|
Strike Wave Of 1945–1946
The strike wave of 1945–1946 (also called the great strike wave of 1946) was a series of massive post-war labor strikes after World War II from 1945 to 1946 in the United States spanning numerous industries and public utilities. In the year after V-J Day, more than five million American workers were involved in strikes, which lasted on average four times longer than those during the war. They were the largest strikes in American labor history.From Class War to Cold War , John Newsinger Other strikes occurred across the world including in and . < ...
|
Post-war
In Western usage, the phrase post-war era (or postwar era) usually refers to the time since the end of World War II. More broadly, a post-war period (or postwar period) is the interval immediately following the end of a war. A post-war period can become an interwar period or interbellum, when a war between the same parties resumes at a later date (such as the period between World War I and World War II). By contrast, a post-war period marks the cessation of armed conflict entirely. Post–World War II Chronology of the post–World War II era The term "post-war" can have different meanings in different countries and refer to a period determined by local considerations based on the effect of the war there. Some examples of post-war events are (in chronological order) ;The Cold War (1947–1991) The Cold War was a geopolitical conflict between the capitalist and liberal democratic United States of America, the authoritarian and Communist Marxist–Leninist Union of Soviet Soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Auto Workers (UAW) Strike Of 1945–1946
The International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace, and Agricultural Implement Workers of America, better known as the United Auto Workers (UAW), is an American Labor unions in the United States, labor union that represents workers in the United States (including Puerto Rico) and Canada. It was founded as part of the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) in the 1930s and grew rapidly from 1936 to the 1950s. The union played a major role in the liberal wing of the Democratic Party under the leadership of Walter Reuther (president 1946–1970). It was known for gaining high wages and pensions for Automobile industry, auto workers, but it was unable to unionize auto plants built by foreign-based car makers in the South after the 1970s, and it went into a steady decline in membership; reasons for this included increased automation, decreased use of labor, movements of manufacturing (including reaction to NAFTA), and increased globalization. UAW members in the 21st century wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Disputes In The United States
Labour or labor may refer to: * Childbirth, the delivery of a baby * Labour (human activity), or work ** Manual labour, physical work ** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer ** Organized labour and the labour movement, consisting principally of labour unions ** The Labour Party (UK) Literature * ''Labor'' (journal), an American quarterly on the history of the labor movement * ''Labour/Le Travail'', an academic journal focusing on the Canadian labour movement * ''Labor'' (Tolstoy book) or ''The Triumph of the Farmer or Industry and Parasitism'' (1888) Places * La Labor, Honduras * Labor, Koper, Slovenia Other uses * ''Labor'' (album), a 2013 album by MEN * Labor (area), a Spanish customary unit * "Labor", an episode of TV series '' Superstore'' * Labour (constituency), a functional constituency in Hong Kong elections * Labors, fictional robots in ''Patlabor'' People with the surname * Earle Labor (born 1928), professor of American litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Strikes In The United States
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of '' captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
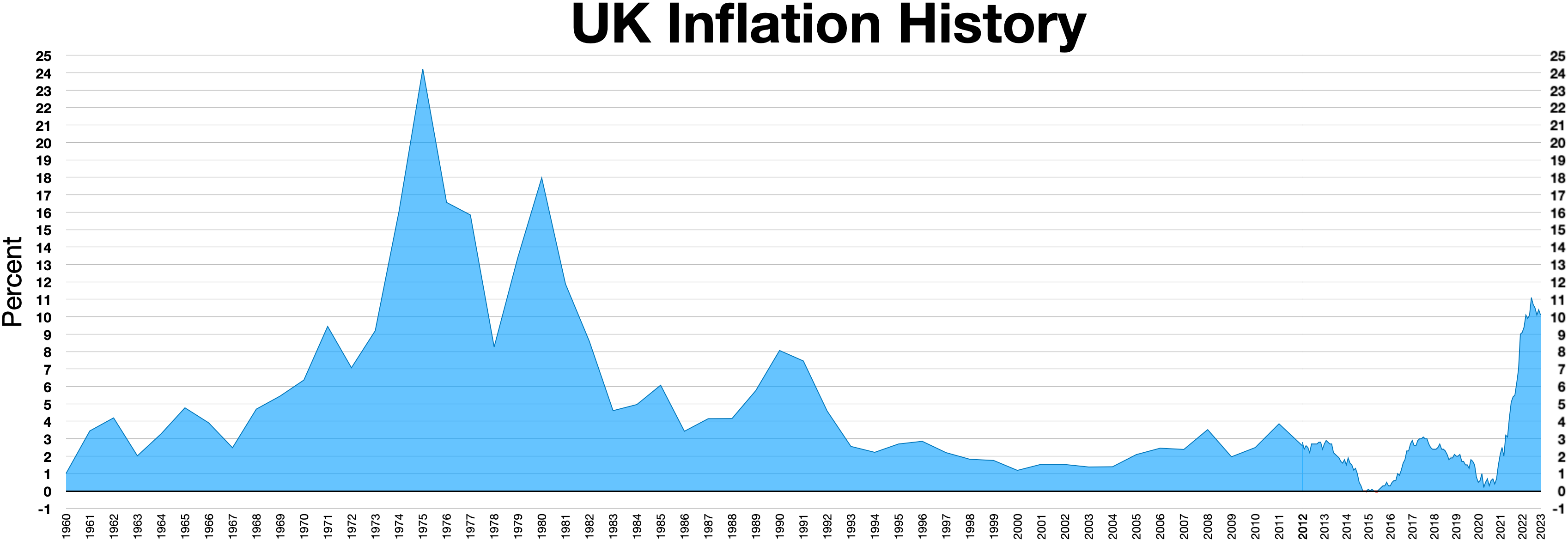
Winter Of Discontent
The Winter of Discontent was the period between November 1978 and February 1979 in the United Kingdom characterised by widespread strikes by private, and later public, sector trade unions demanding pay rises greater than the limits Prime Minister James Callaghan and his Labour Party government had been imposing, against Trades Union Congress (TUC) opposition, to control inflation. Some of these industrial disputes caused great public inconvenience, exacerbated by the coldest winter Winter of 1962–1963 in the United Kingdom, in 16 years, in which severe storms isolated many remote areas of the country. A strike by workers at Ford Motor Company, Ford in late 1978 was settled with a pay increase of 17 per cent, well above the 5 per cent limit the government was holding its own workers to with the intent of setting an example for the private sector to follow, after a resolution at the Labour Party's annual conference urging the government not to intervene passed overwhelmingly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1945 United Kingdom General Election
The 1945 United Kingdom general election was a national election held on 5 July 1945, but polling in some constituencies was delayed by some days, and the counting of votes was delayed until 26 July to provide time for overseas votes to be brought to Britain. The governing Conservative Party sought to maintain its position in Parliament but faced challenges from public opinion about the future of the United Kingdom in the post-war period. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill proposed to call for a general election in Parliament, which passed with a majority vote less than two months after the conclusion of the Second World War in Europe. The election's campaigning was focused on leadership of the country and its postwar future. Churchill sought to use his wartime popularity as part of his campaign to keep the Conservatives in power after a wartime coalition had been in place since 1940 with the other political parties, but he faced questions from public opinion surrounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taft–Hartley Act
The Labor Management Relations Act of 1947, better known as the Taft–Hartley Act, is a United States federal law that restricts the activities and power of labor unions. It was enacted by the 80th United States Congress over the veto of President Harry S. Truman, becoming law on June 23, 1947. Taft–Hartley was introduced in the aftermath of a major strike wave in 1945 and 1946. Though it was enacted by the Republican-controlled 80th Congress, the law received significant support from congressional Democrats, many of whom joined with their Republican colleagues in voting to override Truman's veto. The act continued to generate opposition after Truman left office, but it remains in effect. The Taft–Hartley Act amended the 1935 National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), prohibiting unions from engaging in several unfair labor practices. Among the practices prohibited by the Taft–Hartley act are jurisdictional strikes, wildcat strikes, solidarity or political strikes, secondary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeremy Brecher
Jeremy Brecher is a historian, documentary filmmaker, activist, and author of books on Labor economics, labor and social movements. Career Labor History In 1969, Brecher and other collaborators including Paul Mattick Jr., Paul Mattick, Jr., Stanley Aronowitz, and Peter Rachleff began sporadically publishing a magazine and pamphlet series called ''Root & Branch'' drawing on the tradition of workers councils and adapting them to contemporary America. In 1975 they published the collection ''Root & Branch: The Rise of the Workers’ Movements''. History from Below Funded by the National Endowment for the Humanities and the Connecticut Humanities Council, the project involved participation of more than 200 workers and community members who provided documents, participated in interviews, served on an advisory committee, and reviewed the project’s products. Brecher has continued to create community-based historical and cultural products in the Naugatuck Valley. From 1988 to 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Strike
A general strike refers to a strike action in which participants cease all economic activity, such as working, to strengthen the bargaining position of a trade union or achieve a common social or political goal. They are organised by large coalitions of political, social, and labour organizations and may also include rallies, marches, boycotts, civil disobedience, non-payment of taxes, and other forms of direct or indirect action. Additionally, general strikes might exclude care workers, such as teachers, doctors, and nurses. Historically, the term general strike has referred primarily to solidarity action, which is a multi-sector strike that is organised by trade unions who strike together in order to force pressure on employers to begin negotiations or offer more favourable terms to the strikers; though not all strikers may have a material interest in the negotiations, they all have a material interest in maintaining and strengthening the collective efficacy of strikes as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania behind Philadelphia, and the List of United States cities by population, 68th-largest city in the U.S. with a population of 302,971 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city anchors the Pittsburgh metropolitan area of Western Pennsylvania; its population of 2.37 million is the largest in both the Ohio Valley and Appalachia, the Pennsylvania metropolitan areas, second-largest in Pennsylvania, and the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 27th-largest in the U.S. It is the principal city of the greater Pittsburgh–New Castle–Weirton combined statistical area that extends into Ohio and West Virginia. Pitts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollywood Black Friday
Hollywood Black Friday, or Hollywood Bloody Friday, is the name given, in the history of organized labor in the United States, to October 5, 1945. On that date, a six-month strike by the set decorators represented by the Conference of Studio Unions (CSU) boiled over into a bloody riot at the gates of Warner Bros.' studios in Burbank, California. The strikes helped the passage of the Taft–Hartley Act in 1947 and led to the eventual breakup of the CSU and reorganization of the rival International Alliance of Theatrical Stage Employees (IATSE) leadership. Background The Conference of Studio Unions was then an international union belonging to the United Brotherhood of Carpenters and Joiners and represented the carpenters, painters, cartoonists, and several other crafts working for the studios in Hollywood. Seventy-seven set decorators broke away from IATSE to form the Society of Motion Picture Interior Decorators (SMPID) and negotiated an independent contract with the producers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |