|
Akiyama Nobutomo
was a samurai during the Sengoku period in Japan. He is known as one of the "Twenty-Four Generals of Takeda Shingen". Nobutomo also served under Shingen's son, Takeda Katsuyori. Biography In 1531, Akiyama Nobutomo was born at in Kai province. His father was Akiyama Nobutou, a descendant of Takeda Mitsutomo, and a member of a cadet branch of the Takeda clan. When Nobutomo came of age, he entered into the service of Takeda Shingen, patriarch of the clan and lord of Kai province, in the mountainous area of central Japan. In 1547, during the campaign for the Ina district, Nobutomo fought with excellence and was granted a fief in the northern half of Ina, present day Kamiina District in Nagano prefecture. Nobutomo continued his service, most often tasked in a defensive role and holding such castles as Takatō Castle and Iida Castle. During this time, Nobutomo acquired the nickname (literally: ''Raging Bull of the Takeda Clan''). By 1568, Nobutomo was esteemed enough to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
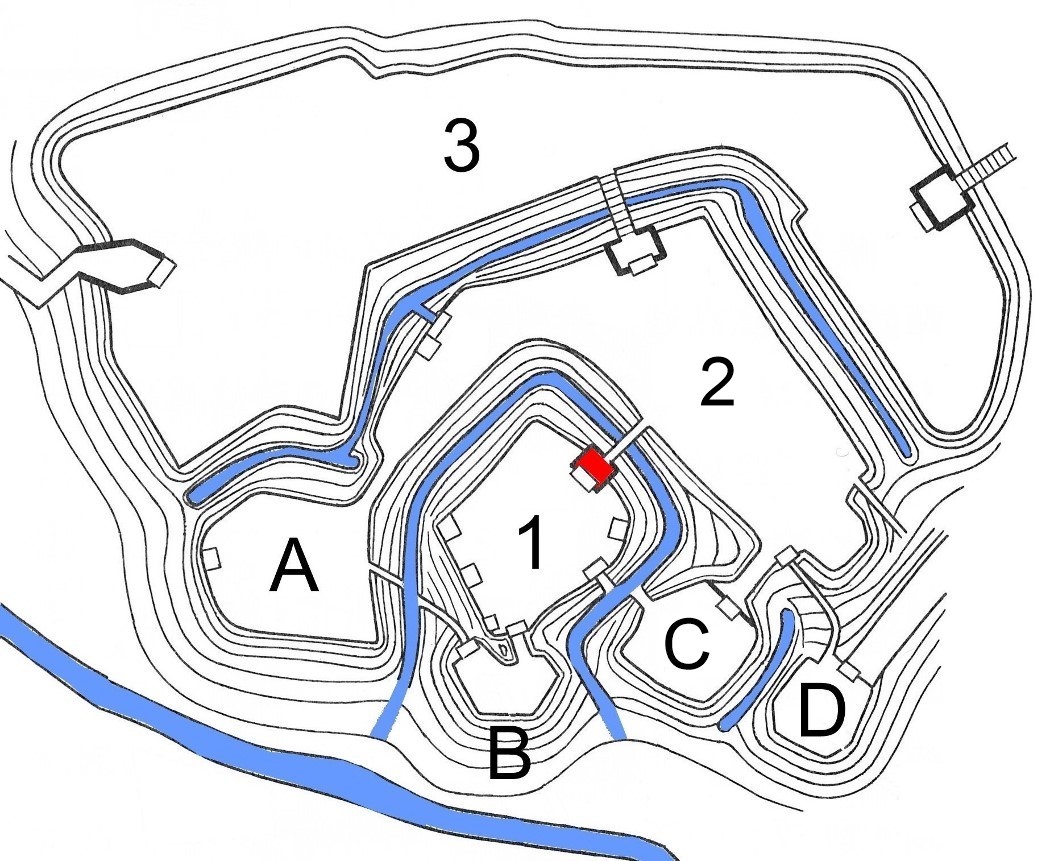
Takatō Castle
is a Japanese castle located in the city of Ina, southern Nagano Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Takatō Castle was home to a cadet branch of the Naitō clan, '' daimyō'' of Takatō Domain. The castle was also known as . Built sometime in the 16th century, it is now largely ruins. Situation Takato Castle is located on a hill in former Takatō Town on the eastern edge of central Ina Valley in southern Nagano Prefecture. The location was a crossroads on the Akiba Kaidō, a highway connecting Tōtōmi province with the Suwa region of Shinano and Kai Province and a road which led to the western portion of the Ina valley and Mino Province. When viewed from the standpoint of Kai Province, the area was a key point in the control of southern Shinano. The castle site overlooks the confluence of the Mibugawa River and the Fujisawa River, which forms part of its natural defenses. Deep trenches, earthen ramparts and stone walls in concentric rings form the defen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nagashino
The took place in 1575 near Nagashino Castle on the plain of Shitaragahara in the Mikawa Province of Japan. Takeda Katsuyori attacked the castle when Okudaira Sadamasa rejoined the Tokugawa, and when his original plot with Oga Yashiro for taking Okazaki Castle, the capital of Mikawa, was discovered. The Oda arquebusiers decisively defeated the cavalry tactics of the Takeda, who lost two-thirds of their army. The battle is often cited as a turning point in Japanese warfare and the first "modern" Japanese battle. Background Takeda Katsuyori attacked the castle on 16 June, using Takeda gold miners to tunnel under the walls, rafts to ferry samurai across the rivers, and siege towers. On 22 June the siege became a blockade, complete with palisades and cables strewn across the river. Sadamasa's wife, Kamehime, was the daughter of Tokugawa Ieyasu. She helped to defend the castle by sending a letter with Torii Suneemon which asked her father for reinforcements. Torii reached Okazaki, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oda Katsunaga
was a Japanese samurai of the Sengoku period through early Azuchi-Momoyama Period, who was the fifth son of Oda Nobunaga. At a very young age, Katsunaga, then known as "Gobomaru", was given in adoption to Toyama Kagetou and his wife, Lady Otsuya, at Iwamura Castle. Lady Otsuya was Oda Nobunaga's aunt. In 1572, the castle was captured by Takeda forces under Akiyama Nobutomo, and Gobomaru, then four years old, became a hostage of the Takeda. In 1581, Takeda Katsuyori released Gobomaru (Katsunaga) to the Oda clan, who returned him to Iwamura Castle, which had been re-taken during his absence. Honnō-ji Incident One year later in 1582, Katsunaga accompanied his father to Honnō-ji. Following the attack on Honno-ji and the death of Nobunaga, Akechi Mitsuhide attacked Nijō Castle, where Nobunaga's son Nobutada was staying. During the fight, Katsunaga was killed and Nobutada committed '' seppuku''. Family *Father: Oda Nobunaga (1536-1582) * Brothers: ** Oda Nobutada (1557-15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Iwamura Castle
The siege of Iwamura was a military event which occurred in 1572 in Japan, concurrent with Takeda Shingen's push into Tōtōmi Province and the Battle of Mikatagahara. Akiyama Nobutomo, one of Shingen's " Twenty-Four Generals," set his eye on the great ''yamashiro'' (mountain castle) of Iwamura when Tōyama Kagetō, the commander of the castle's garrison, fell ill and died. Akiyama negotiated the castle's surrender with Lady Otsuya, who was not only Tōyama's widow but the aunt of Oda Nobunaga. The heir to the castle was a four-year-old boy called Gobōmaru, the fifth son of Oda Nobunaga, who had been given to Tōyama to adopt and raise as his own. Gobomaru was taken to the Takeda home in Kai province as a hostage. In accordance with the surrender treaty, Lady Otsuya Lady Otsuya (おつやの方 ''Otsuya no Kata'') was a Japanese female samurai (onna-musha) from the Sengoku period. She was the aunt of the famous samurai Oda Nobunaga, the wife of Tōyama Kagetō and fost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mikatagahara
The was a battle of the Sengoku period of Japan fought between Takeda Shingen and Tokugawa Ieyasu in Mikatagahara, Tōtōmi Province on 25 January 1573. Shingen attacked Ieyasu at the plain of Mikatagahara north of Hamamatsu during his campaign against Oda Nobunaga while seeking a route from Kōfu to Kyoto. The Tokugawa-Oda force was almost totally annihilated by the Takeda after being encircled and many of Ieyasu's retainers were killed in the battle. Ieyasu and his surviving men were forced to retreat before launching a minor counterattack to delay Shingen's march towards Kyoto. Background In October 1572, after having concluded alliances with his rivals to the east (the Later Hōjō clan of Odawara and the Satomi clan of Awa), and after waiting for the snow to close off the northern mountain passes against his northern rival, Uesugi Kenshin, Takeda Shingen led an army of 30,000 men south from his capital of Kōfu into Tōtōmi Province, while Yamagata Masakage led a seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mino Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today southern Gifu Prefecture. Mino was bordered by Ōmi to the west, Echizen and Hida to the north, and Shinano to the east, and Ise, Mikawa, and Owari to the south. Its abbreviated form name was . Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Mino was ranked as one of the 13 "great countries" (大国) in terms of importance, and one of the "near countries" (近国) in terms of distance from the capital. The provincial capital and ''ichinomiya'' were located in what is now the town of Tarui. Historical record "Mino" is an ancient place name, and appears in ''mokkan'' wooden tags from the ruins of Asuka-kyō, Fujiwara-kyō, and other ancient sites, but using the ''kanji'' "三野国". Per the ''Kujiki'', there were originally three separate countries in Mino, centered around what is now Ōgaki, Ōno, and Kakamigahara. Each had its own ''Kuni no miyatsuko'', and together with Motosu (in eastern Gifu) and Mugetsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikawa Province
was an old province in the area that today forms the eastern half of Aichi Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Mikawa''" in . Its abbreviated form name was . Mikawa bordered on Owari, Mino, Shinano, and Tōtōmi Provinces. Mikawa is classified as one of the provinces of the Tōkaidō. Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Mikawa was ranked as a "superior country" (上国) and a "near country" (近国) in terms of its distance from the capital. History Mikawa is mentioned in records of the Taika Reform dated 645, as well as various Nara period chronicles, including the Kujiki, although the area has been settled since at least the Japanese Paleolithic period, as evidenced by numerous remains found by archaeologists. Early records mention a "Nishi-Mikawa no kuni" and a "Higashi-Mikawa no kuni", also known as . Although considered one administrative unit under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, this division (roughly based at the Yasaku River) pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tōtōmi Province
was a province of Japan in the area of Japan that is today western Shizuoka Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Tōtōmi''" in . Tōtōmi bordered on Mikawa, Suruga and Shinano Provinces. Its abbreviated form name was . The origin of its name is the old name of Lake Hamana. History Tōtōmi was one of the original provinces of Japan established in the Nara period under the Taihō Code. The original capital of the province was located in what is now Iwata, and was named Mitsuke – a name which survived into modern times as Mitsuke-juku, a post station on the Tōkaidō. Under the ''Engishiki'' classification system, Tōtōmi was ranked as a "superior country" (上国) in terms of importance, and one of the 16 "middle countries" (中国) in terms of distance from the capital. During the early Muromachi period, Tōtōmi was ruled nominally by the Imagawa clan before coming under control of the Shiba clan._However,_by_the_Sengoku_period.html" ;"title="DF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fellow Oda subordinate Toyotomi Hideyoshi. The son of a minor daimyo, Ieyasu once lived as a hostage under daimyo Imagawa Yoshimoto on behalf of his father. He later succeeded as daimyo after his father's death, serving as a vassal and general of the Oda clan, and building up his strength under Oda Nobunaga. After Oda Nobunaga's death, Ieyasu was briefly a rival of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, before declaring his allegiance and fighting on his behalf. Under Toyotomi, Ieyasu was relocated to the Kanto plains in eastern Japan, away from the Toyotomi power base in Osaka. He built his castle in the fishing village of Edo (now Tokyo). He became the most powerful daimyo and the most senior officer under the Toyotomi regime. Ieyasu preserved his strength i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period. He is regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan. Nobunaga was head of the very powerful Oda clan, and launched a war against other ''daimyō'' to unify Japan in the 1560s. Nobunaga emerged as the most powerful ''daimyō'', overthrowing the nominally ruling shogun Ashikaga Yoshiaki and dissolving the Ashikaga Shogunate in 1573. He conquered most of Honshu island by 1580, and defeated the ''Ikkō-ikki'' rebels in the 1580s. Nobunaga's rule was noted for innovative military tactics, fostering of free trade, reforms of Japan's civil government, and the start of the Momoyama historical art period, but also for the brutal suppression of those who refused to cooperate or yield to his demands. Nobunaga was killed in the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582, when his retainer Akechi Mitsuhide ambushed him in Kyoto and forced him to commit . Nobunaga was succeeded by Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who along with Toku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |