|
Sri Pada
Adam's Peak is a tall conical mountain located in central Sri Lanka. It is well known for the Sri Pada ( si, ශ්රී පාද), i.e., "sacred footprint", a rock formation near the summit, which in Buddhist tradition is held to be the footprint of the Buddha, in Hindu tradition that of Hanuman or Shiva (), i.e., "Mountain of Shiva's Light", and in some Islamic and Christian traditions that of Adam, or that of St. Thomas. Geography The mountain is located in the southern reaches of the Central Highlands in the Ratnapura District and Nuwara Eliya District of the Sabaragamuwa Province and Central Province —lying about northeast of Ratnapura and southwest of Hatton. The surrounding region is largely forested hills, with no mountain of comparable size nearby. The region along the mountain is a wildlife reserve, housing many species varying from elephants to leopards, and including many endemic species. Adam's Peak is important as a watershed. The districts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratnapura District
Ratnapura ( Sinhala: රත්නපුර දිස්ත්රික්කය, Tamil: இரத்தினபுரம் மாவட்டம்) is a district of Sri Lanka in the Sabaragamuwa Province. The gem-mining centre of Sri Lanka is also a major crossroad between southern plains and the hill country to the east. A bustling market city servicing most of the surrounding towns. Many of the prominent gem dealers in Sri Lanka operate from this town. There is a route to Sri Pada from Ratnapura direction. Excursions include Sinharaja Forest Reserve and Udawalawe National Park. The surrounding area is a popular trekking destination and a good place for bird watching. Religion The majority of the population are Buddhists. Other religions include Hinduism, Islam and Christianity.Department of Census and StatisticThe Census of Population and Housing of Sri Lanka-2011/ref> Major cities * Ratnapura (Municipal Council) Large towns * Balangoda (Urban Council) * Embili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saman (deity)
Saman (also called Sumana, Sumana Saman, si, සුමන සමන් දෙවි) is a deity, subject to local and indigenous belief and worship in Sri Lanka. The name Saman means "good minded". His character is of historical significance for the Sinhalese people and veneration especially to all the Buddhists. God Maha Sumana Saman is depicted crowned and bejeweled, holding a lotus flower in his right or left hand and accompanied by a white elephant. According to Mahavamsa, the early chronicle of Sri Lanka, Saman is considered one of the guardian deities of the island and Buddhism in the country. Natha, Upulvan, Vibhishana and Kataragama are the other guardian deities. Nayakkar dynasty from South India introduced the goddess Pattini replacing god Saman, during the period of Kandyan Kingdom. Saman is the guardian (patron deity) or the presiding deity of Sabaragamuwa and the Sri Pada mountain. Accordingly, his main shrine or devalaya is at Ratnapura, where an annual festival i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
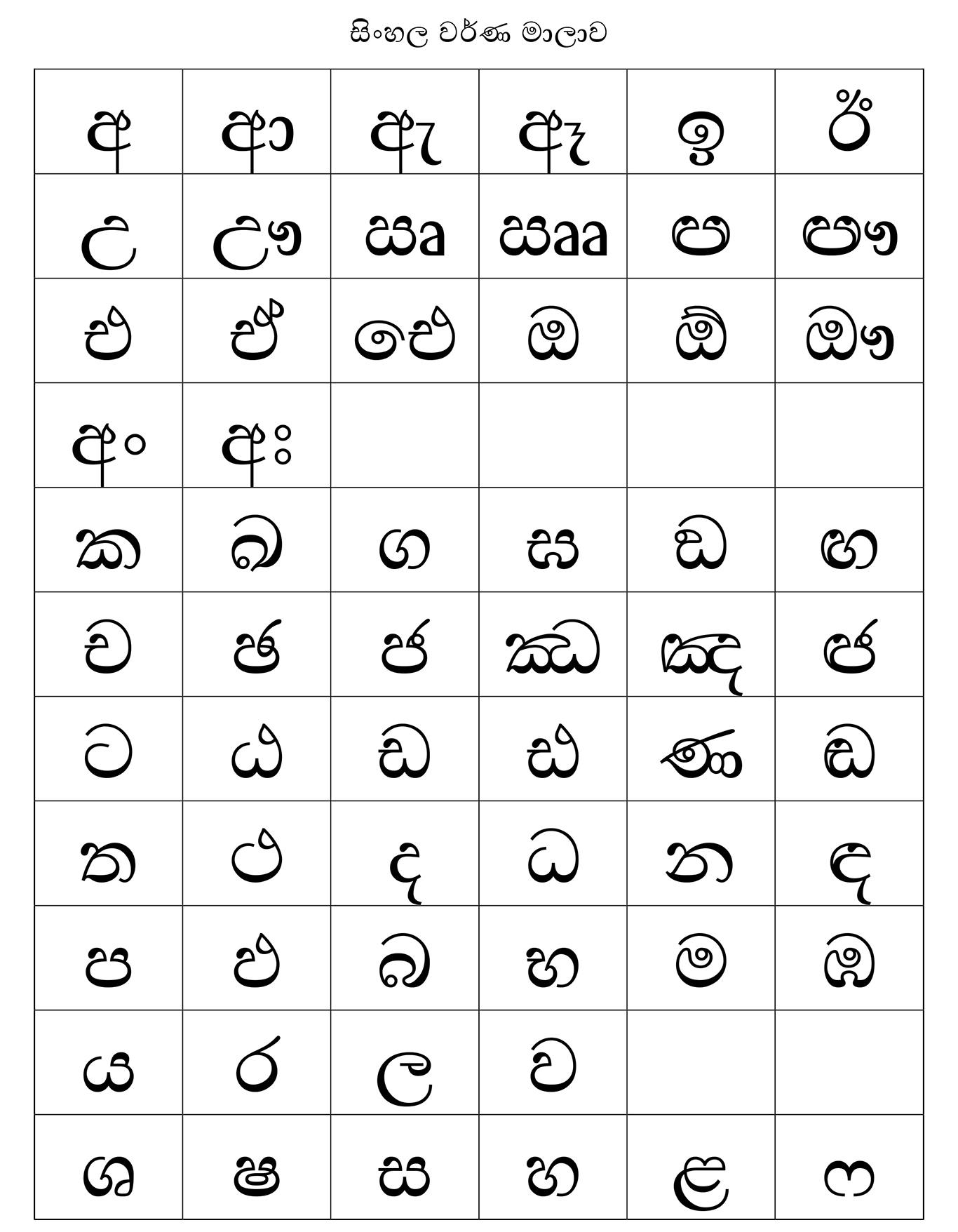
Sinhalese Language
Sinhala ( ; , ''siṁhala'', ), sometimes called Sinhalese (), is an Indo-Aryan language primarily spoken by the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka, who make up the largest ethnic group on the island, numbering about 16 million. Sinhala is also spoken as the first language by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 2 million people as of 2001. It is written using the Sinhala script, which is a Brahmic script closely related to the Grantha script of South India. Sinhala is one of the official and national languages of Sri Lanka. Along with Pali, it played a major role in the development of Theravada Buddhist literature. The early form of the Sinhala language, is attested as early as the 3rd century BCE. The language of these inscriptions with long vowels and aspirated consonants is a Prakrit similar to Magadhi, a regional associate of the Middle Indian Prakrits that has been used during the time of the Buddha. The closest relatives are the Vedda language (an endangered, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-identity within the local In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and '' jhana''. He di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pali
Pali () is a Middle Indo-Aryan liturgical language native to the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pāli Canon'' or ''Tipiṭaka'' as well as the sacred language of ''Theravāda'' Buddhism.Stargardt, Janice. ''Tracing Thoughts Through Things: The Oldest Pali Texts and the Early Buddhist Archaeology of India and Burma.'', Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, 2000, page 25. Early in the language's history, it was written in the Brahmi script. Origin and development Etymology The word 'Pali' is used as a name for the language of the Theravada canon. The word seems to have its origins in commentarial traditions, wherein the (in the sense of the line of original text quoted) was distinguished from the commentary or vernacular translation that followed it in the manuscript. K. R. Norman suggests that its emergence was based on a misunderstanding of the compound , with being interpreted as the name of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinhalese People
Sinhalese people ( si, සිංහල ජනතාව, Sinhala Janathāva) are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the island of Sri Lanka. They were historically known as Hela people ( si, හෙළ). They constitute about 75% of the Sri Lankan population and number more than 16.2 million. The Sinhalese identity is based on language, cultural heritage and nationality. The Sinhalese people speak Sinhala, an insular Indo-Aryan language, and are predominantly Theravada Buddhists, although a minority of Sinhalese follow branches of Christianity and other religions. Since 1815, they were broadly divided into two respective groups: The 'Up-country Sinhalese' in the central mountainous regions, and the 'Low-country Sinhalese' in the coastal regions; although both groups speak the same language, they are distinguished as they observe different cultural customs. According to the Mahavamsa and the Dipavamsa, a third–fifth century treatise written in Pali by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting impact on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Old Indo-Aryan language varieties. The most archaic of these is the Vedic Sanskrit found in the Rig Veda, a colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahagiri Dambaya
Min Mahagiri ( my, မင်းမဟာဂီရိ, ; lit. "Lord of the Great Mountain;" also called Eindwin Nat), son of a famous blacksmith, U Tint Daw. His given name was Maung Tint De (Nga Tinde) or Mr Handsome. He was extremely strong, able to break the tusks of an elephant. The King of Tagaung was worried, lest he attempt to usurp his throne, so Maung Tint De hid himself in a village. As a stratagem, the king married Maung Tint De's sister, Saw Me Ya, also called Myat Hla or Shwe Myet-hna (Golden Face), to become one of his queens. He persuaded Saw Me Ya to ask her brother to come out of hiding so that he could be given a high office. However, when Maung Tint De came out of hiding, the king had him arrested and burned alive tied to a champac (''sagawabin'') tree. His sister (see below) also died with him and the two became evil Nats resident in that tree, periodically feasting on people who happened to come near the tree. The King of Tagaung (''Tagaung Min'') had the tree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



