|
Tactical Ignoring
Silent treatment is the refusal to communicate verbally and electronically with someone who is trying to communicate and elicit a response. It may range from just sulking to malevolent abusive controlling behaviour. It may be a passive-aggressive form of emotional abuse in which displeasure, disapproval and contempt is exhibited through nonverbal gestures while maintaining verbal silence. Clinical psychologist Harriet Braiker identifies it as a form of manipulative punishment. It may be used as a form of social rejection; according to the social psychologist Kipling Williams it is the most common form of ostracism. Origin of term The term originated from "treatment" through silence, which was fashionable in prisons in the 19th century. In use since the prison reforms of 1835, the silent treatment was used in prisons as an alternative to physical punishment, as it was believed that forbidding prisoners from speaking, calling them by a number rather than their name, and making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D0CBF360-5405-4792-BCDF-3FA379C2FAF
D, or d, is the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''dee'' (pronounced ), plural ''dees''. History The Semitic letter Dāleth may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are many different Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek and Latin, the letter represented ; in the Etruscan alphabet the letter was archaic, but still retained (see letter B). The equivalent Greek letter is Delta, Δ. Architecture The minuscule (lower-case) form of 'd' consists of a lower-story left bowl and a stem ascender. It most likely developed by gradual variations on the majuscule (capital) form 'D', and today now composed as a stem with a full lobe to the right. In handwriting, it was common to start the arc to the left of the vertical stroke, resulting in a serif at the top of the arc. This serif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workplace Bullying
Workplace bullying is a persistent pattern of mistreatment from others in the workplace that causes either physical or emotional harm. It can include such tactics as verbal, nonverbal, psychological, and physical abuse, as well as humiliation. This type of workplace aggression is particularly difficult because, unlike the typical school bully, workplace bullies often operate within the established rules and policies of their organization and their society. In the majority of cases, bullying in the workplace is reported as having been done by someone who has authority over the victim. However, bullies can also be peers, and rarely subordinates. Research has also investigated the impact of the larger organizational context on bullying as well as the group-level processes that impact on the incidence and maintenance of bullying behaviour. Bullying can be covert or overt. It may be missed by superiors; it may be known by many throughout the organization. Negative effects are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolation To Facilitate Abuse
Isolation (physical, social or emotional) is often used to facilitate power and control over someone for an abusive purpose. This applies in many contexts such as workplace bullying,Rayner C, Hoel H, Cooper CL Workplace Bullying: What we know, who is to blame and what can we do? (2001)Peyton PR Dignity at Work: Eliminate Bullying and Create a Positive Working Environment (2003) elder abuse, domestic abuse, child abuse, and cults. Isolation reduces the opportunity of the abused to be rescued or escape from the abuse. It also helps disorient the abused and makes the abused more dependent on the abuser. The degree of power and control over the abused is contingent upon the degree of their physical or emotional isolation. Isolation of the victim from the outside world is an important element of psychological control. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guilt Trip
A guilt trip is a feeling of guilt or responsibility, especially an unjustified one induced by someone else. Overview Creating a guilt trip in another person may be considered to be manipulation in the form of punishment for a perceived transgression. George K. Simon interprets the guilt trip as a special kind of intimidation tactic. A manipulator suggests to the conscientious victim that he or she does not care enough, is too selfish or has it easy. This usually results in the victim feeling bad, keeping them in a self-doubting, anxious and submissive position. There are limited studies examining guilt trips, and those studies tend to focus on guilt trips in parent–child relationships.Humeny C (2013)A Qualitative Investigation of a Guilt Trip Conference Paper Conference: Institute of Cognitive Science, Carleton University Spring Proceedings Types Three types of guilt trip are proposed: * Tongue-in-cheek * Moral education * Side effect. See also References Further r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghosting (behavior)
Ghosting, also known as simmering or icing, is a colloquial term which describes the practice of ending all communication and contact with another person without any apparent warning or justification and ignoring any subsequent attempts to communicate. The term originated in the early 2000s, typically referring to dating and romantic relationships. In the following decade, media reported a rise in ghosting, which has been attributed to the increasing use of social media and online dating apps. The term has also expanded to refer to similar practices among friends, family members, employers and businesses. The most common cause of ghosting in a personal relationship is to avoid emotional discomfort in a relationship. A person ghosting typically has little acknowledgment of how it will make the other person feel. Ghosting is associated with negative mental health effects on the person on the receiving end and has been described by some mental health professionals as a passive-aggres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destabilisation
The word destabilisation can be applied to a wide variety of contexts such as attempts to undermine political, military or economic power. Psychology In a psychological context it is used as a technique in brainwashing and abuse to disorient and disarm the victim. In the context of workplace bullying Workplace bullying is a persistent pattern of mistreatment from others in the workplace that causes either physical or emotional harm. It can include such tactics as verbal, nonverbal, psychological, and physical abuse, as well as humiliation ..., destabilisation applied to the victim may involve: * failure to acknowledge good work and value the victim's efforts * allocation of meaningless tasks * removal of areas of responsibility without consultation * repeated reminders of blunders * setting up to fail * shifting of goal posts without telling the victim * persistent attempts to demoralise the victim Destabilisation could also denote the extreme end of disinhibiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Shoulder
"Cold shoulder" is a phrase used to express dismissal or the act of disregarding someone. Its origin is attributed to Sir Walter Scott in a work published in 1816, which is in fact a mistranslation of an expression from the Vulgate Bible. There is also a commonly repeated incorrect folk etymology. The expression "cold shoulder" has been used in many literary works, and has entered into the vernacular. It has been used as a description of aloofness and disdain, a contemptuous look over one's shoulder,Hodgson, p. 153. and even in the context of a woman attempting to decline the advances of an aggressive man.Palmatier, p. 73. Overall, it remains widely popular as a phrase for describing the act of ignoring someone or something, or giving an unfriendly response.Helterbran, p. 22. Etymology The first recorded use of the expression was in 1816 by Sir Walter Scott in the Scots language, in '' The Antiquary''. This expression is a mistranslation of the Latin phrase ''dederunt umerum rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parent Management Training
Parent management training (PMT), also known as behavioral parent training (BPT) or simply parent training, is a family of treatment programs that aims to change parenting behaviors, teaching parents positive reinforcement methods for improving pre-school and school-age children's behavior problems (such as aggression, hyperactivity, temper tantrums, and difficulty following directions). PMT is one of the most investigated treatments available for disruptive behavior, particularly oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) and conduct disorder (CD); it is effective in reducing child disruptive behavior and improving parental mental health. PMT has also been studied as a treatment for disruptive behaviors in children with other conditions. Limitations of the existing research on PMT include a lack of knowledge on mechanisms of change and the absence of studies of long-term outcomes. PMT may be more difficult to implement when parents are unable to participate fully due to psychopathology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punishment
Punishment, commonly, is the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual, meted out by an authority—in contexts ranging from child discipline to criminal law—as a response and deterrent to a particular action or behavior that is deemed undesirable or unacceptable. It is, however, possible to distinguish between various different understandings of what punishment is. The reasoning for punishment may be to condition a child to avoid self-endangerment, to impose social conformity (in particular, in the contexts of compulsory education or military discipline), to defend norms, to protect against future harms (in particular, those from violent crime), and to maintain the law—and respect for rule of law—under which the social group is governed. and violates the law or rules by which the group is governed. Punishment may be self-inflicted as with self-flagellation and mortification of the flesh in the religious setting, but is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
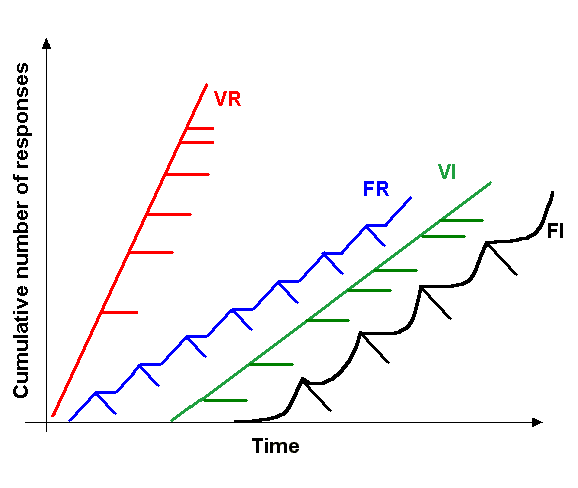
Negative Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Behavior Analysis
Applied behavior analysis (ABA), also called behavioral engineering, is a psychological intervention that applies empirical approaches based upon the principles of respondent and operant conditioning to change behavior of social significance.See also footnote number "(1)" of nd the whole "What is ABA?" section of Where the same definition is given, (or quoted), and it credits (or mentions) both the source "Baer, Wolf & Risley, 1968" (Drs. Donald Baer, PhD, Montrose Wolf, PHD and Todd R. Risley, PhD, (Professor Emeritus of Psychology at the University of Alaska) were psychologists who developed science of applied behavior analysis) and ianother source, called "Sulzer-Azaroff & Mayer, 1991". Beth Sulzer-Azaroff is a psychologist at University of Massachusetts Amherst, Department of Psychology It is the applied form of behavior analysis; the other two forms are radical behaviorism (or the philosophy of the science) and the experimental analysis of behavior (or basic experi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |