|
Susan Gerbi
Susan Gerbi (born 1944) is the George Eggleston Professor of Biochemistry and a professor of biology at Brown University. Early life and education Susan Gerbi received her B.A. degree in zoology from Barnard College in 1965. She was a postdoctoral fellow at the Max-Planck-Institut für Biologie in Tübingen, Germany. Research career Gerbi received her PhD from Yale University in 1970 for her work with Joseph Gall; she and Gall developed the technique of in situ hybridization, which is used to localize RNA or DNA in tissue. After earning her doctorate, she completed a fellowship at the Max Planck Institute before returning to the United States and establishing her own laboratory. Between 1998 and 2001, she published research detailing a method to determine the nucleotide where DNA replication begins for a gene and showed that in yeast and other eukaryotes, this site is adjacent to the origin recognition complex binding site. Her recent research has covered conservation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments. Biologists are able to study life at multiple levels of organization, from the molecular biology of a cell to the anatomy and physiology of plants and animals, and evolution of populations.Based on definition from: Hence, there are multiple subdisciplines within biology, each defined by the nature of their research questions and the tools that they use. Like other scientists, biologists use the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Women's History Project
The National Women's History Alliance (NWHA) is an American non-profit organization dedicated to honoring and preserving women's history. The NWHA was formerly known as the National Women's History Project. Based out of Santa Rosa, California since 1980, it was started by women's history activists Molly Murphy MacGregor, Mary Ruthsdotter, Maria Cuevas, Paula Hammett and Bette Morgan. The National Women's History Alliance started by leading a coalition that successfully lobbied Congress to designate March as Women's History Month, now celebrated across the country. Today, the National Women's History Alliance is known nationally as the only clearinghouse providing information and training in multicultural women’s history for educators, community organizations, and parents-for anyone wanting to expand their understanding of the historic contributions of women. History Over 30 years of "Writing Women Back into History" From a Grassroots Organization into a National Institution � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Association For The Advancement Of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is an American international non-profit organization with the stated goals of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific responsibility, and supporting scientific education and science outreach for the betterment of all humanity. It is the world's largest general scientific society, with over 120,000 members, and is the publisher of the well-known scientific journal ''Science''. History Creation The American Association for the Advancement of Science was created on September 20, 1848, at the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was a reformation of the Association of American Geologists and Naturalists. The society chose William Charles Redfield as their first president because he had proposed the most comprehensive plans for the organization. According to the first constitution which was agreed to at the September 20 meeting, the goal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States by population, seventh-least populous, with slightly fewer than 1.1 million residents 2020 United States census, as of 2020, but it is the List of U.S. states by population density, second-most densely populated after New Jersey. It takes its name from Aquidneck Island, the eponymous island, though most of its land area is on the mainland. Rhode Island borders Connecticut to the west; Massachusetts to the north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to the south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Island Sound. It also shares a small maritime border with New York (state), New York. Providence, Rhode Island, Providence is its capital and most populous city. Native Americans lived around Narragansett Bay for thousands of years before English settler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society For Cell Biology
The American Society for Cell Biology (ASCB) is a professional society that was founded in 1960.American Society for Cell Biology records - Historical Note , Albin O. Kuhn Library & Gallery, . Accessed February 28, 2011. Its mission statement says: History On 6 April 1959 the passed a resolution for the establishm ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
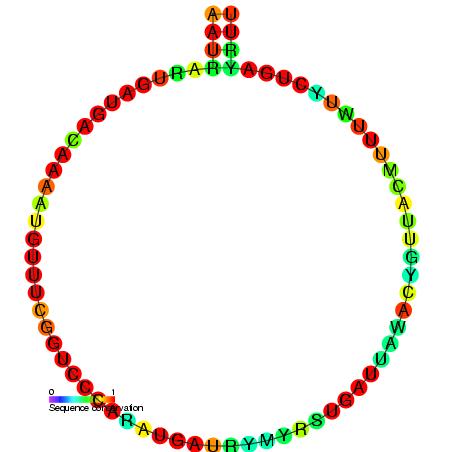
Small Nuclear RNA
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is a class of small RNA molecules that are found within the splicing speckles and Cajal bodies of the cell nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The length of an average snRNA is approximately 150 nucleotides. They are transcribed by either RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. Their primary function is in the processing of pre-messenger RNA (hnRNA) in the nucleus. They have also been shown to aid in the regulation of transcription factors (7SK RNA) or RNA polymerase II (B2 RNA), and maintaining the telomeres. snRNA are always associated with a set of specific proteins, and the complexes are referred to as small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNP, often pronounced "snurps"). Each snRNP particle is composed of a snRNA component and several snRNP-specific proteins (including Sm proteins, a family of nuclear proteins). The most common human snRNA components of these complexes are known, respectively, as: U1 spliceosomal RNA, U2 spliceosomal RNA, U4 spliceosomal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Nucleolar RNA
In molecular biology, Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes. snoRNA guided modifications After transcription, nascent rRNA molecules (termed pre-rRNA) undergo a series of processing steps to generate the mature rRNA molecule. Prior to cleavage by exo- and endonucleases, the pre-rRNA undergoes a complex pattern of nucleoside modifications. These include methylations and pseudouridylations, guided by snoRNAs. *Methylation is the attachment or substitution of a methyl group onto various substrates. The rRNA of humans contain approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connections". Pearson Education. San Francisco: 2003. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. But in the three-domain system, based upon molecular analysis, prokaryotes are divided into two domains: ''Bacteria'' (formerly Eubacteria) and ''Archaea'' (formerly Archaebacteria). Organisms with nuclei are placed in a third domain, Eukaryota. In the study of the origins of life, prokaryotes are thought to have arisen before eukaryotes. Besides the absence of a nucleus, prokaryotes also lack mitochondria, or most of the other membrane-bound organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. It was once thought that prokaryotic cellular components within the cytop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form SSU rRNA, small and LSU rRNA, large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and Translation (biology), translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins by mass. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, Base pair, base-pairing within these sequences commonly forms stem-loop configurations. The length and position of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Recognition Complex
In molecular biology, origin recognition complex (ORC) is a multi-subunit DNA binding complex (6 subunits) that binds in all eukaryotes and archaea in an ATP-dependent manner to origins of replication. The subunits of this complex are encoded by the ORC1, ORC2, ORC3, ORC4, ORC5 and ORC6 genes. ORC is a central component for eukaryotic DNA replication, and remains bound to chromatin at replication origins throughout the cell cycle. ORC directs DNA replication throughout the genome and is required for its initiation. ORC and Noc3p bound at replication origins serve as the foundation for assembly of the pre-replication complex (pre-RC), which includes Cdc6, Tah11 (a.k.a. Cdt1), and the Mcm2-Mcm7 complex. Pre-RC assembly during G1 is required for replication licensing of chromosomes prior to DNA synthesis during S phase. Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of Orc2, Orc6, Cdc6, and MCM by the cyclin-dependent protein kinase Cdc28 regulates initiation of DNA replication, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |