|
Tagetes Lunulata
''Tagetes'' () is a genusSoule, J. A. 1996. Infrageneric Systematics of Tagetes. Pgs. 435-443 in Compositae: Systematics, Proceedings of the International Compositae Conference, Kew 1994, Vol. I, Eds. D.J.N. Hind & H.J. Beentje. of annual or perennial, mostly herbaceous plants in the family Asteraceae. They are among several groups of plants known in English as marigolds. The genus ''Tagetes'' was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. These plants are native to Mexico, growing naturally since Mexico's valley down to the south and even reaching several other Latinamerican countries, but some species have become naturalized around the world. One species, '' T. minuta'', is considered a noxious invasive plant in some areas. Description ''Tagetes'' species vary in size from 0.1 to 2.2 m tall. Most species have pinnate green leaves. Blooms naturally occur in golden, orange, yellow, and white colors, often with maroon highlights. Floral heads are typically (1-) to 4–6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagetes Erecta
''Tagetes erecta'', the Aztec marigold, Mexican marigold, big marigold, ''cempazúchitl'' or ''cempasúchil'', is a species of flowering plant in the genus ''Tagetes'' native to Mexico. Despite being native to the Americas, it is often called the African marigold. In Mexico, this plant is found in the wild in the states of México, Michoacán, Puebla, and Veracruz. This plant reaches heights of between . The Aztecs gathered the wild plant as well as cultivating it for medicinal, ceremonial and decorative purposes. It is widely cultivated commercially with many cultivars in use as ornamental plants, and for the cut-flower trade. Some authorities regard ''Tagetes patula'' (the French marigold) as a synonym of ''Tagetes erecta''. Description It is a herbaceous annual or perennial plant whose height ranges from 30–110 cm. The root is cylindrical, pivoting, with a fibrous and shallow branching system. The stem is striated, sometimes ridged, smooth or slightly with villi, cyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagetes Patula
''Tagetes patula'', the French marigold, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to Mexico and Guatemala with several naturalised populations in many other countries. It is widely cultivated as an easily grown bedding plant, with thousands of different cultivars in brilliant shades of yellow and orange. Some authorities regard ''Tagetes patula'' as a synonym of ''Tagetes erecta'', the Mexican marigold. Name The Latin specific epithet ''patula'' means “with a spreading habit”. Description ''Tagetes patula'' is an annual, occasionally reaching tall by wide. In some climates it flowers from July to October. In its native habitat of the highlands of central Mexico, blooms are produced from September to killing frost. Achenes ripen and are shed within two weeks of the start of bloom. The heads contain mostly hermaphrodite (having both male and female organs) florets and are pollinated primarily by beetles in the wild, as well as by tachinid flies and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, the roe deer, and the moose. Male deer of all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. In this they differ from permanently horned antelope, which are part of a different family (Bovidae) within the same order of even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla). The musk deer (Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains (Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in heraldry, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock forage and silage, and as soil-enhancing green manure. Well-known legumes include beans, soybeans, chickpeas, peanuts, lentils, lupins, mesquite, carob, tamarind, alfalfa, and clover. Legumes produce a botanically unique type of fruit – a simple dry fruit that develops from a simple carpel and usually dehisces (opens along a seam) on two sides. Legumes are notable in that most of them have symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria in structures called root nodules. For that reason, they play a key role in crop rotation. Terminology The term ''pulse'', as used by the United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), is reserved for legume crops harvested solely for the dry seed. This excludes green beans and green peas, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
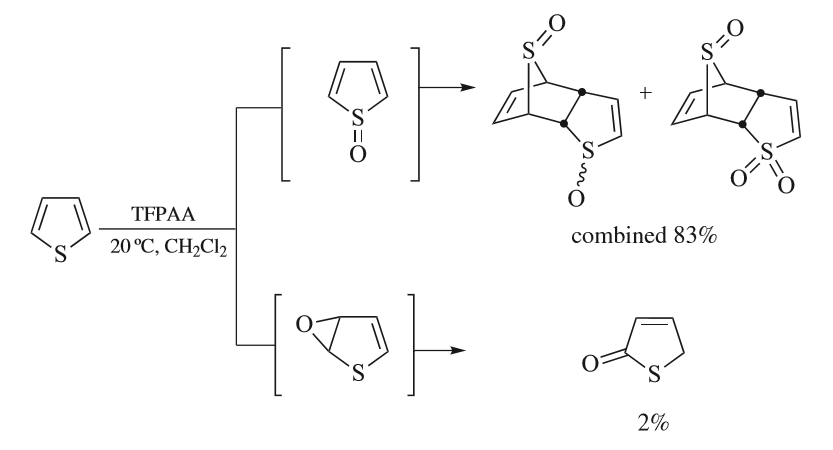
Thiophenes
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a planar five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. It is a colorless liquid with a benzene-like odor. In most of its reactions, it resembles benzene. Compounds analogous to thiophene include furan (C4H4O), selenophene (C4H4Se) and pyrrole (C4H4NH), which each vary by the heteroatom in the ring. Isolation and occurrence Thiophene was discovered as a contaminant in benzene. It was observed that isatin (an indole) forms a blue dye if it is mixed with sulfuric acid and crude benzene. The formation of the blue indophenin had long been believed to be a reaction of benzene itself. Viktor Meyer was able to isolate thiophene as the actual substance responsible for this reaction. Thiophene and especially its derivatives occur in petroleum, sometimes in concentrations up to 1–3%. The thiophenic content of oil and coal is removed via the hydrodesulfurization (HDS) pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae. Wild potato species can be found from the southern United States to southern Chile. The potato was originally believed to have been domesticated by Native Americans independently in multiple locations,University of Wisconsin-Madison, ''Finding rewrites the evolutionary history of the origin of potatoes'' (2005/ref> but later genetic studies traced a single origin, in the area of present-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia. Potatoes were domesticated there approximately 7,000–10,000 years ago, from a species in the ''Solanum brevicaule'' complex. Lay summary: In the Andes region of South America, where the species is indigenous, some close relatives of the potato are cultivated. Potatoes were introduced to Europe from the Americas by the Spanish in the second half of the 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the chief commercial crop is ''N. tabacum''. The more potent variant ''N. rustica'' is also used in some countries. Dried tobacco leaves are mainly used for smoking in cigarettes and cigars, as well as pipes and shishas. They can also be consumed as snuff, chewing tobacco, dipping tobacco, and snus. Tobacco contains the highly addictive stimulant alkaloid nicotine as well as harmala alkaloids. Tobacco use is a cause or risk factor for many deadly diseases, especially those affecting the heart, liver, and lungs, as well as many cancers. In 2008, the World Health Organization named tobacco use as the world's single greatest preventable cause of death. Etymology The English word ''tobacco'' originates from the Spanish word "tabaco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chili Pepper
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for their pungency. Chili peppers are widely used in many cuisines as a spice to add "heat" to dishes. Capsaicin and related compounds known as capsaicinoids are the substances giving chili peppers their intensity when ingested or applied topically. While ''chili peppers'' are (to varying degrees) pungent or "spicy", there are other varieties of capsicum such as bell peppers (UK: peppers) which generally provide additional sweetness and flavor to a meal rather than “heat.” Chili peppers are believed to have originated somewhere in Central or South America. and were first cultivated in Mexico. After the Columbian Exchange, many cultivars of chili pepper spread around the world, used for both food and traditional medicine. This led to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eggplant
Eggplant ( US, Canada), aubergine ( UK, Ireland) or brinjal (Indian subcontinent, Singapore, Malaysia, South Africa) is a plant species in the nightshade family Solanaceae. ''Solanum melongena'' is grown worldwide for its edible fruit. Most commonly purple, the spongy, absorbent fruit is used in several cuisines. Typically used as a vegetable in cooking, it is a berry by botanical definition. As a member of the genus ''Solanum'', it is related to the tomato, chili pepper, and potato, although those are of the New World while the eggplant is of the Old World. Like the tomato, its skin and seeds can be eaten, but, like the potato, it is usually eaten cooked. Eggplant is nutritionally low in macronutrient and micronutrient content, but the capability of the fruit to absorb oils and flavors into its flesh through cooking expands its use in the culinary arts. It was originally domesticated from the wild nightshade species ''thorn'' or ''bitter apple'', '' S. incanum'',Tsao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , from which the English word ''tomato'' derived. Its domestication and use as a cultivated food may have originated with the indigenous peoples of Mexico. The Aztecs used tomatoes in their cooking at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and after the Spanish encountered the tomato for the first time after their contact with the Aztecs, they brought the plant to Europe, in a widespread transfer of plants known as the Columbian exchange. From there, the tomato was introduced to other parts of the European-colonized world during the 16th century. Tomatoes are a significant source of umami flavor. They are consumed in diverse ways: raw or cooked, and in many dishes, sauces, salads, and drinks. While tomatoes are fruits� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companion Planting
Companion planting in gardening and agriculture is the planting of different crops in proximity for any of a number of different reasons, including pest control, pollination, providing habitat for beneficial insects, maximizing use of space, and to otherwise increase crop productivity. Companion planting is a form of polyculture. Companion planting is used by farmers and gardeners in both industrialized and developing countries for many reasons. Many of the modern principles of companion planting were present many centuries ago in forest gardens in Asia, and thousands of years ago in Mesoamerica. History In China, mosquito ferns (''Azolla'' spp.) have been used for at least a thousand years as companion plants for rice crops. They host a cyanobacterium (''Anabaena azollae'') that fixes nitrogen from the atmosphere, and they block light from plants that would compete with the rice. Companion planting was practiced in various forms by the indigenous peoples of the Americas pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with Arthropod, arthropods, Tardigrade, tardigrades and other moulting animalia, animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike platyhelminthe, flatworms, have tubular digestion, digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)