|
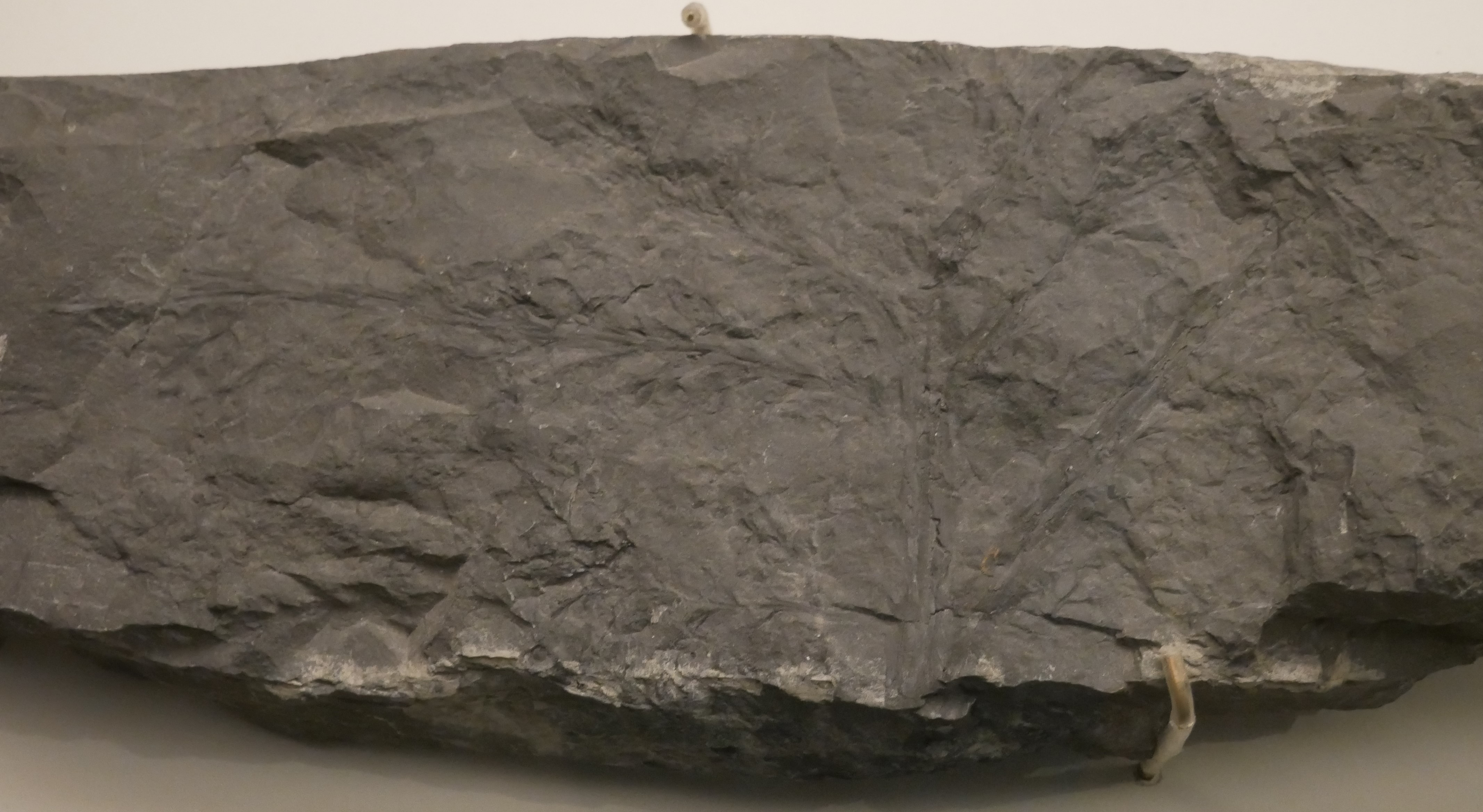
Progymnosperm
The progymnosperms are an extinct group of woody, spore-bearing plants that is presumed to have evolved from the trimerophytes, and eventually gave rise to the seed plants, gymnosperms, ancestral to gymnosperms, acrogymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). They have been treated formally at the rank (botany), rank of division Progymnospermophyta or class Progymnospermopsida (as opposite). The stratigraphically oldest known examples belong to the Middle Devonian order the Aneurophytales, with forms such as ''Protopteridium'', in which the vegetative organs consisted of relatively loose clusters of axes. ''Tetraxylopteris'' is another example of a genus lacking leaves. In more advanced aneurophytaleans such as ''Aneurophyton'' these vegetative organs started to look rather more like fronds, and eventually during Late Devonian times the aneurophytaleans are presumed to have given rise to the pteridosperm order, the Lyginopteridales. In Late Devonian times, another group of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeopteris
''Archaeopteris'' is an extinct genus of progymnosperm tree with fern-like leaves. A useful index fossil, this tree is found in strata dating from the Upper Devonian to Lower Carboniferous (), the oldest fossils being 385 million years old, and had global distribution. Until the 2007 discovery of '' Wattieza'', many scientists considered ''Archaeopteris'' to be the earliest known tree. Bearing buds, reinforced branch joints, and branched trunks similar to today's wood, it is more reminiscent of modern seed-bearing trees than other spore bearing taxa; It combines characteristics of woody trees and herbaceous ferns, and belongs to the progymnosperms, a group of extinct plants with gymnosperm-like wood but that produce spores rather than seeds. Taxonomy John William Dawson described the genus in 1871. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaīos'', "ancient"), and (''ptéris'', "fern"). ''Archaeopteris'' was originally classified as a fern, and it remained classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
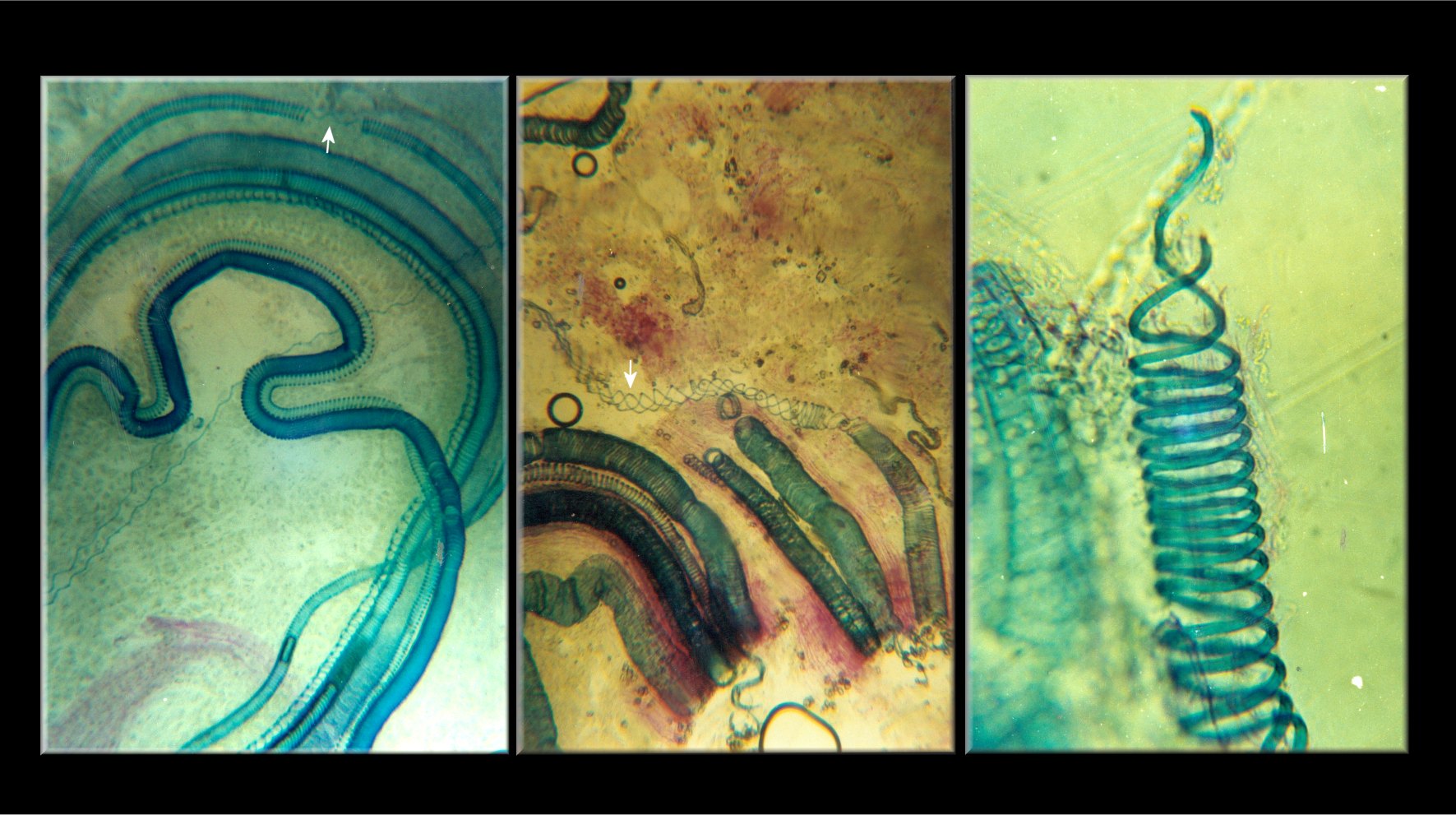
Tetraxylopteris
'' Tetraxylopteris'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants of the Middle to Upper Devonian (around ). Fossils were first found in New York State, USA. A second species was later found in Venezuela. Description Fossils of ''Tetraxylopteris'' have so far been discovered in two locations. ''T. schmidtii'' was named from the Catskill Clastic Wedge, New York State, United States of America, in rocks of Middle to Upper Devonian age (around ). ''T. reposana'' was found in the Campo Chico Formation, north-west Venezuela, in beds believed to be of Frasnian age (). The overall shape of ''Tetraxylopteris'' consisted of a complex system of branches. The main stem was 'pseudomonopodial', i.e. it divided dichotomously to produce side stems while the main stem maintained its identity. The main and side stems then bore three orders of branches (i.e. the first branches from the stems divided twice more). (There were possibly four orders in ''T. reposana''.) The branches were arranged in opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterosporous
Heterospory is the production of spores of two different sizes and sexes by the sporophytes of land plants. The smaller of these, the microspore, is male and the larger megaspore is female. Heterospory evolved during the Devonian period from isospory independently in several plant groups: the clubmosses, the ferns including the arborescent horsetails, and progymnosperms. This occurred as part of the process of evolution of the timing of sex differentiation.Sussex, I.M. (1966) The origin and development of heterospory in vascular plants. Chapter 9 in ''Trends in Plant morphogenesis'', ed. by E.G. Cutter, Longmans. Origin of heterospory Heterospory evolved due to natural selection that favoured an increase in propagule size compared with the smaller spores of homosporous plants. Heterosporous plants, similar to anisosporic plants, produce two different sized spores in separate sporangia that develop into separate male and female gametophytes. It is proposed that the emergence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyginopteridales
The Lyginopteridales were the archetypal pteridosperms: They were the first plant fossils to be described as pteridosperms and, thus, the group on which the concept of pteridosperms was first developed;Oliver, F. W. & Scott, D. H. (1904). "On the structure of the Palaeozoic seed ''Lagenostoma Lomaxi'', with a statement of the evidence upon which it is referred to ''Lyginodendron''." ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B,'' 197: 193-247. they are the stratigraphically oldest-known pteridosperms, occurring first in late Devonian strata;Rothwell, G. W., Scheckler, S. E. & Gillespie, W. H. (1989). "''Elkinsia'' gen. nov., a Late Devonian gymnosperm with cupulate ovules." ''Botanical Gazette,'' 150: 170-189. and they have the most primitive features, most notably in the structure of their ovules.Long, A. G. (1959). "On the structure of ''Calymmatotheca kidstoni'' Calder (emended) and ''Genomosperma latens'' gen. et sp. nov. from the Calciferous Sand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aneurophyton
''Aneurophyton'' is a genus of extinct vascular plants that belong to the Aneurophytales, a class of progymnosperms. The genus is primarily known from records of two well-known species found in mostly Middle Devonian and Upper Devonian (late Eifelian to Famennian) outcrops in Belgium, China (West Junggar), Germany, and the United States (New York). Some uncertain species within the genus are also recorded from Middle Devonian outcrops in Kazakhstan, Russia (Timan and Siberia), and the Ukraine. While a number of species have been described in the paleobotanical literature, the genus likely only contains two well-circumscribed species, ''A. germanicum'' and ''A. doui'', and possibly a third species, ''A. olnense'', from Fammenian outcrops in Belgium. If the ages of the Early Devonian (Emsian) records of ''A. germanicum'' reported from Siberia are confirmed, these would constitute the oldest records of this genus. See also *Progymnosperm The progymnosperms are an extinct group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosperms
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμνόσπερμος ( el, γυμνός, translit=gymnos, lit=naked, label=none and el, σπέρμα, translit=sperma, lit=seed, label=none), literally meaning 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds (called ovules in their unfertilized state). The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or leaves, which are often modified to form cones, or solitary as in yew, ''Torreya'', ''Ginkgo''. Gymnosperm lifecycles involve alternation of generations. They have a dominant diploid sporophyte phase and a reduced haploid gametophyte phase which is dependent on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noeggerathiales
Noeggerathiales is a now-extinct order of vascular plants. The fossil range of the order extends from the Upper Carboniferous to the upper Permian (Lopingian). Due to gaps in the fossil record, the group is incompletely known and poorly defined, and their taxonomic status and position in the plant kingdom are uncertain. The Noeggerathiales have been proposed in the evolutionary scheme in two remotely related groups of vascular plants, the Pteropsida and the Sphenopsida. Noeggerathiales have been previously linked to horsetails and ferns, but are currently believed to be progymnosperms. Noeggerathiales had a tree fern The tree ferns are arborescent (tree-like) ferns that grow with a trunk elevating the fronds above ground level, making them trees. Many extant tree ferns are members of the order Cyatheales, to which belong the families Cyatheaceae (scaly tree ... like appearance, with leaves sprouting from the top of an unbranched trunk. They were primarily confined to the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeopteridales
The Archaeopteridales are an extinct order of plants belonging to Progymnospermae, and dominant forest trees of the Late Devonian. They reproduced with spores rather than seeds. References Middle Devonian plants Prehistoric plant orders Late Devonian plants Middle Devonian first appearances Late Devonian extinctions {{devonian-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyniopsida
The rhyniophytes are a group of extinct early vascular plants that are considered to be similar to the genus ''Rhynia'', found in the Early Devonian (around ). Sources vary in the name and rank used for this group, some treating it as the class Rhyniopsida, others as the subdivision Rhyniophytina or the division Rhyniophyta. The first definition of the group, under the name Rhyniophytina, was by Banks, since when there have been many redefinitions, including by Banks himself. "As a result, the Rhyniophytina have slowly dissolved into a heterogeneous collection of plants ... the group contains only one species on which all authors agree: the type species ''Rhynia gwynne-vaughanii''". When defined very broadly, the group consists of plants with dichotomously branched, naked aerial axes ("stems") with terminal spore-bearing structures (sporangia). The rhyniophytes are considered to be stem group tracheophytes (vascular plants). Definitions The group was described as a subdivision of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheophyta
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, and the term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |