|
Geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct investigations across a wide range of scientific disciplines. The term ''geophysics'' classically refers to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational, magnetic fields, and electromagnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical Survey
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure. Hence, detection and analysis of the electric and Magnetic fields is very crucial. As the Electromagnetic and gravitational waves are multi-dimensional signals, all the 1-D transformation techniques can be extended for the analysis of these signals as well. Hence this article also discusses multi-dimensional signal processing techniques. Geophysical surveys may use a great variety of sensing instruments, and data may be collected from above or below the Earth's surface or from aerial, orbital, or marine platforms. Geophysical surveys have many applications in geology, archaeology, mineral and energy exploration, oceanography, and engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
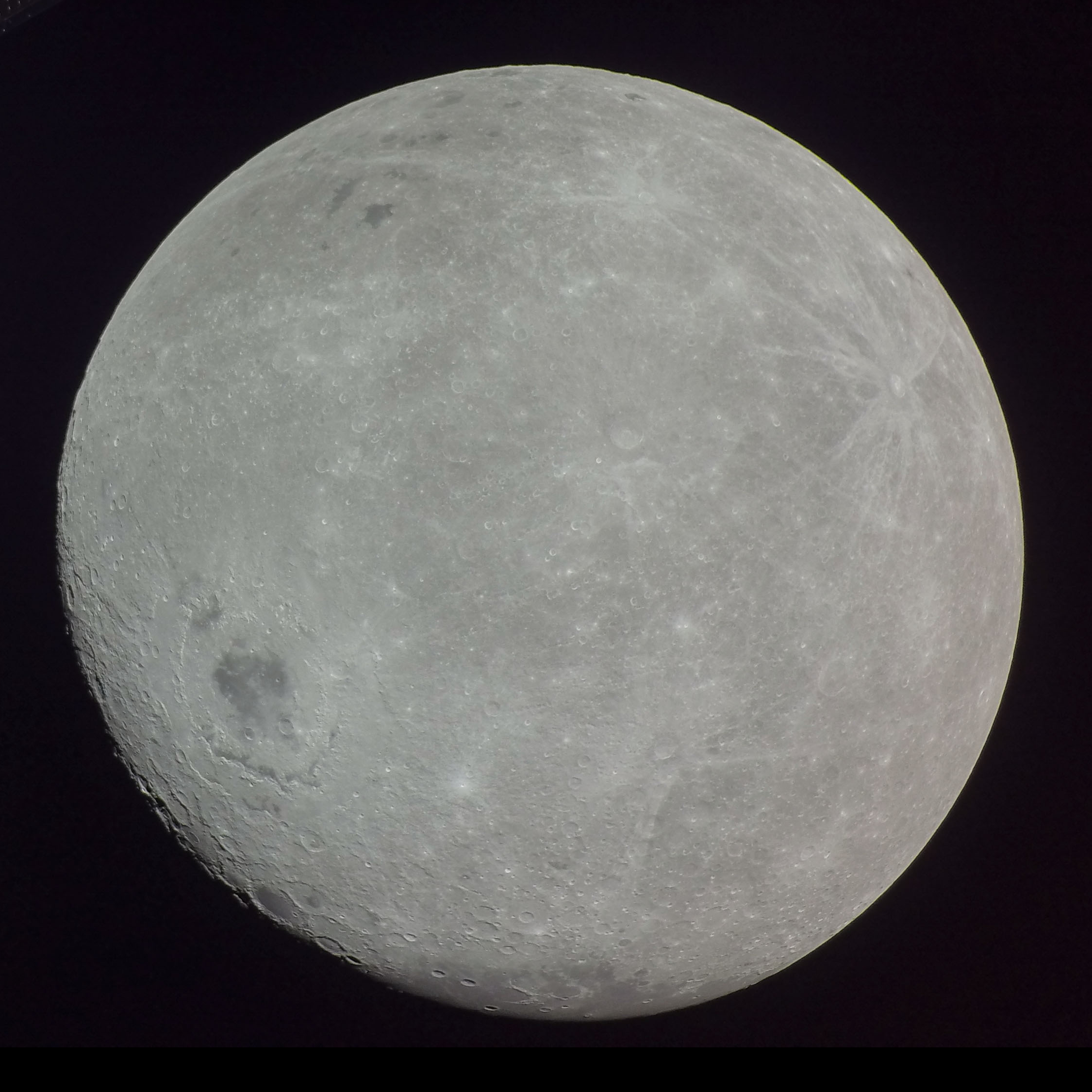
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (Lunar month#Synodic month, lunar month) of 29.5 Earth days. This is the product of Earth's gravitation having tidal forces, tidally pulled on the Moon until one part of it stopped rotating away from the near side of the Moon, near side, making always the same lunar surface face Earth. Conversley, the gravitational pull of the Moon, on Earth, is the main driver of Earth's tides. In geophysical definition of planet, geophysical terms, the Moon is a planetary-mass object or satellite planet. Its mass is 1.2% that of the Earth, and its diameter is , roughly one-quarter of Earth's (about as wide as the contiguous United States). Within the Solar System, it is the List of Solar System objects by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics
Geophysical fluid dynamics, in its broadest meaning, is the application of fluid dynamics to naturally occurring flows, such as lava, oceans, and atmospheres, on Earth and other planets. Two physical features that are common to many of the phenomena studied in geophysical fluid dynamics are rotation of the fluid due to the planetary rotation and stratification (layering). The applications of geophysical fluid dynamics do not generally include the circulation of the mantle, which is the subject of ''geodynamics'', or fluid phenomena in the magnetosphere. Ocean circulation and air circulation are typically studied in oceanography and meteorology. Fundamentals To describe the flow of geophysical fluids, equations are needed for conservation of momentum (or Newton's second law) and conservation of energy. The former leads to the Navier–Stokes equations which cannot be solved analytically (yet). Therefore, further approximations are generally made in order to be able to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Hazards
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides - including submarine landslides, tropical cyclones, volcanic activity and wildfires. Additional natural hazards include blizzards, dust storms, firestorms, hails, ice storms, sinkholes, thunderstorms, tornadoes and tsunamis. A natural disaster can cause loss of life or damage property. It typically causes economic damage. How bad the damage is depends on how well people are prepared for disasters and how strong the buildings, roads, and other structures are. Scholars have argued the term "natural disaster" is unsuitable and should be abandoned. Instead, the simpler term ''disaster'' could be used. At the same time, the type of hazard would be specified. A disaster happens when a natural or human-made hazard impacts a vulnerable community. It re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
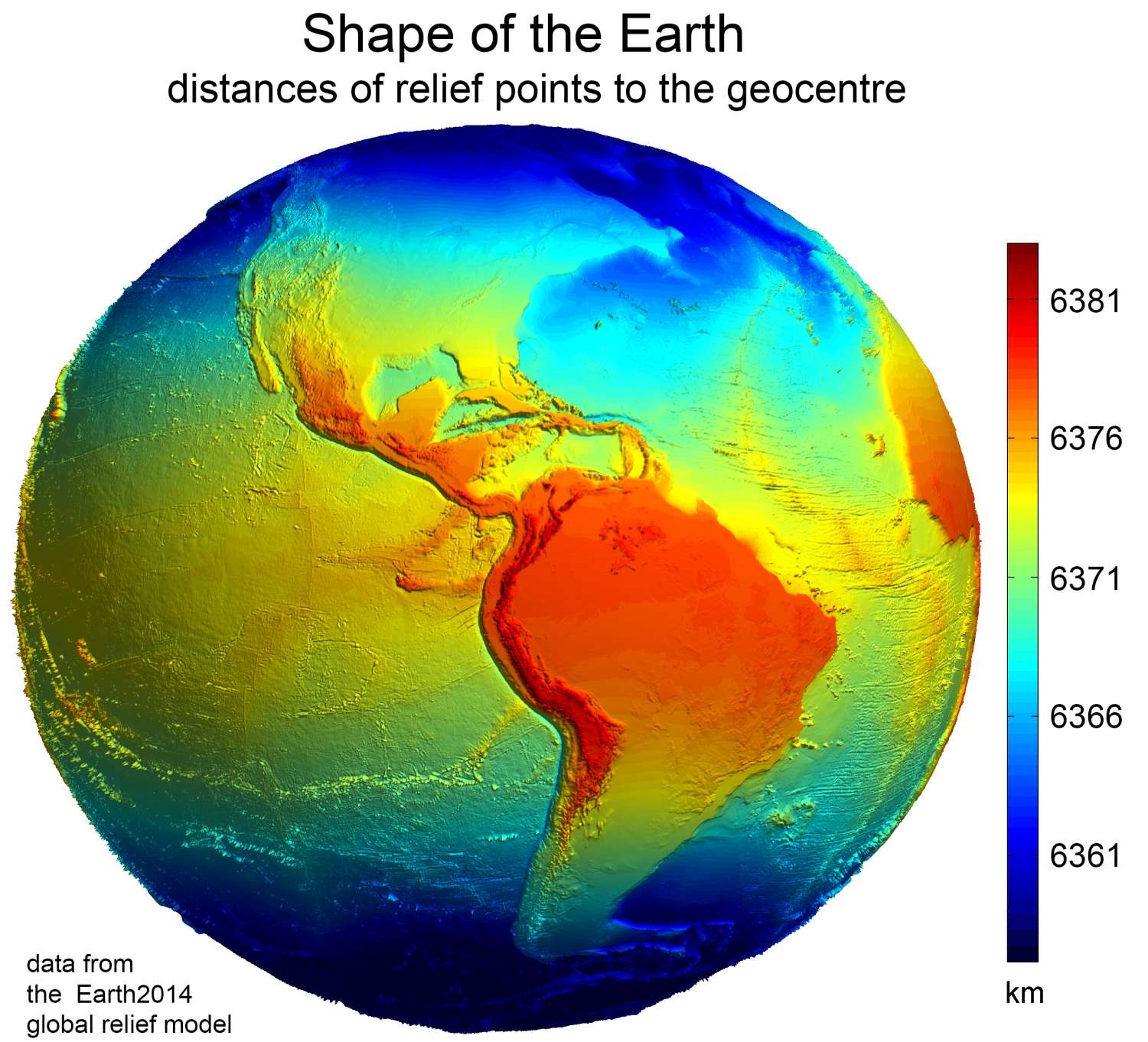
Figure Of The Earth
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is satisfactory for geography, astronomy and many other purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including ellipsoid) have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, hydrographers, and geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely complicated. The Pythagorean concept of a spherical Earth offers a simple surface that is easy to deal with mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from structure of Earth, Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole (Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada) actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Geophysics
Exploration geophysics is an applied branch of geophysics and economic geology, which uses physical methods at the surface of the Earth, such as seismic, gravitational, magnetic, electrical and electromagnetic, to measure the physical properties of the subsurface, along with the anomalies in those properties. It is most often used to detect or infer the presence and position of economically useful geological deposits, such as ore minerals; fossil fuels and other hydrocarbons; Geothermal energy, geothermal reservoirs; and groundwater reservoirs. It can also be used to detect the presence of unexploded ordnance. Exploration geophysics can be used to directly detect the target style of mineralization by measuring its physical properties directly. For example, one may measure the density contrasts between the dense iron ore and the lighter silicate host rock, or one may measure the electrical conductivity contrast between conductive sulfide minerals and the resistive silicate host roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Science
Natural science or empirical science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and reproducibility of findings are used to try to ensure the validity of scientific advances. Natural science can be divided into two main branches: list of life sciences, life science and Outline of physical science, physical science. Life science is alternatively known as biology. Physical science is subdivided into branches: physics, astronomy, Earth science and chemistry. These branches of natural science may be further divided into more specialized branches (also known as fields). As empirical sciences, natural sciences use tools from the formal sciences, such as mathematics and logic, converting information about nature into measurements that can be explained as clear statements of the "laws of science, laws of nature". Mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, achieved the Unification of theories in physics#Unification of gravity and astronomy, first great unification in physics and established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and Leibniz–Newton calculus controversy, shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for formulating calculus, infinitesimal calculus, though he developed calculus years before Leibniz. Newton contributed to and refined the scientific method, and his work is considered the most influential in bringing forth modern science. In the , Newton formulated the Newton's laws of motion, laws of motion and Newton's law of universal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodestone
Lodestones are naturally magnetization, magnetized pieces of the mineral magnetite. They are naturally occurring magnets, which can attract iron. The property of magnetism was first discovered in Ancient history, antiquity through lodestones. Pieces of lodestone, suspended so they could turn, were the first magnetic compasses, and their importance to early navigation is indicated by the name ''lodestone'', which in Middle English means "course stone" or "leading stone", from the now-obsolete meaning of '':wikt:lode, lode'' as "journey, way". Lodestone is one of only a very few minerals that is found naturally magnetized. Magnetite is black or brownish-black, with a metallic lustre (mineralogy), luster, a Mohs scale of mineral hardness, Mohs hardness of 5.5–6.5 and a black streak (mineralogy), streak. Origin The process by which lodestone is created has long been an open question in geology. Only a small amount of the magnetite on the Earth is found magnetized as lodest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitigation
Mitigation is the reduction of something harmful that has occurred or the reduction of its harmful effects. It may refer to measures taken to reduce the harmful effects of hazards that remain ''in potentia'', or to manage harmful incidents that have already occurred. It is a stage or component of emergency management and of risk management. The theory of mitigation is a frequently used element in criminal law and is often used by a judge to try cases such as murder, where a perpetrator is subject to varying degrees of responsibility as a result of one's actions. Disaster mitigation An all-hazards approach to disaster management considers all known hazards and their natural and anthropogenic potential risks and impacts, with the intention of ensuring that measures taken to mitigate one type of risk do not increase vulnerability to other types of risks. Proactive disaster mitigation (also hazard mitigation) measures are generally more effective than reactive measures in eliminatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |