ketene dimers is in the sizing of paper and cardboard, as well as in the hydrophobation of cellulose fibers. The products thus modified are distinguished by higher mechanical strengths and less penetration of water, inks or printing inks. AKD's feature hydrophobic alkyl groups extending from a beta-propiolactone ring. A specific example is derived from the dimerization of the ketene of stearic acid. This ketene is generated by pyrolysis of stearoyl chloride. AKD's react with the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose via esterification reaction. The esterification is competiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Brightener
Optical brighteners, optical brightening agents (OBAs), fluorescent brightening agents (FBAs), or fluorescent whitening agents (FWAs), are chemical compounds that absorb light in the ultraviolet and violet region (usually 340-370 nm) of the electromagnetic spectrum, and re-emit light in the blue region (typically 420-470 nm) through the phenomenon of fluorescence. These additives are often used to enhance the appearance of color of fabric and paper, causing a "whitening" effect; they make intrinsically yellow/orange materials look less so, by compensating the deficit in blue and purple light reflected by the material, with the blue and purple optical emission of the fluorophore. Properties The most common classes of compounds with this property are the stilbenes, e.g., 4,4′-diamino-2,2′-stilbenedisulfonic acid. Older, non-commercial fluorescent compounds include umbelliferone, which absorbs in the UV portion of the spectrum and re-emit it in the blue portion of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobe
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. The term ''hydrophobic''—which comes from the Ancient Greek (), "having a fear of water", constructed Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophile
A hydrophile is a molecule or other molecular entity that is intermolecular force, attracted to water molecules and tends to be dissolution (chemistry), dissolved by water.Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon'' Oxford: Clarendon Press. In contrast, hydrophobes are not attracted to water and may seem to be repelled by it. Hygroscopics ''are'' attracted to water, but are not dissolved by water. Molecules A hydrophilic molecule or portion of a molecule is one whose interactions with water and other polar substances are more Thermodynamics, thermodynamically favorable than their interactions with oil or other hydrophobic solvents. They are typically charge-polarized and capable of hydrogen bonding. This makes these molecules soluble not only in water but also in Solvent#Solvent classifications, polar solvents. Hydrophilic molecules (and portions of molecules) can be contrasted with hydrophobic molecules (and portions of molecules). In some cases, both hydrophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphiphile
In chemistry, an amphiphile (), or amphipath, is a chemical compound possessing both hydrophilic (''water-loving'', polar) and lipophilic (''fat-loving'', nonpolar) properties. Such a compound is called amphiphilic or amphipathic. Amphiphilic compounds include surfactants and detergents. The phospholipid amphiphiles are the major structural component of cell membranes. Amphiphiles are the basis for a number of areas of research in chemistry and biochemistry, notably that of lipid polymorphism. Organic compounds containing hydrophilic groups at both ends of the molecule are called bolaamphiphilic. The micelles they form in the aggregate are prolate. Structure The lipophilic group is typically a large hydrocarbon moiety, such as a long chain of the form CH3(CH2)n, with n > 4. The hydrophilic group falls into one of the following categories: # charged groups #* anionic. Examples, with the lipophilic part of the molecule represented by ''R'', are: #** carboxylates: RCO2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |