|
Surat–Malda Town Express
The 13425 / 13426 Surat–Malda Town Express is an Express train running between of Gujarat and of West Bengal. It operates as train number 13425 from Malda Town to Surat and as train number 13426 in the reverse direction, serving the states of Gujarat Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ..., Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Jharkhand and West Bengal. Coach composite The train consists of 22 coaches: * 1 AC II Tier * 5 AC III Tier * 8 Sleeper class * 6 General Unreserved * 2 Seating cum Luggage Rake Services 13425 Malda Town–Surat Express covers the distance of 2137 km in 40 hours 20 mins (53 km/h) and in 41 hours 40 mins as 13426 Surat–Malda Town Express (51 km/h). As the average speed of the train is below , as per Indian Railway rules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Express Trains In India
Express trains are express rail services of India. Express trains make a small number of stops, unlike ordinary passenger or local trains. Because of their limited stops, these trains are able to obtain the highest speeds of any trains in India. An express train is one where the average speed, excluding halts, is greater than 42 km/h. Including halts the average speed often is below 42 km/h. Although this is pretty slow as compared to international standards, the "Express" trains here mean faster than the ordinary passenger and local trains. In some cases, trains run express where there is an overlapping passenger train service available, and run as passenger train, where there is no supplemental passenger service. Superfast Superfast trains are express trains which make still fewer stops, as compared to ordinary express trains, achieving still shorter journey times. Tickets cost more than ordinary express trains as they have "superfast surcharge" added to them. Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
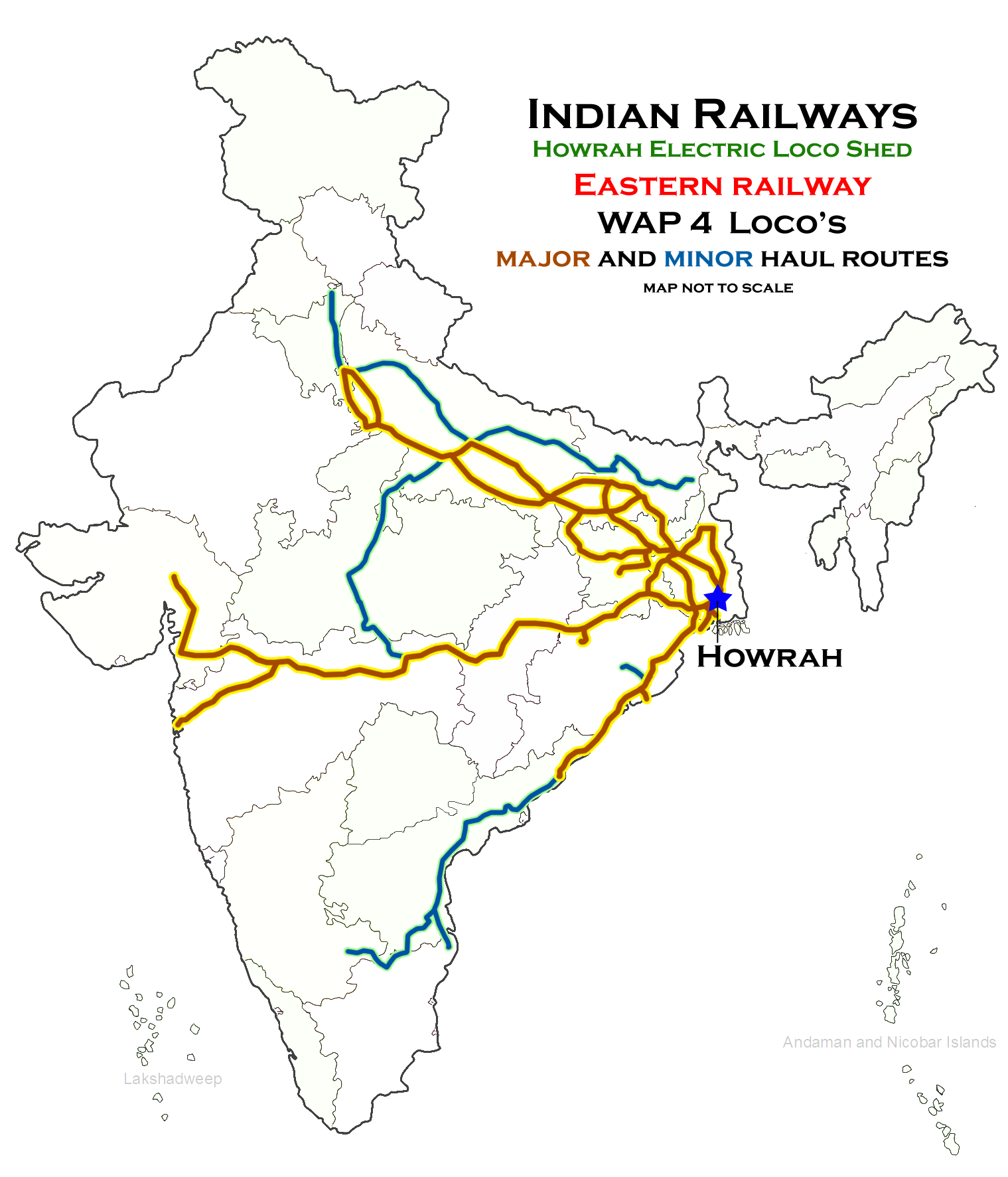
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah
Electric Loco Shed, Howrah is a motive power depot performing locomotive maintenance and repair facility for electric locomotives of the Indian Railways, located at Howrah of the Eastern Railway zone in West Bengal, India. It is one of the two electric locomotive sheds of the Eastern Railway, the others being at Asansol (ASN). there are 150 locomotives in the shed. History Steam locomotive sheds used to exist at Howrah until the late 1970s. After Eastern Railway set a deadline to eliminate all steam locomotive operations by 1990, a push was given towards establishing electric locomotion as the primary motive power, and the steam locomotive sheds was decommissioned. To meet the needs of exponentially increasing rail traffic on the new continuous broad-gauge lines from Kolkata to rest of India with the completion of gauge conversion, the Howrah was selected by Indian Railways for a new electric locomotive shed. New electric locomotive shed was inaugurated in the late 2001s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Surat
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations. Transport infrastructure consists of both fixed installations, including roads, railways, airways, waterways, canals, and pipelines, and terminals such as airports, railway stations, bus stations, warehouses, trucking terminals, refueling depots (including fueling docks and fuel stations), and seaports. Terminals may be used both for interchange of passengers and cargo and for maintenance. Means of transport are any of the different kinds of transport facilities used to carry people or cargo. They may include vehicles, riding animals, and pack animals. Vehicles may incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Gujarat
Rail or rails may refer to: Rail transport *Rail transport and related matters *Rail (rail transport) or railway lines, the running surface of a railway Arts and media Film * ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini * ''Rail'' (1967 film), a film by Geoffrey Jones for British Transport Films *'' Mirattu'' or ''Rail'', a Tamil-language film and its Telugu dub Magazines * ''Rail'' (magazine), a British rail transport periodical * ''Rails'' (magazine), a former New Zealand based rail transport periodical Other arts *The Rails, a British folk-rock band * Rail (theater) or batten, a pipe from which lighting, scenery, or curtains are hung Technology *Rails framework or Ruby on Rails, a web application framework *Rail system (firearms), a mounting system for firearm attachments *Front engine dragster *Runway alignment indicator lights, a configuration of an approach lighting system *Rule Augmented Interconnect Layout, a specification for expressing guidelines for prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Bihar
This article deals with the system of transport in Bihar, both public and private. Road transport Bihar has national highways with total length of and state highways with total length of . Also. Bihar has of proposed Expressways. Expressways National Highways State Highways Rail transport The railway network in Bihar is excellent and provides first-rate citizen centric railway services to the people. Most of the cities have a railway junction that facilitates railway travel across the state. You can easily travel from one part of the state to the other by trains. Urban Rail * Patna Metro - Under construction * Patna Monorail - Proposed * Patna tram - defunct since 1903 Water transport Bihar is connected by National Waterways No. 1 which established in October 1986. This National Waterways has fixed terminals at Haldia, BISN (Kolkata), Pakur, Farrakka and Patna. This National Waterways has also floating terminals facilities at Haldia, Kolkata, Diamo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udyog Karmi Express
The 12943 / 12944 Valsad–Kanpur Central Udyog Karmi Express is a Superfast Express express train of the Indian Railways in the Western Railway zone that runs between Valsad and Kanpur in India. It operates as train number 12943 from Valsad to Kanpur Central and as train number 12944 in the reverse direction serving the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. The train has been named 'Udyog Karmi' which translates to Industrial Worker in Devanagari as the train connects the two important industrial cities of Valsad & Kanpur in their respective states of Gujarat & Uttar Pradesh. Coaches The 12943 / 12944 Valsad–Kanpur Central Udyog Karmi Express presently has 2 AC 2 tier 6 AC 3 tier, 8 Sleeper Class, 4 Unreserved/General, 1 End on Generator and 1 Seating cum Luggage Rake coaches. It does not carry a pantry car. As is customary with most train services in India, coach composition may be amended at the discretion of Indian Railways dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shramik Express
The 19051 / 19052 Valsad–Muzaffarpur Shramik Express is an Express train running between Valsad of Gujarat and Muzaffarpur of Bihar. It operates as train number 19051 from Valsad to Muzaffarpur Junction and as train number 19052 in the reverse direction, serving the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Coach composition The train consists of 23 coaches: * 1 AC II cum AC III tier(AB1) * 1 AC III tier(B1) * 14 Sleeper class(SL) * 5 General Unreserved(GEN) * 2 Seating cum Luggage Rake(SLR) Services 19051 Valsad–Muzaffarpur Shramik Express covers the distance of 1782 km in 32 hours 35 mins (57 km/h) & in 35 hours as 19052 Muzaffarpur–Valsad Shramik Express (53 km/h). As the average speed of the train is below , as per Indian Railway rules, its fare does not includes a Superfast surcharge. Route & Halts The important halts of the train are: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Traction The 19051 / 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapti Ganga Express
The 19045 / 19046 Tapti Ganga Express is an Express train running between of Gujarat and of Bihar. The train is named for the Tapti River in Surat and the Ganga River in Chhapra. It was introduced in 1990 by George Fernandes to run between Surat and , but in Railway Budget 2012–13 it was extended up to Chhapra Junction. It operates as train number 09045 from Surat to Chhapra Junction and as train number 09046 in the reverse direction, serving the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. Coach composition The train consists of 22 coaches: * 4 AC III Tier * 11 Sleeper class * 1 Pantry car * 4 General Unreserved * 2 EOG cum Luggage Rake Services 19045 Surat–Chhapra Tapti Ganga Express covers the distance of 1728 km in 32 hours 45 mins (53 km/hr) & in 33 hours 40 mins as 19046 Chhapra–Surat Tapti Ganga Express (51 km/hr). As the average speed of the train is below , as per Indian Railway rules, its fare doesn't include a Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WAP-4
The Indian locomotive class WAP-4 is a class of 25 kV AC electric locomotives that was developed in 1993 by Chittaranjan Locomotive Works for Indian Railways. The model name stands for broad gauge (W), AC Current (A), Passenger traffic (P) engine, 4th generation (4). They entered service in late 1994. A total of 778 WAP-4 were built at CLW between 1993 and 2015, which made them the most numerous class of mainline electric passenger locomotive until the WAP-7. The WAP-4 is one of the most successful locomotives of Indian Railways serving both passenger and freight trains for over 28 years. This class provided the basic design for other locomotives like the WAP-6 . Despite the introduction of more modern types of locomotives like WAP-7, a significant number are still in use, both in mainline duties. Production of this class was halted in December 2015 with locomotive number 25051 being the last unit to be rolled out. As of September 2022, all locomotives except those lost in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digha–Malda Town Express
The Digha–Malda Town Express is an Express train belonging to Eastern Railway zone that runs between and in India. It is currently being operated with 13417/13418 train numbers on a weekly basis. Service The 13417/Digha–Malda Town Express has an average speed of 45 km/h and covers 656 km in 14h 30m. The 13418/Malda Town–Digha Express has an average speed of 44 km/h and covers 656 km in 10h 35m. Route and stops The important stops of the train are: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Coach composition The train has standard ICF rakes with a maximum speed of 110 km/h. The train consists of 12 coaches: * 1 AC III Tier * 3 sleeper coaches * 6 general * 2 seating cum luggage rake Traction Both trains are hauled by an Asansol Loco Shed-based WAM-4 electric locomotive from Digha to Durgapur and thence by an Andal Loco Shed-based WDM-3A diesel locomotive to Malda Town and back. Direction reversal Train reverses its direction: * R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Railway Zone
The Eastern Railway (abbreviated ER) is among the 19 zones of the Indian Railways. Its headquarters is at Fairley Place, Kolkata and comprises four divisions: , , , and . Each division is headed by a Divisional Railway Manager (DRM). The name of the division denotes the name of the city where the divisional headquarters is located. Eastern Railway oversees the largest and second largest rail complexes in the country, Howrah Junction and Sealdah railway station, and also contains the highest number of A1 and A Category Stations like , , , , Kolkata, , Barddhaman, Rampurhat Junction, , Jasidih, Bandel and Naihati. Eastern Railways operates India's oldest train, Kalka Mail. History The East Indian Railway (EIR) Company was incorporated in 1845 to connect eastern India with Delhi. The first train ran here between and on 15 August 1854. The train left Howrah station at 8:30 a.m. and reached Hooghly in 91 minutes. The management of the East Indian Railway was taken over by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ; ) is a state in eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It has an area of . It is the 15th largest state by area, and the 14th largest by population. Hindi is the official language of the state. The city of Ranchi is its capital and Dumka its sub-capital. The state is known for its waterfalls, hills and holy places; Baidyanath Dham, Parasnath, Dewri and Rajrappa are major religious sites. The state was formed on 15 November 2000, after carving out what was previously the southern half of Bihar. Jharkhand suffers from what is sometimes termed a resource curse: it accounts for more than 40% of the mineral resources of India, but 39.1% of its population is below the poverty line and 19.6% of children under five years of age are malnourished. Jharkhand is primarily rural, with about 24% of its population living in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |