|
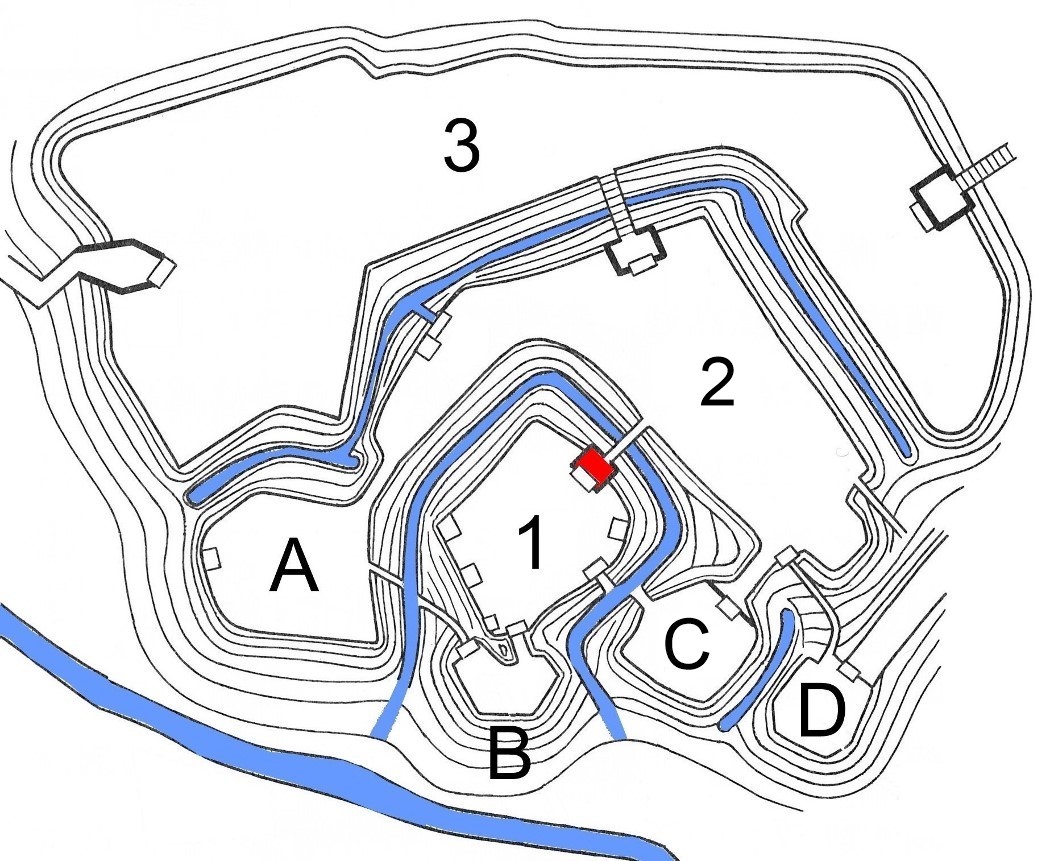
Takatō Castle
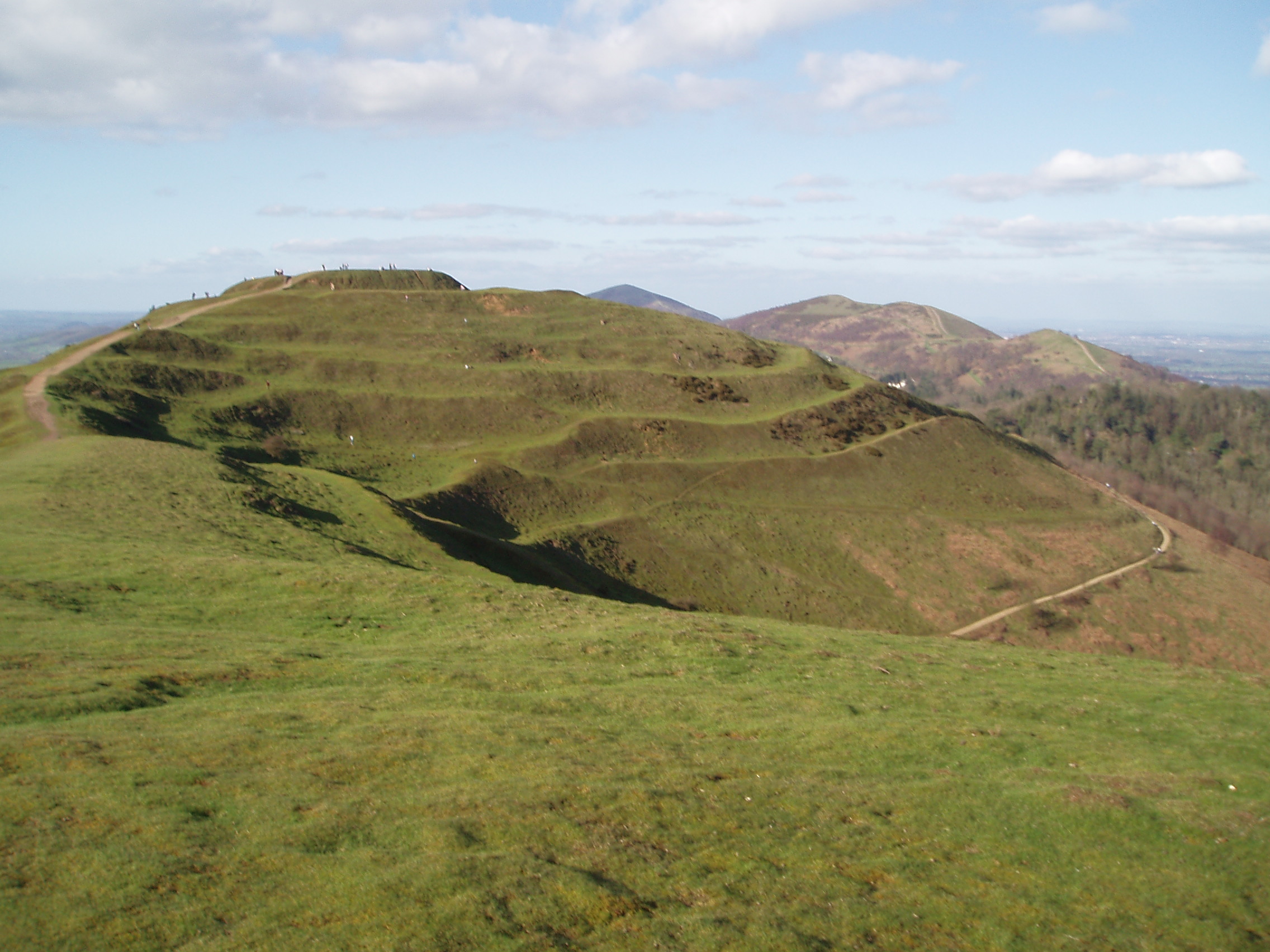
is a Japanese castle located in the city of Ina, southern Nagano Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Takatō Castle was home to a cadet branch of the Naitō clan, ''daimyō'' of Takatō Domain. The castle was also known as . Built sometime in the 16th century, it is now largely in ruins. Layout Takato Castle is located on a hill in the former Takatō Town on the eastern edge of central Ina Valley in southern Nagano Prefecture. The location was a crossroads on the Akiba Kaidō, a highway connecting Tōtōmi province with the Suwa region of Shinano and Kai Province and a road which led to the western portion of the Ina valley and Mino Province. When viewed from the standpoint of Kai Province, the area was a key point in the control of southern Shinano. The castle site overlooks the confluence of the Mibugawa River and the Fujisawa River, which forms part of its natural defenses. Deep trenches, earthen ramparts and stone walls in concentric rings form the defensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ina, Nagano
is a city located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 68,177 in 27587 households, and a population density of 100 persons per km2. The total area of the city is . In 2016, the former town of Takatō, now part of Ina, was selected as one of The Most Beautiful Villages in Japan. Geography Ina is located in south-central Nagano prefecture. It is bordered to the east by the Akaishi Mountains, including Mount Nyukasa (1955 meters), Mount Nokogiri (2685 meters), Mount Senjō (3033 meters), and Mount Shiomi (3047 meters). The Tenryū River runs through the city. Surrounding municipalities *Nagano Prefecture ** Komagane ** Shiojiri ** Suwa ** Chino ** Suwa District: Fujimi ** Kamiina District: Minowa, Minamiminowa, Miyada ** Shimoina District: Ōshika ** Kiso District: Kiso (town) *Yamanashi Prefecture ** Minami-Alps ** Hokuto *Shizuoka Prefecture ** Aoi-ku, Shizuoka Climate The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart (fortification)
In fortification architecture, a rampart is a length of Embankment (earthworks), embankment or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, Human settlement, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth and/or masonry.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 241. Darvill, Timothy (2008). ''Oxford Concise Dictionary of Archaeology'', 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, p. 376. . Types The composition and design of ramparts varied from the simple mounds of earth and stone, known as dump ramparts, to more complex earth and timber defences (box ramparts and timberlaced ramparts), as well as ramparts with stone revetments. One particular type, common in Central Europe, used earth, stone and timber posts to form a ''Pfostenschlitzmauer'' or "post-slot wall". Vitrified ramparts were composed of stone that was subsequently fired, possibly to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto
Kyoto ( or ; Japanese language, Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan's largest and most populous island of Honshu. , the city had a population of 1.46 million, making it the List of cities in Japan, ninth-most populous city in Japan. More than half (56.8%) of Kyoto Prefecture's population resides in the city. The city is the cultural anchor of the substantially larger Greater Kyoto, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 3.8 million people. It is also part of the even larger Keihanshin, Keihanshin metropolitan area, along with Osaka and Kobe. Kyoto is one of the oldest municipalities in Japan, having been chosen in 794 as the new seat of Japan's imperial court by Emperor Kanmu. The original city, named Heian-kyō, was arranged in accordance with traditional Chinese feng shui following the model of the ancient Chinese capitals of Chang'an and Luoyang. The emperors of Japan ruled fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods. He was the and regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. He is sometimes referred as the "Demon Daimyō" and "Demon King of the Sixth Heaven". Nobunaga was an influential figure in Japanese history and is regarded as one of the three great unifiers of Japan, along with his Affinity (medieval), retainers, Toyotomi Hideyoshi and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Nobunaga paved the way for the successful reigns of Hideyoshi and Ieyasu by consolidating power, as head of the very powerful Oda clan, through a series of wars against other ''daimyō'' beginning in the 1560s. The period when Nobunaga and Hideyoshi were in power is called the Azuchi–Momoyama period. The name "Azuchi–Momoyama" comes from the fact that Nobunaga's castle, Azuchi Castle, was located in Azuchi, Shiga; while Fushimi Castle, where Hideyoshi lived after his retirement, was located in Momoyama. Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takeda Katsuyori
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' (military lord) of the Sengoku period, who was famed as the head of the Takeda clan and the successor to the legendary warlord Takeda Shingen. He was son-in-law of Hojo Ujiyasu, ''daimyō'' of Hojo clan. Early life He was the son of Takeda Shingen, Shingen by the daughter of Suwa Yorishige (daimyo), Suwa Yorishige (posthumous name: ). Shingen led a campaign to take Suwa territory in 1542 and defeated Yorishige, who later committed suicide. Shingen took Yorishige's daughter as a concubine. Katsuyori's children included Takeda Nobukatsu and Katsuchika. Katsuyori, first known as , succeeded to his mother's Suwa clan and gained Takatō Castle as the seat of his domain. After his elder brother Takeda Yoshinobu died, Katsuyori's son Nobukatsu became heir to the Takeda clan, making Katsuyori the ''de facto'' ruler of the Takeda clan. Takeda Katsuyori built Shinpu Castle, a new and larger castle at Nirasaki and transferred his residence there in 1581. Milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akiyama Nobutomo
was a samurai during the Sengoku period in Japan. He is known as one of the "Twenty-Four Generals of Takeda Shingen". Nobutomo also served under Shingen's son, Takeda Katsuyori. Biography In 1527, Akiyama Nobutomo was born at in Kai province. His father was Akiyama Nobutou, a descendant of Takeda Mitsutomo, and a member of a cadet branch of the Takeda clan. When Nobutomo came of age, he entered into the service of Takeda Shingen, patriarch of the clan and lord of Kai province, in the mountainous area of central Japan. In 1547, during the campaign for the Ina district, Nobutomo fought with excellence and was granted a fief in the northern half of Ina, present day Kamiina District in Nagano prefecture. Nobutomo continued his service, most often tasked in a defensive role and holding such castles as Takatō Castle and Iida Castle. During this time, Nobutomo acquired the nickname (literally: ''Raging Bull of the Takeda Clan''). By 1568, Nobutomo was esteemed enough to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamamoto Kansuke (general)
was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period. He was known as one of the " Twenty-Four Generals of Takeda Shingen". Also known by his formal name, Haruyuki (晴幸). He was a brilliant strategist, and is particularly known for his plan which led to success in the fourth battle of Kawanakajima against Uesugi Kenshin. However, Kansuke never lived to see his plan succeed; thinking it to have failed, he charged headlong into the enemy ranks, dying in battle. Biography Kansuke's origins are not known for certain, but he is believed to have originated from Ushikubo, a town in Mikawa Province, which was then under the suzerainty of the Imagawa clan. He came to Kai and began to serve Takeda Shingen in 1543, receiving a position as an infantry commander (''ashigaru-taishō'' 足軽大将). Legend says that Kansuke was blind in one eye and lame, but a fierce warrior and military strategist nevertheless. In various works of art, he is depicted holding a naginata as a support for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takeda Clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan active from the late Heian period until the late 16th century. The clan was historically based in Kai Province in present-day Yamanashi Prefecture. The clan reached its greatest influence under the rule of Takeda Shingen, one of the most famous rulers of the period. History Origin The Takeda are descendants of the Emperor Seiwa (858–876), the 56th Emperor of Japan, and are a branch of the Minamoto clan (Seiwa Genji), by Minamoto no Yoshimitsu (1056–1127), son of the '' Chinjufu-shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoriyoshi (988-1075), and brother to the famous Minamoto no Yoshiie (1039–1106). Minamoto no Yoshikiyo (1075–1149), son of Yoshimitsu, was the first to take the name of Takeda, which he took when his father granted him Takeda domain in Hitachi Province; thereafter, he was known as Takeda Yoshikiyo. Kamakura to early Azuchi–Momoyama periods In the 12th century, at the end of the Heian period, the Takeda family-controlled Kai Province. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suwa Yorishige (daimyo)
(1516–1544) was a Japanese samurai, ''daimyo'' (military lord) of Shinano province and head of the Suwa clan. He was defeated by Takeda Shingen, and his daughter Suwa Goryōnin (諏訪御料人, real name unknown) was taken as Shingen's concubine. She later gave birth to the Takeda clan heir Takeda Katsuyori. Suwa Yorishige fought Takeda Nobutora in the 1531 ''Battle of Shiokawa no gawara''. Suwa Yorishige was then defeated by Takeda Shingen was daimyō, daimyo of Kai Province during the Sengoku period of Japan. Known as "the Tiger of Kai", he was one of the most powerful daimyo of the late Sengoku period, and credited with exceptional military prestige. Shingen was based in a p ... in the 1542 Battle of Sezawa and the Siege of Uehara. Following the Siege of Kuwabara, he committed suicide. References 1516 births 1542 deaths Samurai {{Suwa Faith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamakura Period
The is a period of History of Japan, Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura by the first ''shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle between the Taira clan, Taira and Minamoto clan, Minamoto clans. The period is known for the emergence of the samurai, the warrior caste, and for the establishment of feudalism in Japan. There are various theories as to the year in which the Kamakura period and Kamakura shogunate began. In the past, the most popular theory was that the year was 1192, when Minamoto no Yoritomo was appointed . Later, the prevailing theory was that the year was 1185, when Yoritomo established the , which controlled military and police power in various regions, and the , which was in charge of tax collection and land administration. Japanese history textbooks as of 2016 do not specify a specific year for the beginning of the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suwa Clan
The , also known as the Jin or Miwa clan (神氏, ''Miwa Uji (clan), uji / Miwa-shi'' or ''Jinshi'') was a Japanese ''Shake (social class), shake'' and samurai family. Originating from the area encompassing Lake Suwa in Shinano Province (modern-day Nagano Prefecture), it was originally a family of priests who served at the Suwa taisha, Upper Shrine of Suwa located on the southwestern side of the lake. By the Kamakura period, it thrived as a prominent samurai clan with close ties to the Kamakura Shogunate, shogunate. Surviving the fall of both the Kamakura shogunate and the Southern Court, Southern Imperial Court which it supported, its feud with local rival clans, and frequent clashes with its neighbor in Kai Province, Kai, the Takeda clan, during the Sengoku period (which ended in the extinction of the main family), by the Edo period the clan had split into two branches: one ruling the Suwa Domain of Shinano Province, Shinano as ''daimyō'', with the other continuing to serve a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai
The samurai () were members of the warrior class in Japan. They were originally provincial warriors who came from wealthy landowning families who could afford to train their men to be mounted archers. In the 8th century AD, the imperial court downsized the national army and delegated the security of the countryside to these privately trained warriors. Eventually the samurai clans grew so powerful that they became the ''de facto'' rulers of the country. In the aftermath of the Gempei War (1180-1185), Japan formally passed into military rule with the founding of the first shogunate. The status of samurai became heredity by the mid-eleventh century. By the start of the Edo period, the shogun had disbanded the warrior-monk orders and peasant conscript system, leaving the samurai as the only men in the country permitted to carry weapons at all times. Because the Edo period was a time of peace, many samurai neglected their warrior training and focused on peacetime activities such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |