|
Tamsin Mather
Tamsin Alice Mather (born 1976) is a British Professor of Earth Sciences at the Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford and a Fellow of University College, Oxford. She studies volcanic processes and their impacts on the Earth's environment and has appeared on the television and radio. Education Mather was born in Bristol on 15 December 1976, the daughter of William Mather and Felicity Mather. She was educated at St John's College, Cambridge, where she was awarded a Master of Science degree in 1999, a Master of Philosophy (MPhil) degree in 2000 and a Doctor of Philosophy degree in 2004. As an undergraduate she studied the Natural Sciences Tripos before switching to the History and Philosophy of Science for her MPhil (in the same MPhil class as Helen Macdonald) and Katherine Angel). She spent a year working abroad before returning to science for her PhD which was completed in the Department of Earth Sciences and investigated the chemistry of volcanic plumes in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villarrica (volcano)
Villarrica ( ) ( es, Volcán Villarrica, arn, Ruka Pillañ) is one of Chile's most active volcanoes, rising above the Lake Villarrica, lake and Villarrica, Chile, town of the same name, south of Santiago. It is also known as Rucapillán, a Mapudungun, Mapuche word meaning "Pillan, great spirit's house" or " the demon's house". It is the westernmost of three large stratovolcanoes that trend northwest to southeast obliquely perpendicular to the Andes, Andean chain along the Mocha-Villarrica Fault Zone, and along with Quetrupillán and the Chilean portion of Lanín, are protected within Villarrica National Park. Guided ascents are popular during summer months. Villarrica, with its lava of basaltic-andesitic composition, is one of a small number worldwide known to have an active (but in this case intermittent) lava lake within its volcanic crater, crater. The volcano usually generates strombolian eruptions with ejection of incandescent pyroclasts and lava flows. Rainfall plus melted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common Academic degree, degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is an earned research degree, those studying for a PhD are required to produce original research that expands the boundaries of knowledge, normally in the form of a Thesis, dissertation, and defend their work before a panel of other experts in the field. The completion of a PhD is often a requirement for employment as a university professor, researcher, or scientist in many fields. Individuals who have earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree may, in many jurisdictions, use the title ''Doctor (title), Doctor'' (often abbreviated "Dr" or "Dr.") with their name, although the proper etiquette associated with this usage may also be subject to the professional ethics of their own scholarly field, culture, or society. Those who teach at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
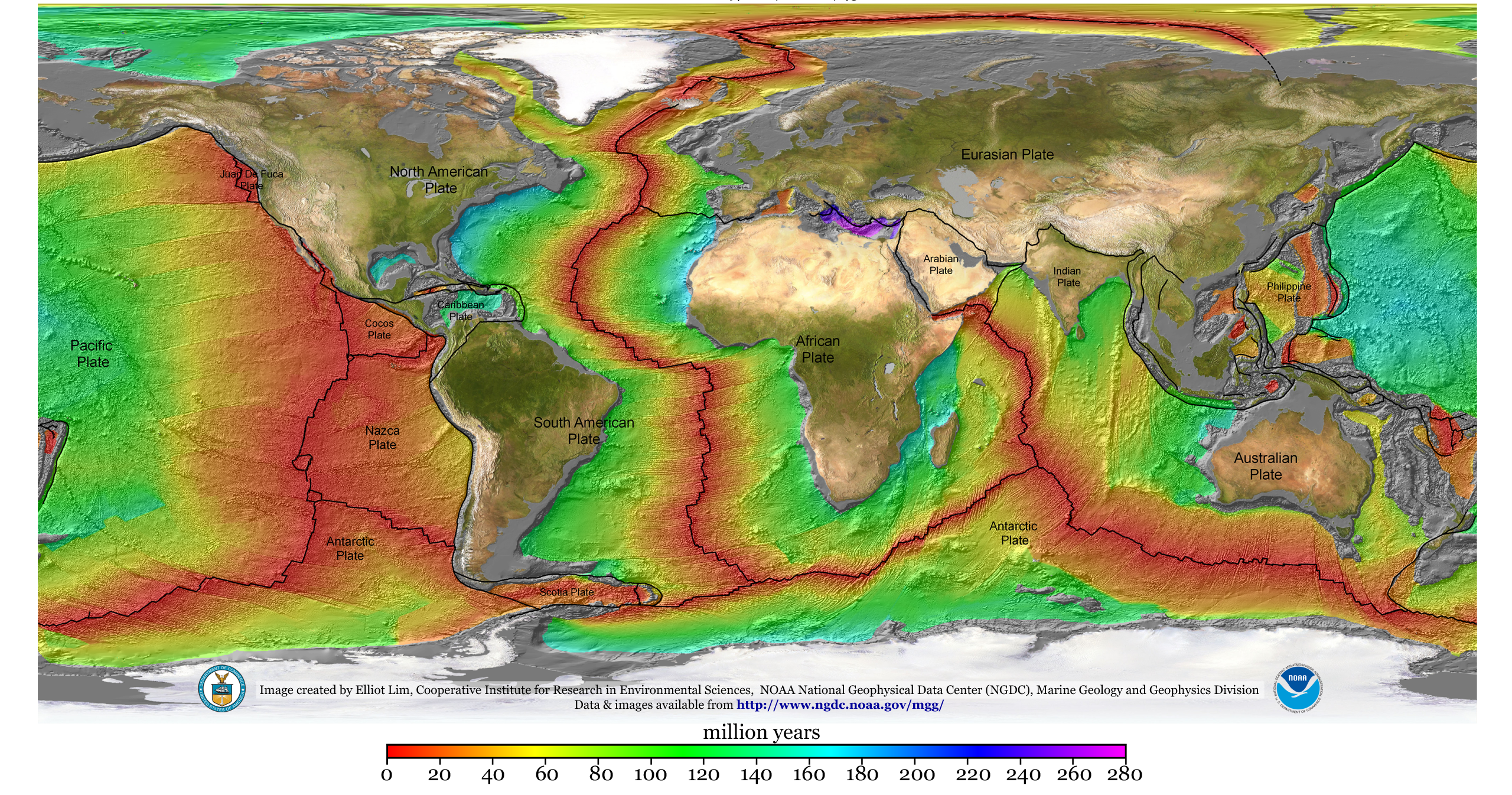
Geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Observation
Earth observation (EO) is the gathering of information about the physical, chemical, and biological systems of the planet Earth. It can be performed via remote-sensing technologies (Earth observation satellites) or through direct-contact sensors in ground-based or airborne platforms (such as weather stations and weather balloons, for example). According to the Group on Earth Observations (GEO), the concept encompasses both " space-based or remotely-sensed data, as well as ground-based or in situ data". Earth observation is used to monitor and assess the status of and changes in natural and built environments. Terminology In Europe, ''Earth observation'' has often been used to refer to satellite-based remote sensing, but the term is also used to refer to any form of observations of the Earth system, including in situ and airborne observations, for example. The GEO, which has over 100 member countries and over 100 participating organizations, uses EO in this broader sense. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time period. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. The word ''tremor'' is also used for Episodic tremor and slip, non-earthquake seismic rumbling. At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and displacing or disrupting the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the country's capital and largest city. , it was estimated to be the second largest city in Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population of six million includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European and African heritage. The main language is Spanish. Indigenous tribes on the Mosquito Coast speak their own languages and English. Originally inhabited by various indigenous cultures since ancient times, the region was conquered by the Spanish Empire in the 16th century. Nicaragua gained independence from Spain in 1821. The Mosquito Coast followed a different historical path, being colonized by the English in the 17th century and later coming under British rule. It became an autonomous territory of Nicaragua in 1860 and its northernmost part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and '' sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Earth Sciences, University Of Cambridge
The Department of Earth Sciences at Cambridge is the University of Cambridge's Earth Sciences department. First formed around 1731, the department incorporates the Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences. History The department's history can be traced back to 1731 when the 1st Woodwardian Professor of Geology was appointed, in accordance with the bequest of John Woodward. The present Department of Earth Sciences was formed by an amalgamation of the Department of Geology, Department of Geodesy and Geophysics and the Department of Mineralogy and Petrology in 1980. The main location of the department is at the Downing Site, Downing St. The Bullard Laboratories, located in West Cambridge on Madingley Rd is a satellite department of the main building. The department incorporates the Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences and the Godwin Laboratory. The department is the home of the Sedgwick Club, which was founded in memory of Adam Sedgwick in 1880, and is the oldest student run geological soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katherine Angel
Katherine Angel is a British academic and writer whose 2012 work of literary non-fiction, ''Unmastered: A Book on Desire, Most Difficult to Tell'', attracted worldwide attention. Life Angel was born in Brussels and earned an undergraduate degree in philosophy. She studied at Harvard University on a JH Choate Fellowship, and earned a Ph.D. in the history of psychiatry and sexuality from the University of Cambridge. She has been a postdoctoral fellow in the history of medicine at Warwick University. Angel is currently a lecturer in creative writing at Birkbeck, University of London. In 2012, Angel published ''Unmastered: A Book on Desire, Most Difficult to Tell'', a literary and experimental meditation on sexual desire. ''Unmastered'' attracted international attention. In 2019, Angel's book ''Daddy Issues'' was published by Peninsula Press. In 2021, ''Tomorrow Sex Will Be Good Again: Women and Desire in the Age of Consent'' was published by Verso. Critical reception ''Unmaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |