|
Archaeopteris
''Archaeopteris'' is an extinct genus of progymnosperm tree with fern-like leaves. A useful List of index fossils, index fossil, this tree is found in Stratum, strata dating from the Upper Devonian to Lower Carboniferous (), the oldest fossils being 385 million years old, and had global distribution. Until the 2007 discovery of ''Wattieza'', many scientists considered ''Archaeopteris'' to be the earliest known tree. Bearing buds, reinforced branch joints, and branched trunks similar to today's Woody plant, woody plants, it is more reminiscent of modern seed-bearing trees than other spore-bearing Taxon, taxa. It combines characteristics of woody trees and herbaceous ferns, and belongs to the progymnosperms, a group of extinct plants more closely related to Seed plant, seed plants than to ferns, but unlike seed plants, reproducing using spores like ferns. Taxonomy John William Dawson described the genus in 1871. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaīos'', "ancient" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John William Dawson
Sir John William Dawson (1820–1899) was a Canadian geologist and university administrator. Life and work John William Dawson was born on 13 October 1820 in Pictou, Nova Scotia, where he attended and graduated from Pictou Academy. Of Scottish descent, Dawson attended the University of Edinburgh to complete his education, and graduated in 1842, having gained a knowledge of geology and natural history from Robert Jameson. Dawson returned to Nova Scotia in 1842, accompanying Sir Charles Lyell on his first visit to that territory. Dawson was subsequently appointed as Nova Scotia's first superintendent of education. Holding the post from 1850 to 1853, he was an energetic reformer of school design, teacher education and curriculum. Influenced by the American educator Henry Barnard, Dawson published a pamphlet titled, "School Architecture; abridged from Barnard's School Architecture" in 1850. One of the many schools built to his design, the Mount Hanley Schoolhouse still survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeopteridales
The Archaeopteridales are an extinct order Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood ... of plants belonging to Progymnospermae, and dominant forest trees of the Late Devonian. They reproduced with spores rather than seeds. They were the evolutionary precursors of the conifers of gymnosperms which also include cycads and gingko. References Middle Devonian plants Prehistoric plant orders Late Devonian plants Middle Devonian first appearances Late Devonian extinctions {{devonian-plant-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( ; ) are a group of woody, perennial Seed plant, seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetophyta, gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in ( and ), and literally means 'naked seeds'. The name is based on the unenclosed condition of their seeds (called ovules in their unfertilized state). The non-encased condition of their seeds contrasts with the seeds and ovules of flowering plants (angiosperms), which are enclosed within an Ovary (botany), ovary. Gymnosperm seeds develop either on the surface of scales or Leaf, leaves, which are often modified to form Conifer cone, cones, or on their own as in Taxus, yew, ''Torreya'', and ''Ginkgo''. The life cycle of a gymnosperm involves alternation of generations, with a dominant diploid sporophyte phase, and a reduced haploid gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geologic time, and assess the interactions between prehistoric organisms and their natural environment. While paleontological observations are known from at least the 6th century BC, the foundation of paleontology as a science dates back to the work of Georges Cuvier in 1796. Cuvier demonstrated evidence for the concept of extinction and how life of the past was not necessarily the same as that of the present. The field developed rapidly over the course of the following decades, and the French word ''paléontologie'' was introduced for the study in 1822, which was derived from the Ancient Greek word for "ancient" and words describing relatedness and a field of study. Further advances in the field accompanied the work of Charles Darwin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class (biology), class, Pinopsida. All Neontology, extant conifers are perennial plant, perennial woody plants with secondary growth. The majority are trees, though a few are shrubs. Examples include Cedrus, cedars, Pseudotsuga, Douglas-firs, Cupressaceae, cypresses, firs, junipers, Agathis, kauri, larches, pines, Tsuga, hemlocks, Sequoioideae, redwoods, spruces, and Taxaceae, yews.Campbell, Reece, "Phylum Coniferophyta". ''Biology''. 7th ed. 2005. Print. p. 595. As of 2002, Pinophyta contained seven families, 60 to 65 genera, and more than 600 living species. Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are ecology, ecologically important. They are the dominant plants over large areas of land, most notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the north; Poland and Slovakia to the west; Hungary, Romania and Moldova to the southwest; and the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and List of cities in Ukraine, largest city, followed by Kharkiv, Odesa, and Dnipro. Ukraine's official language is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. Humans have inhabited Ukraine since 32,000 BC. During the Middle Ages, it was the site of early Slavs, early Slavic expansion and later became a key centre of East Slavs, East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful realm in Europe in the 10th and 11th centuries, but gradually disintegrated into rival regional powers before being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donets Basin
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets (), is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv, Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts) and then again through Russia (Rostov Oblast) to join the river Don, about from the Sea of Azov. The Donets is the fourth-longest river in Ukraine, and the largest in eastern Ukraine, where it is an important source of fresh water. It gives its name to the Donets Basin, known commonly as the Donbas, an important coal-mining and industrial region in Ukraine. Etymology The names ''Don'' and its diminutive ''Donets'' are derived from Iranic, Sarmatian "the river".Mallory, J.P. and Victor H. Mair. ''The Tarim Mummies: Ancient China and the Mystery of the Earliest Peoples from the West''. London: Thames and Hudson, 2000. p. 106 Scytho-Sarmatians inhabited the areas to the north of the Black Sea from 110 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
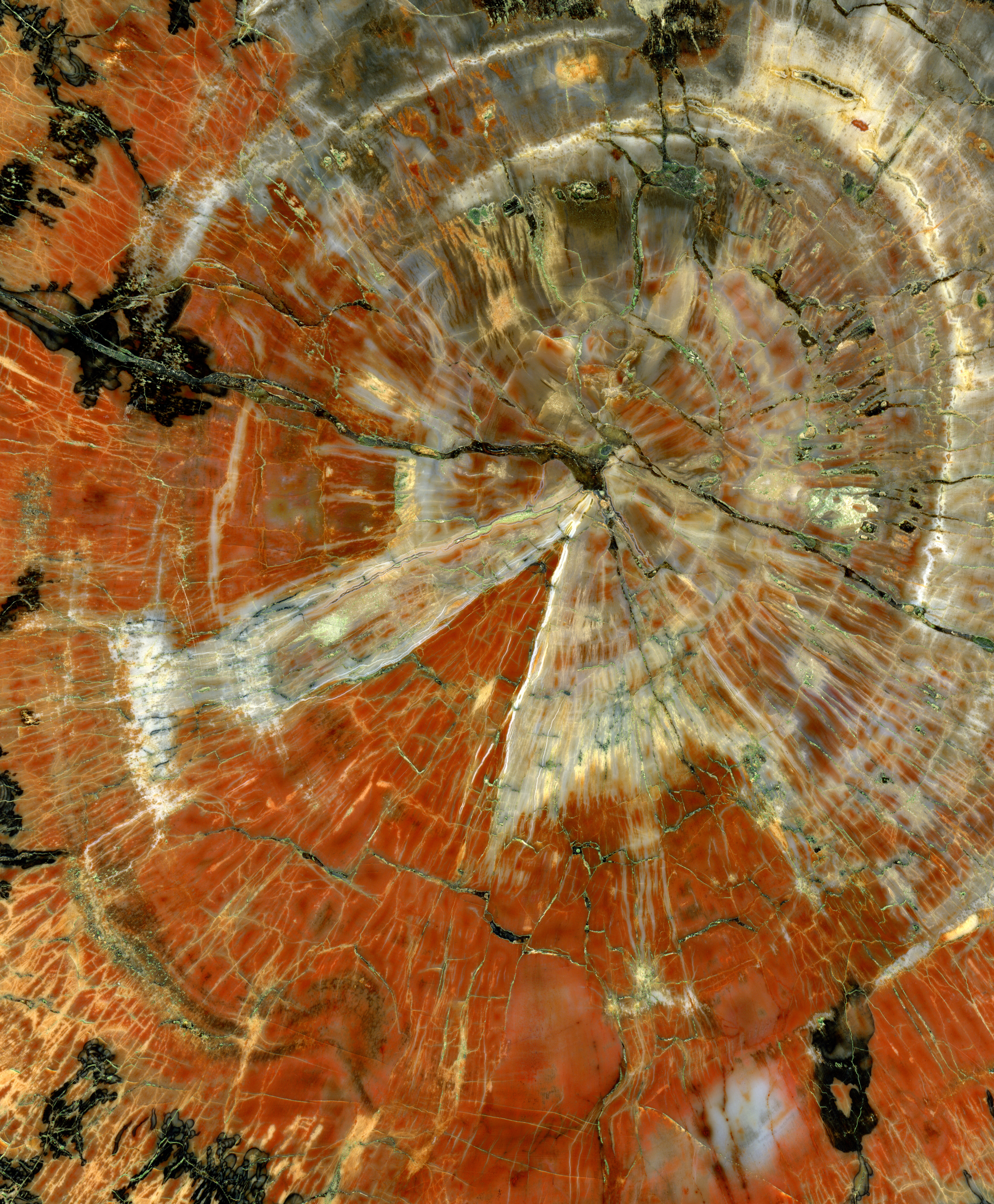
Petrified Wood
Petrified wood (from Ancient Greek meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of ''fossilized wood'', the fossilized remains of terrestrial plant, terrestrial vegetation. ''Petrifaction'' is the result of a tree or tree-like plants having been replaced by stone via a mineralization process that often includes permineralization and replacement. The Carbon-based life, organic materials making up cell walls have been replicated with minerals (mostly silica in the form of opal, chalcedony, or quartz). In some instances, the original structure of the stem tissue may be partially retained. Unlike other plant fossils, which are typically impressions or compressions, petrified wood is a three-dimensional representation of the original organic material. The petrifaction process occurs underground, when wood becomes buried in water or volcanic ash. The presence of water reduces the availability of oxygen which inhibits aerobic dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Zalessky
Mikhail Dmitrievich Zalessky (, ''Mikhail Dmitrievich Zalesskiy''; 15 September 1877 – 22 December 1946) was a Russian paleontologist and paleobotanist. His main focus was an investigation of plant remains in coals and oil shales. In 1911, Zalessky described a new type of petrified wood from the Donets Basin in Ukraine. He called the wood ''Callixylon'', though he did not find any structures other than the trunk. In the 1960s, it was demonstrated that the fossil wood known as ''Callixylon'' and the leaves known as ''Archaeopteris'' were actually part of the same plant. In 1917, he studied kukersite oil shale from Kukruse stage in Estonia. Correspondingly he named that particular oil shale after the German name of the Kukruse manor. Zalessky described oval bodies of kerogen Kerogen is solid, insoluble organic matter in sedimentary rocks. It consists of a variety of organic materials, including dead plants, algae, and other microorganisms, that have been compressed an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |