|
Tetraxylopteris
'' Tetraxylopteris'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants of the Middle to Upper Devonian (around ). Fossils were first found in New York State, USA. A second species was later found in Venezuela. Description Fossils of ''Tetraxylopteris'' have so far been discovered in two locations. ''T. schmidtii'' was named from the Catskill Clastic Wedge, New York State, United States of America, in rocks of Middle to Upper Devonian age (around ). ''T. reposana'' was found in the Campo Chico Formation, north-west Venezuela, in beds believed to be of Frasnian age (). The overall shape of ''Tetraxylopteris'' consisted of a complex system of branches. The main stem was 'pseudomonopodial', i.e. it divided dichotomously to produce side stems while the main stem maintained its identity. The main and side stems then bore three orders of branches (i.e. the first branches from the stems divided twice more). (There were possibly four orders in ''T. reposana''.) The branches were arranged in opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraxylopteris
'' Tetraxylopteris'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants of the Middle to Upper Devonian (around ). Fossils were first found in New York State, USA. A second species was later found in Venezuela. Description Fossils of ''Tetraxylopteris'' have so far been discovered in two locations. ''T. schmidtii'' was named from the Catskill Clastic Wedge, New York State, United States of America, in rocks of Middle to Upper Devonian age (around ). ''T. reposana'' was found in the Campo Chico Formation, north-west Venezuela, in beds believed to be of Frasnian age (). The overall shape of ''Tetraxylopteris'' consisted of a complex system of branches. The main stem was 'pseudomonopodial', i.e. it divided dichotomously to produce side stems while the main stem maintained its identity. The main and side stems then bore three orders of branches (i.e. the first branches from the stems divided twice more). (There were possibly four orders in ''T. reposana''.) The branches were arranged in opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
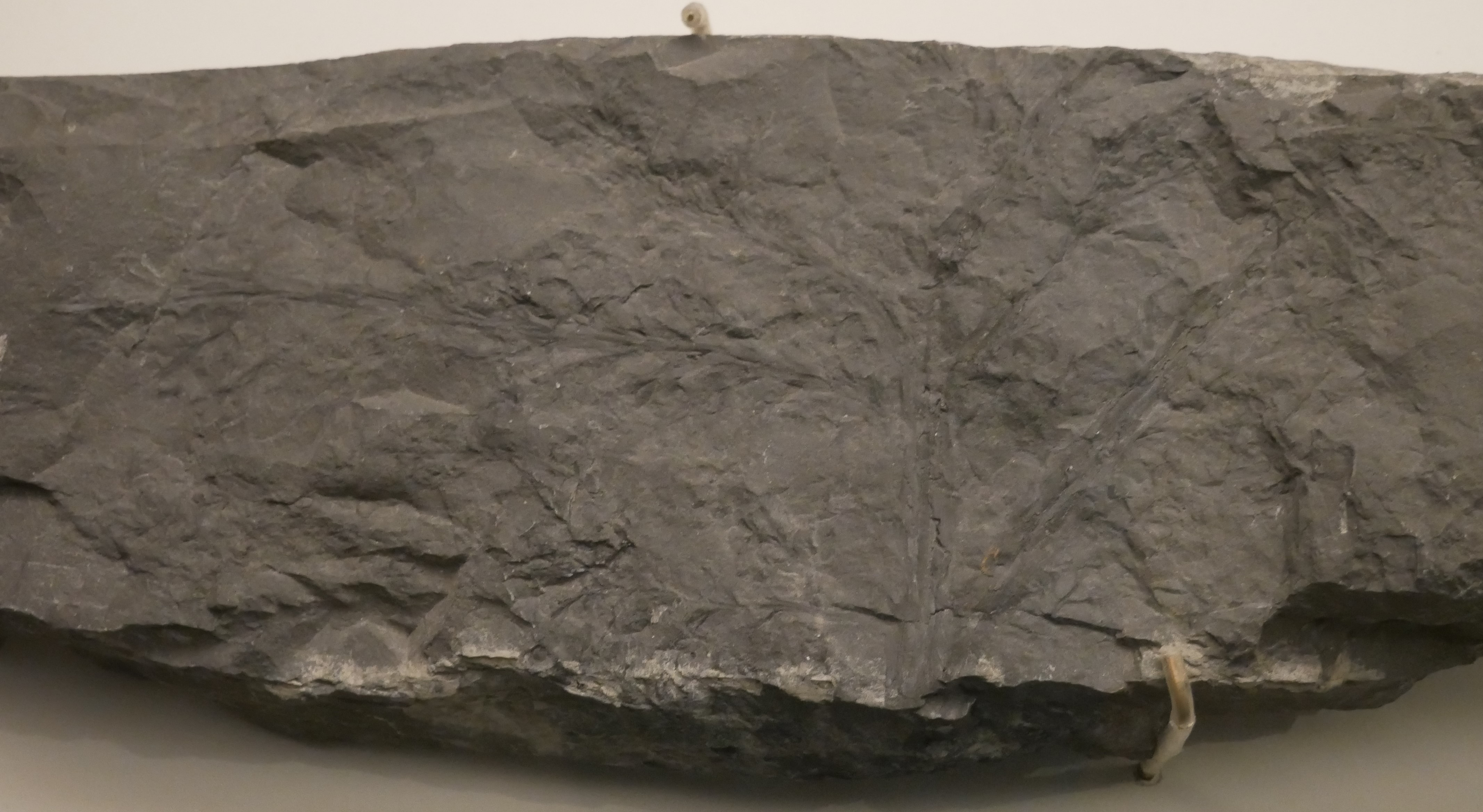
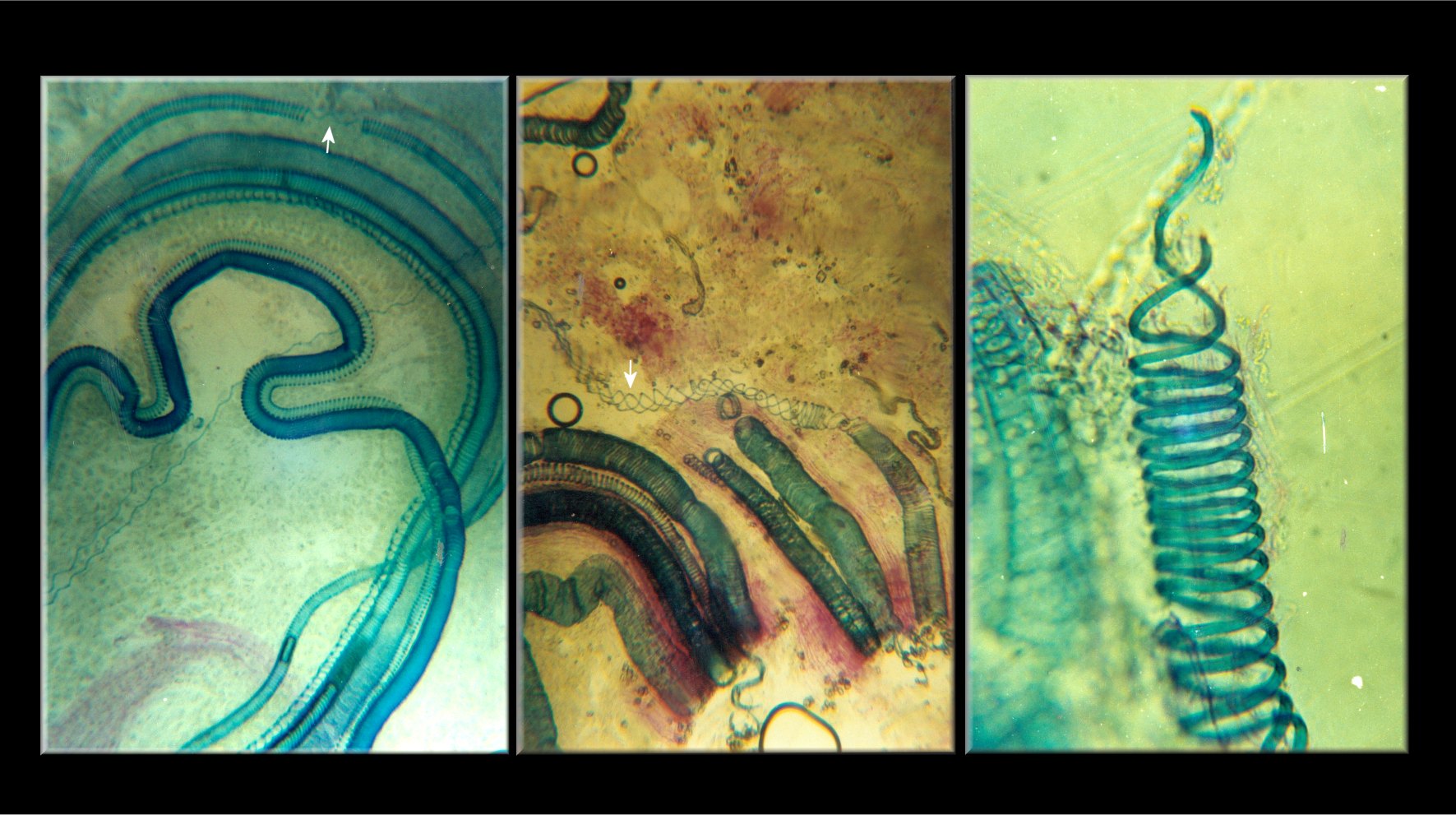
Tetraxylopteris Reposana Sterile Branches
'' Tetraxylopteris'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants of the Middle to Upper Devonian (around ). Fossils were first found in New York State, USA. A second species was later found in Venezuela. Description Fossils of ''Tetraxylopteris'' have so far been discovered in two locations. ''T. schmidtii'' was named from the Catskill Clastic Wedge, New York State, United States of America, in rocks of Middle to Upper Devonian age (around ). ''T. reposana'' was found in the Campo Chico Formation, north-west Venezuela, in beds believed to be of Frasnian age (). The overall shape of ''Tetraxylopteris'' consisted of a complex system of branches. The main stem was 'pseudomonopodial', i.e. it divided dichotomously to produce side stems while the main stem maintained its identity. The main and side stems then bore three orders of branches (i.e. the first branches from the stems divided twice more). (There were possibly four orders in ''T. reposana''.) The branches were arranged in opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progymnosperm
The progymnosperms are an extinct group of woody, spore-bearing plants that is presumed to have evolved from the trimerophytes, and eventually gave rise to the seed plants, gymnosperms, ancestral to gymnosperms, acrogymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). They have been treated formally at the rank (botany), rank of division Progymnospermophyta or class Progymnospermopsida (as opposite). The stratigraphically oldest known examples belong to the Middle Devonian order the Aneurophytales, with forms such as ''Protopteridium'', in which the vegetative organs consisted of relatively loose clusters of axes. ''Tetraxylopteris'' is another example of a genus lacking leaves. In more advanced aneurophytaleans such as ''Aneurophyton'' these vegetative organs started to look rather more like fronds, and eventually during Late Devonian times the aneurophytaleans are presumed to have given rise to the pteridosperm order, the Lyginopteridales. In Late Devonian times, another group of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pertica
''Pertica'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants of the Early to Middle Devonian (around ). It has been placed in the "trimerophytes", a strongly paraphyletic group of early members of the lineage leading to modern ferns and seed plants. Description ''Pertica quadrifaria'' (the type species of the genus) was described in 1972 from compression fossils found in the Trout Valley Formation of northern Maine, USA. It was an upright plant which grew to perhaps as much as a metre (3 ft) in height. It comprised a main, straight stem (axis) with side branches which developed dichotomously, branching many times at increasingly shorter intervals. Some of the terminal branchlets bore masses of erect paired, ellipsoidal sporangia in distinctive tight clusters. The branches were arranged in a spiral pattern, forming four vertical rows. The specific epithet ''quadrifaria'' refers to this growth habit. ''Pertica varia'' was described in 1976 from the Devonian of Eastern Canada. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progymnospermopsida
The progymnosperms are an extinct group of woody, spore-bearing plants that is presumed to have evolved from the trimerophytes, and eventually gave rise to the gymnosperms, ancestral to acrogymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). They have been treated formally at the rank of division Progymnospermophyta or class Progymnospermopsida (as opposite). The stratigraphically oldest known examples belong to the Middle Devonian order the Aneurophytales, with forms such as '' Protopteridium'', in which the vegetative organs consisted of relatively loose clusters of axes. ''Tetraxylopteris'' is another example of a genus lacking leaves. In more advanced aneurophytaleans such as ''Aneurophyton'' these vegetative organs started to look rather more like fronds, and eventually during Late Devonian times the aneurophytaleans are presumed to have given rise to the pteridosperm order, the Lyginopteridales. In Late Devonian times, another group of progymnosperms gave rise to the first re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frasnian
The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Givetian Stage and followed by the Famennian Stage. Major reef-building was under way during the Frasnian Stage, particularly in western Canada and Australia. On land, the first forests were taking shape. In North America, the Antler orogeny peaked, which were contemporary with the Bretonic phase of the Variscan orogeny in Europe. The Frasnian coincides with the second half of the "charcoal gap" in the fossil record, a time when atmospheric oxygen levels were below 13 percent, the minimum necessary to sustain wildfires. North American subdivisions of the Frasnian include * West Falls Group * Sonyea Group * Genesee Group Name and definition The Frasnian Stage was proposed in 1879 by French geologist Jules Gosselet Jules-Auguste Gosselet (19 April 1832 – 20 March 1916) was a French geologist born in Cambrai, France. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Devonian Genus Extinctions
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) In scheduling, tardiness is a measure of a delay in exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Devonian First Appearances
Middle or The Middle may refer to: * Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits. Places * Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man * Middle Bay (other) * Middle Brook (other) * Middle Creek (other) * Middle Island (other) * Middle Lake (other) * Middle Mountain, California * Middle Peninsula, Chesapeake Bay, Virginia * Middle Range, a former name of the Xueshan Range on Taiwan Island * Middle River (other) * Middle Rocks, two rocks at the eastern opening of the Straits of Singapore * Middle Sound, a bay in North Carolina * Middle Township (other) * Middle East Music * "Middle" (song), 2015 * "The Middle" (Jimmy Eat World song), 2001 * "The Middle" (Zedd, Maren Morris and Grey song), 2018 *"Middle", a song by Rocket from the Crypt from their 1995 album ''Scream, Dracula, Scream!'' *"The Middle", a song by Demi Lovato from their debut album ''Don't Forget'' *"The Middle", a song by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Devonian Plants
Middle or The Middle may refer to: * Centre (geometry), the point equally distant from the outer limits. Places * Middle (sheading), a subdivision of the Isle of Man * Middle Bay (other) * Middle Brook (other) * Middle Creek (other) * Middle Island (other) * Middle Lake (other) * Middle Mountain, California * Middle Peninsula, Chesapeake Bay, Virginia * Middle Range, a former name of the Xueshan Range on Taiwan Island * Middle River (other) * Middle Rocks, two rocks at the eastern opening of the Straits of Singapore * Middle Sound, a bay in North Carolina * Middle Township (other) * Middle East Music * "Middle" (song), 2015 * "The Middle" (Jimmy Eat World song), 2001 * "The Middle" (Zedd, Maren Morris and Grey song), 2018 *"Middle", a song by Rocket from the Crypt from their 1995 album ''Scream, Dracula, Scream!'' *"The Middle", a song by Demi Lovato from their debut album ''Don't Forget'' *"The Middle", a song by T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphyllophyte
The euphyllophytes are a clade of plants within the tracheophytes (the vascular plants). The group may be treated as an unranked clade, a division under the name Euphyllophyta or a subdivision under the name Euphyllophytina. The euphyllophytes are characterized by the possession of true leaves ("megaphylls"), and comprise one of two major lineages of extant vascular plants. As shown in the cladogram below, the euphyllophytes have a sister relationship to the lycopodiophytes or lycopsids. Unlike the lycopodiophytes, which consist of relatively few presently living or extant taxa, the euphyllophytes comprise the vast majority of vascular plant lineages that have evolved since both groups shared a common ancestor more than 400 million years ago. The euphyllophytes consist of two lineages, the spermatophytes A spermatophyte (; ), also known as phanerogam (taxon Phanerogamae) or phaenogam (taxon Phaenogamae), is any plant that produces seeds, hence the alternative name seed plant. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |